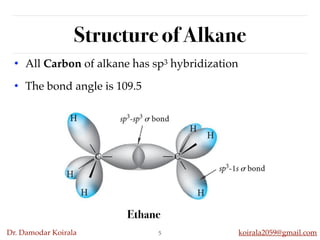
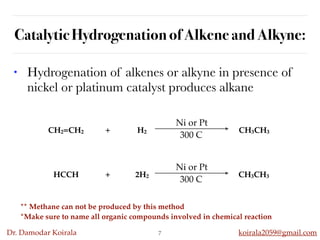
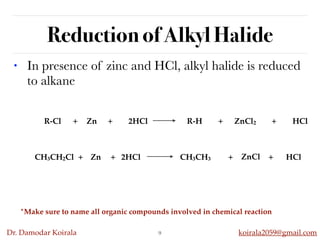
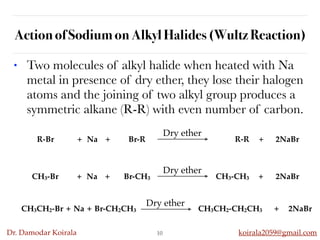
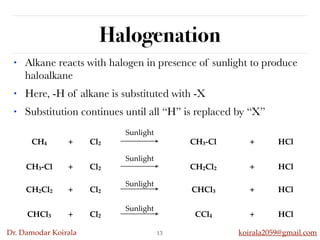
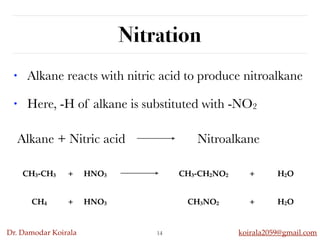
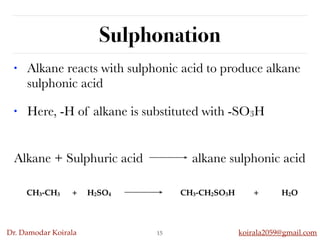
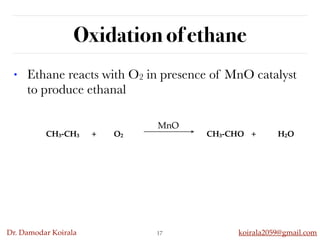
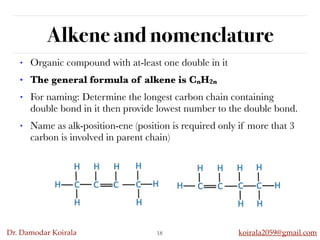
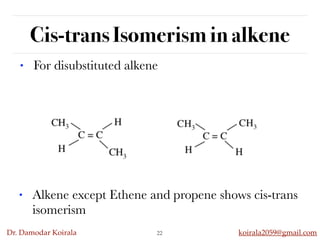
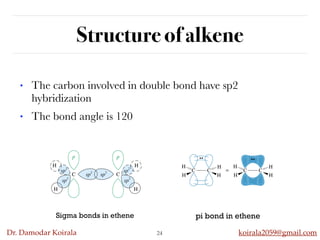
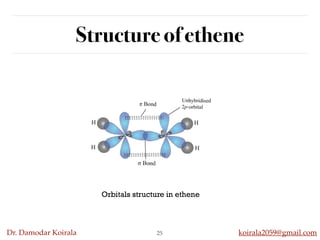
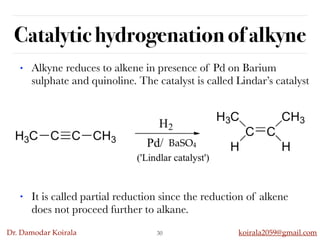
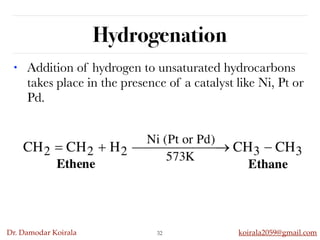
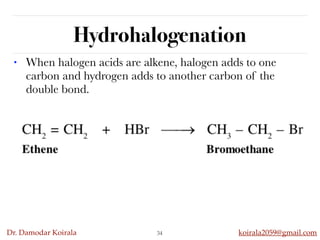
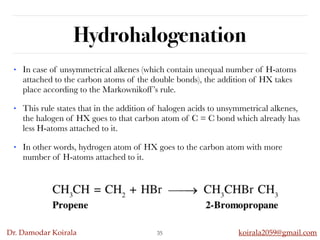
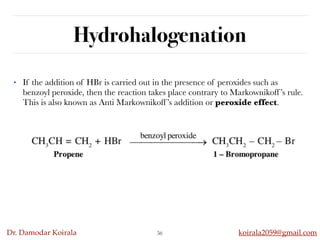
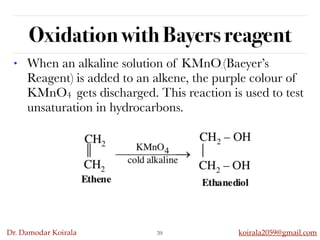
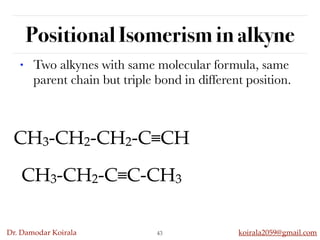
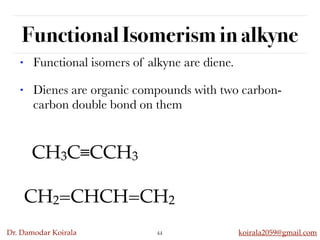
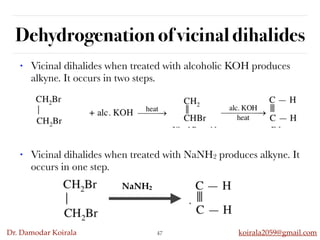
