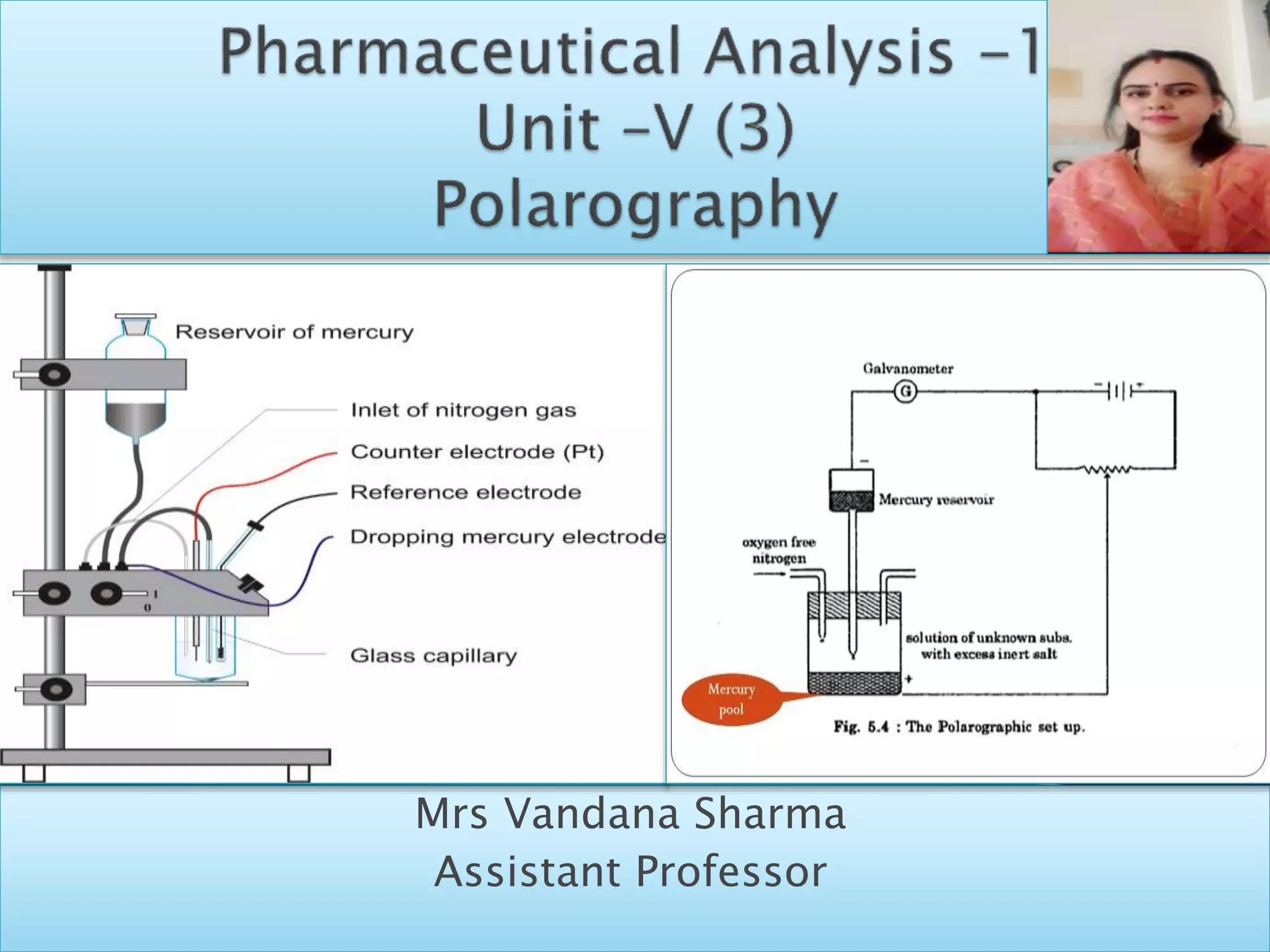
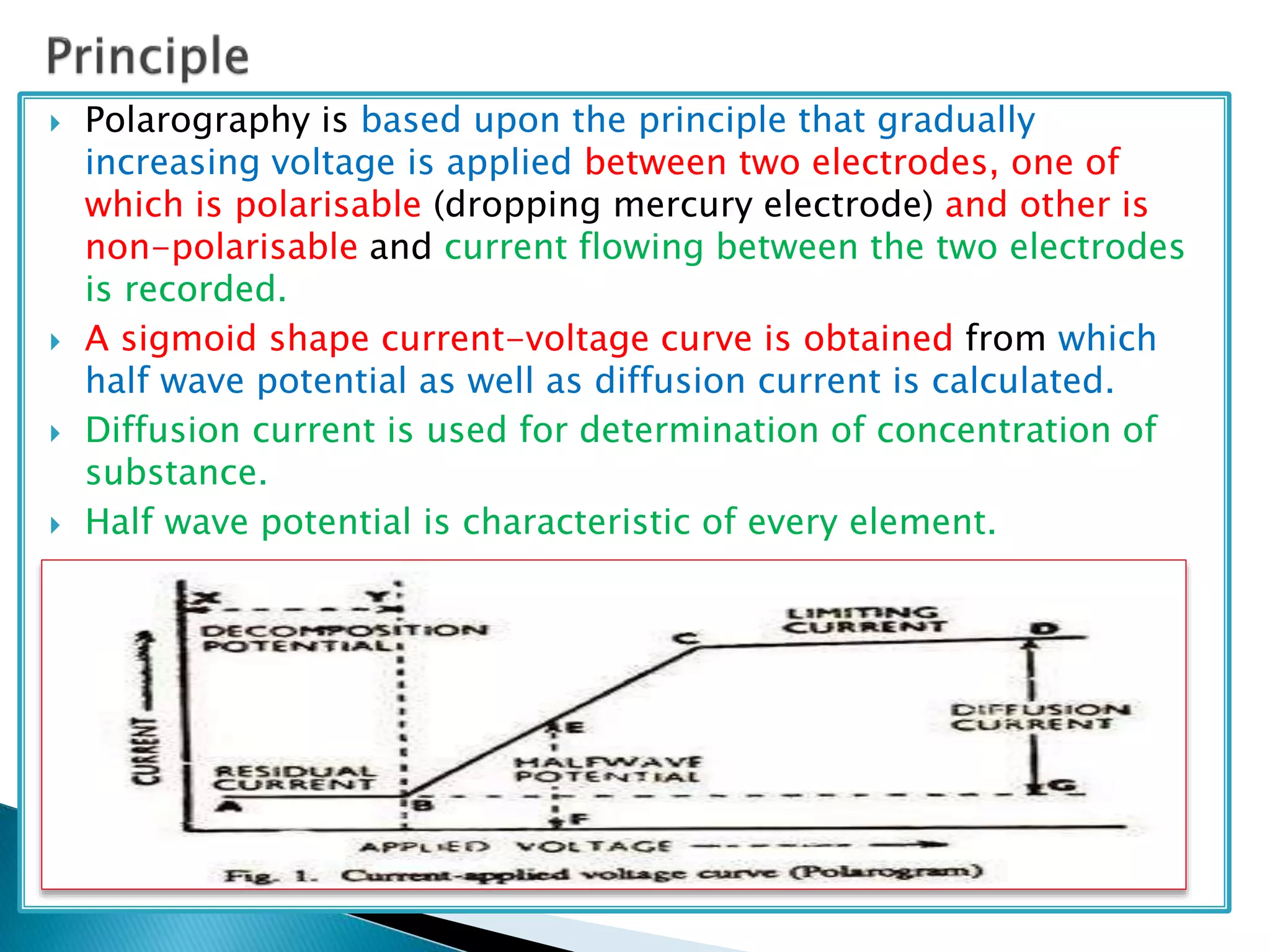
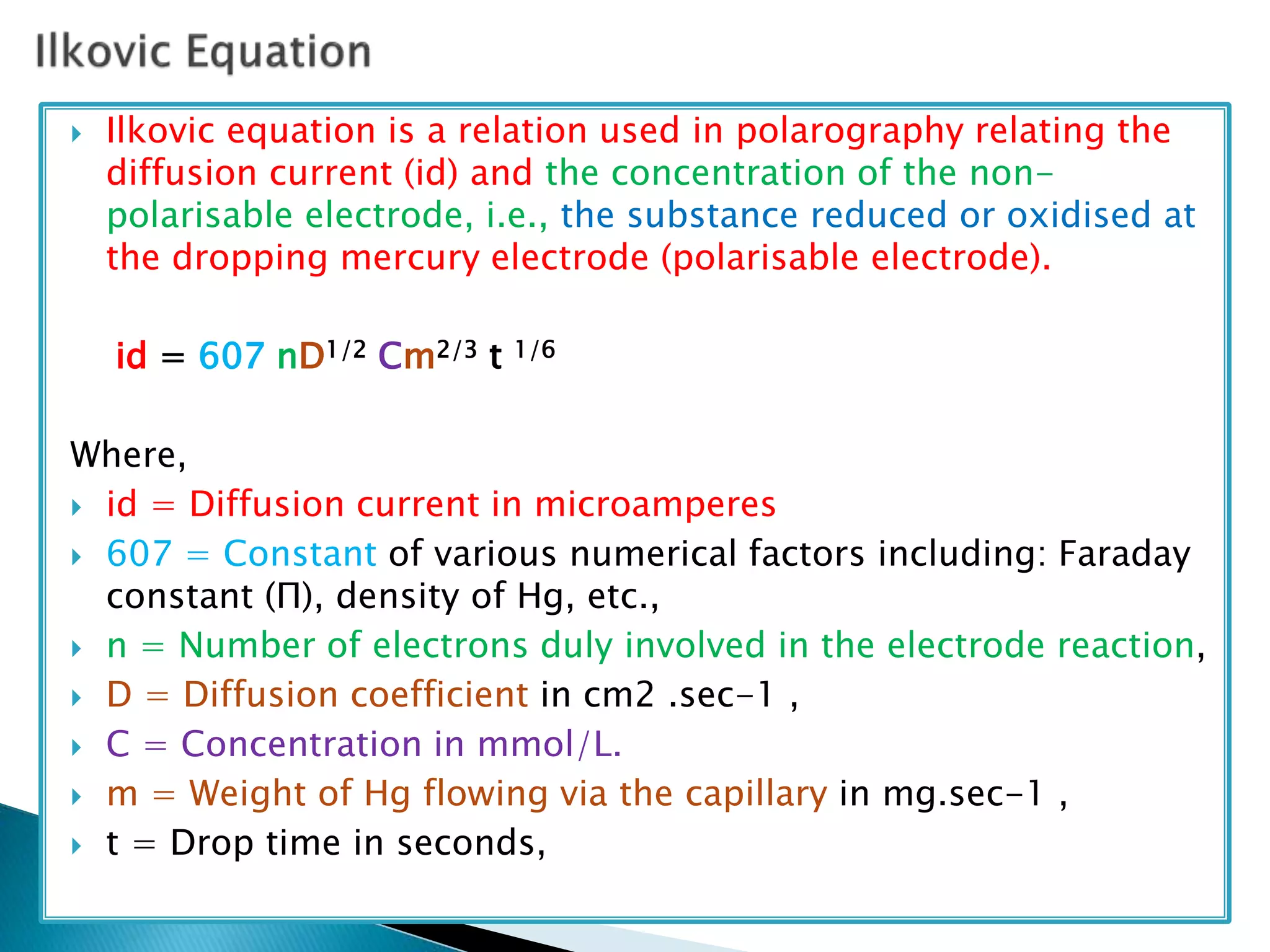
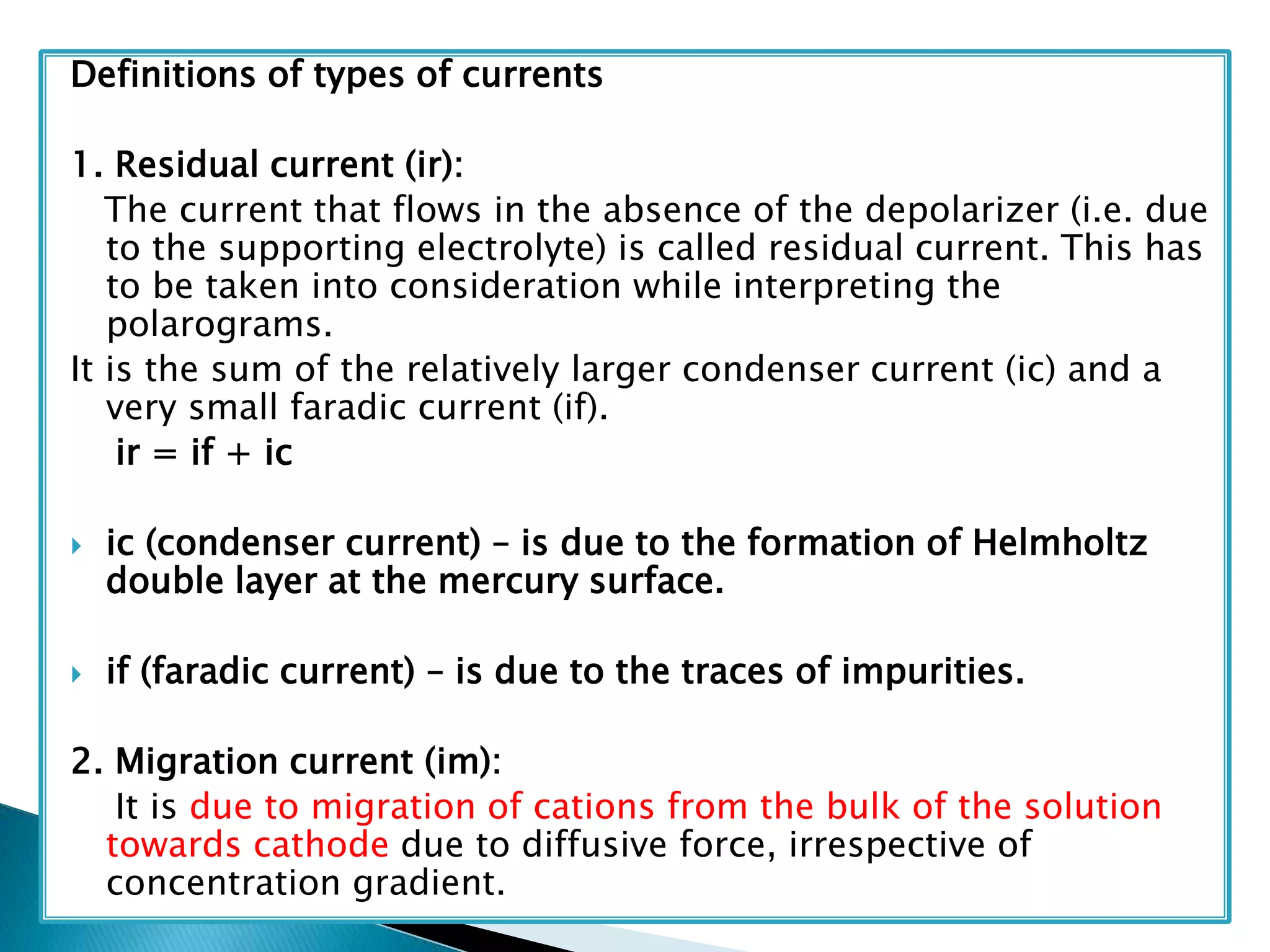
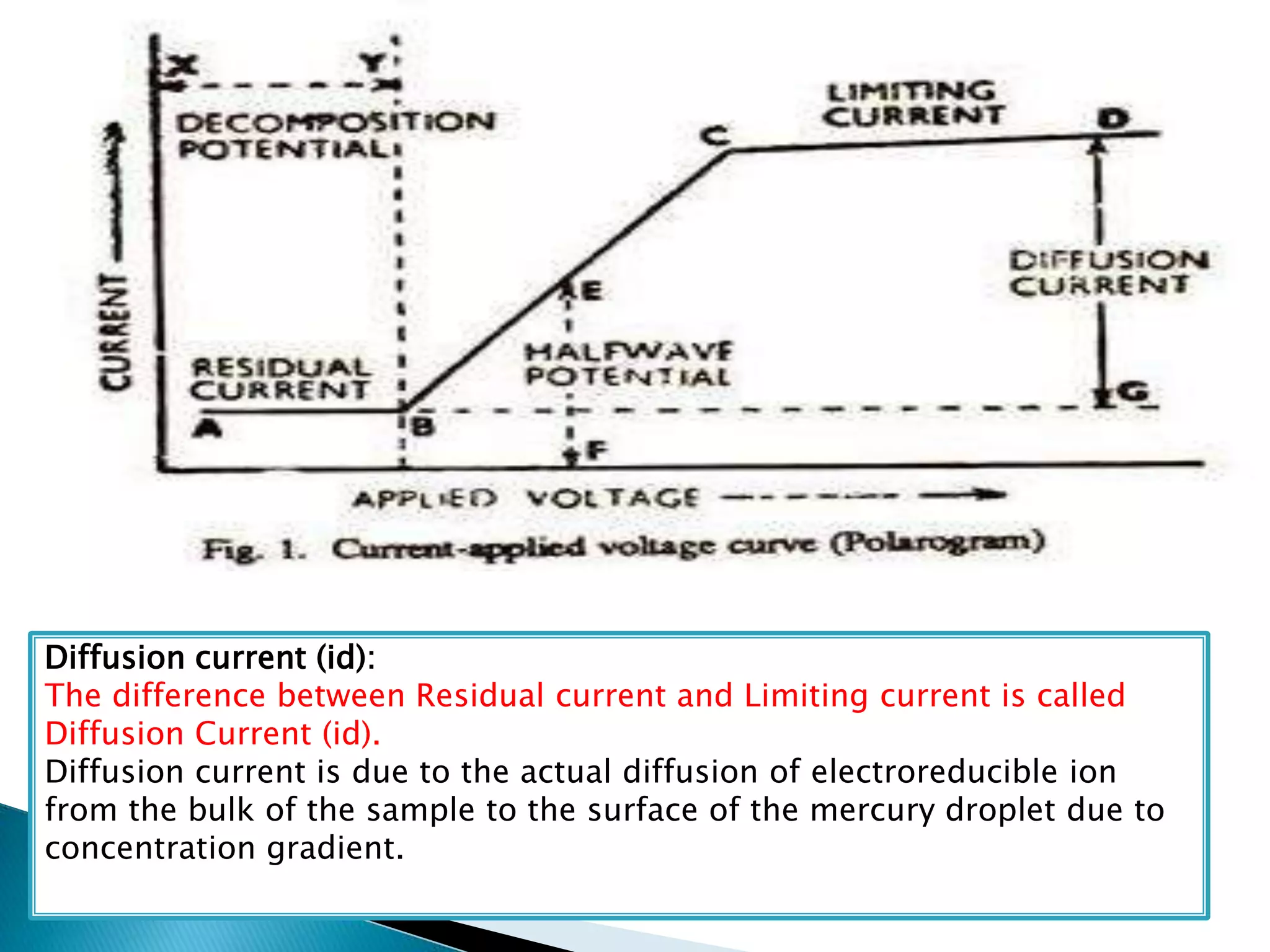
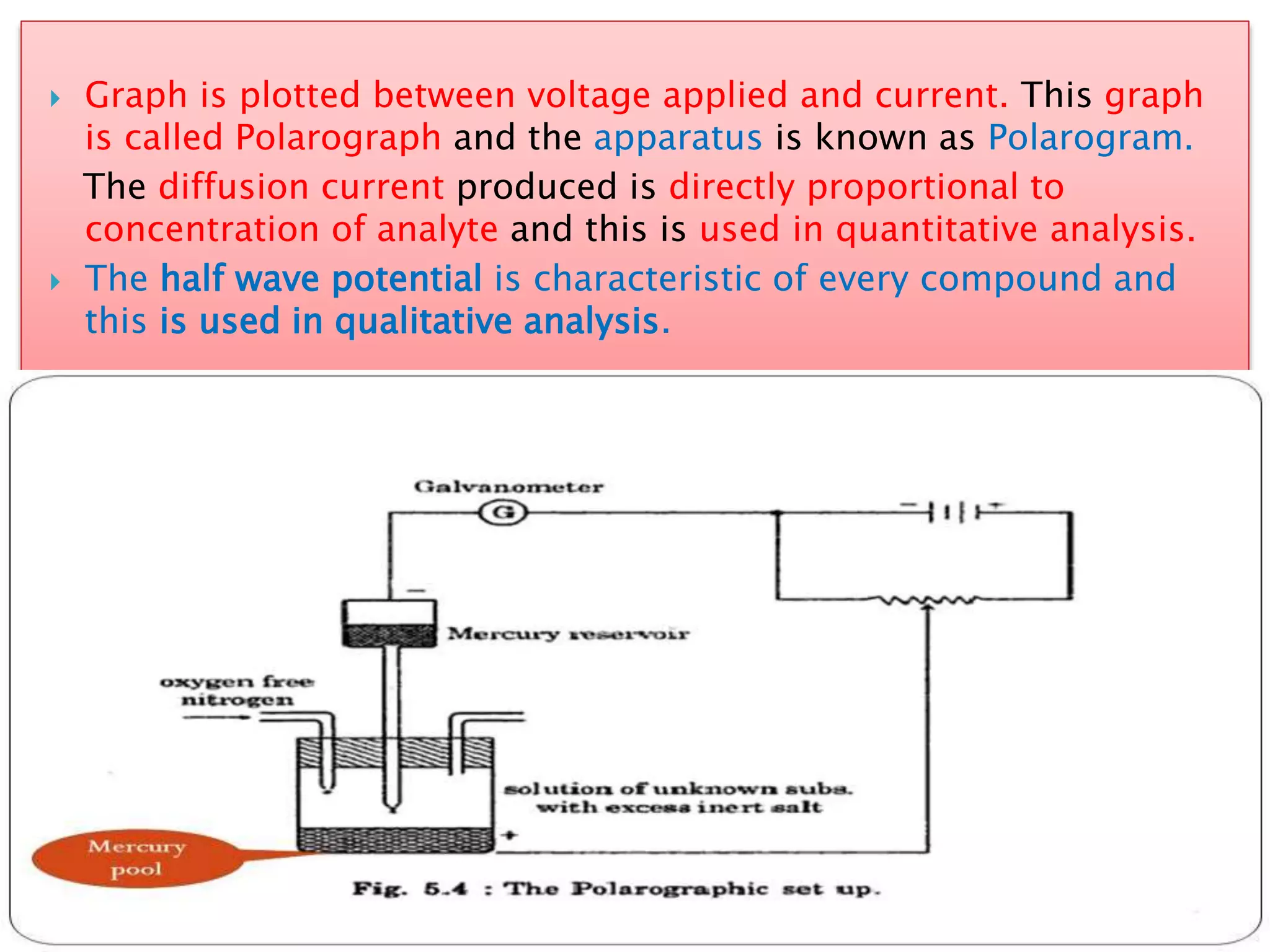
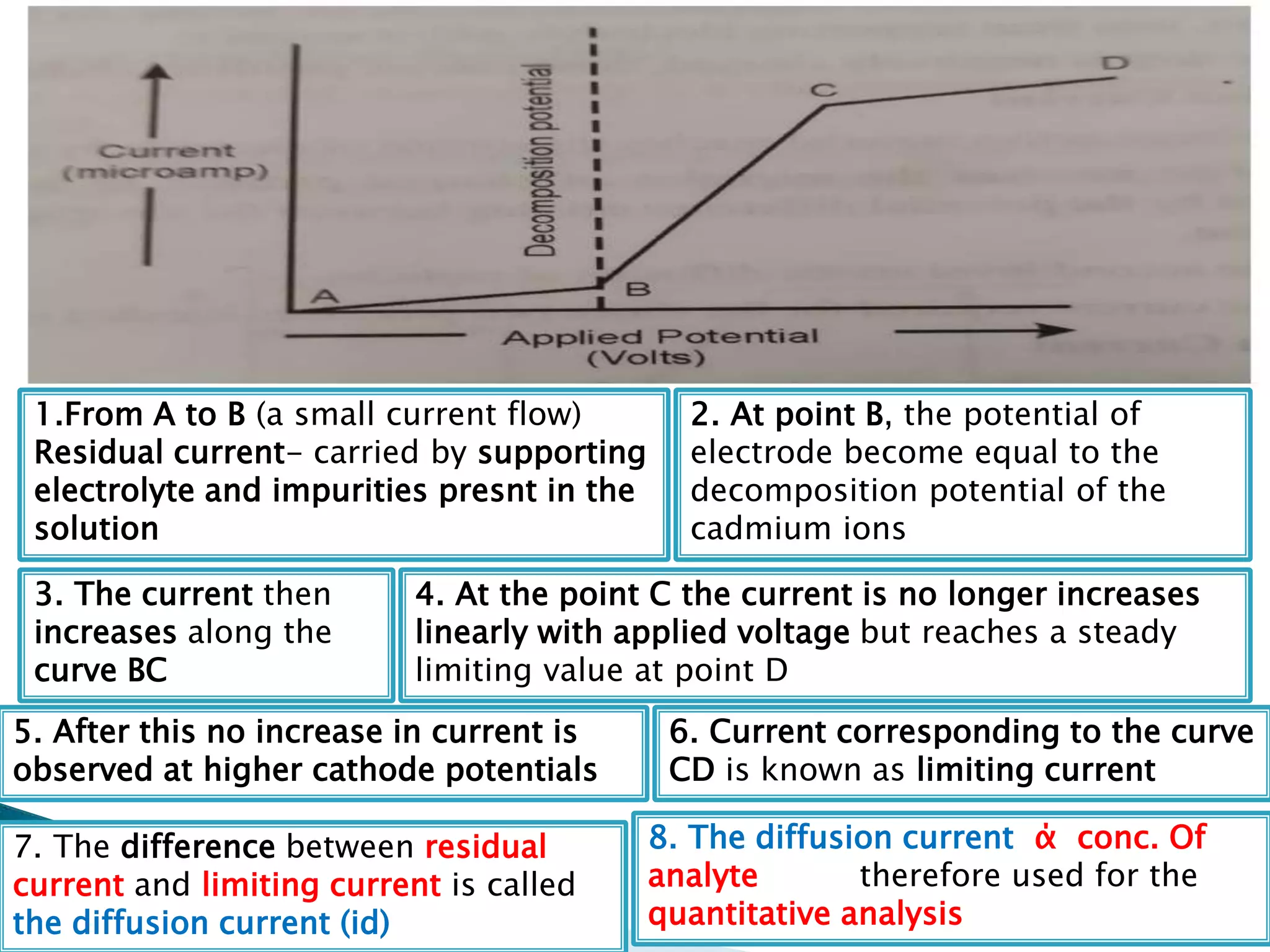
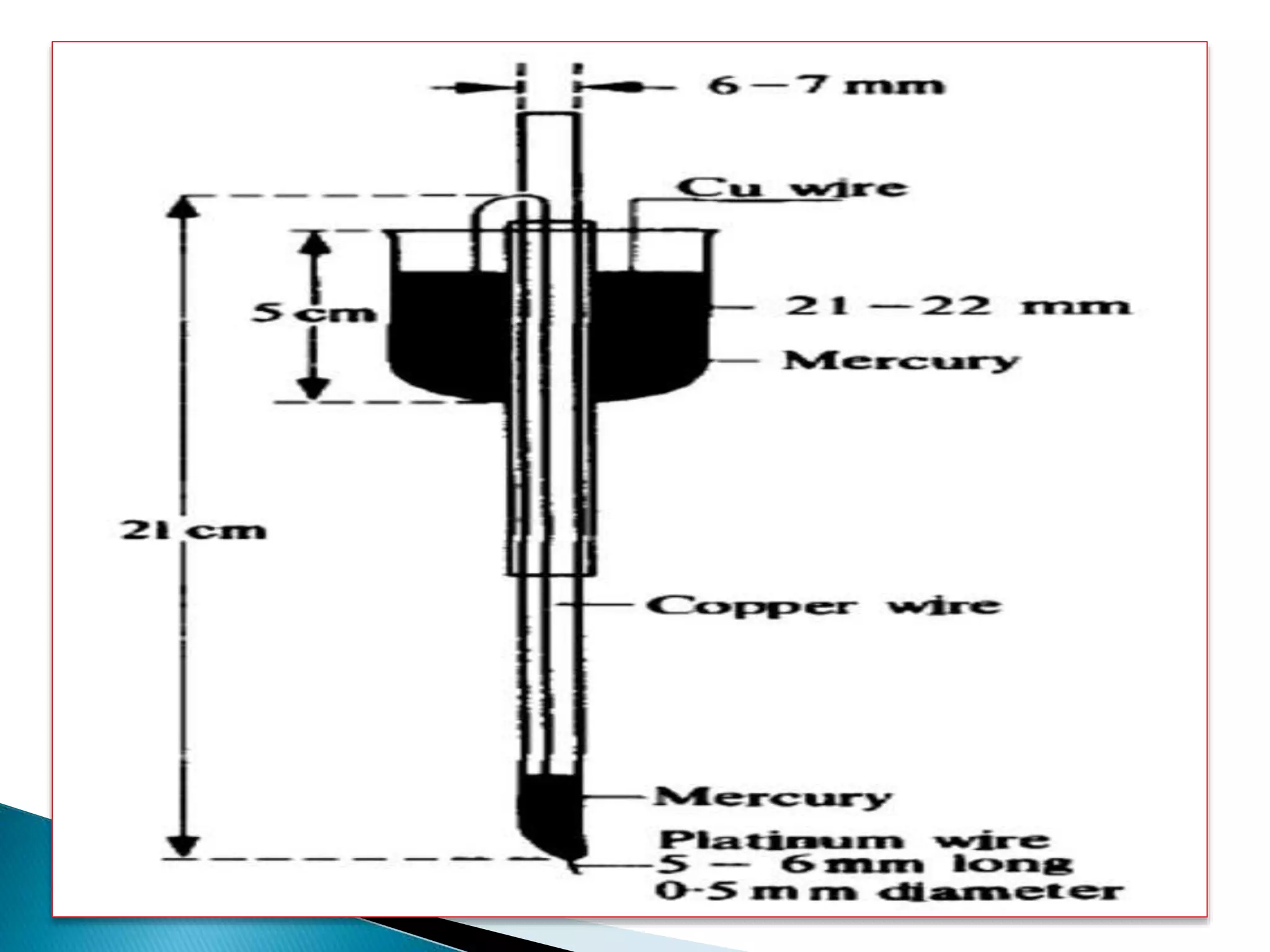
Polarography is an electroanalytical technique that uses a dropping mercury electrode (DME) and measures the current between two electrodes when a gradually increasing voltage is applied. The current-voltage curve obtained is used to determine analyte concentration from the diffusion current and identify species from the characteristic half-wave potential. The Ilkovic equation relates diffusion current to analyte properties like concentration, number of electrons involved, and diffusion coefficient. Polarography finds applications in qualitative and quantitative analysis of metals, drugs, and organic compounds.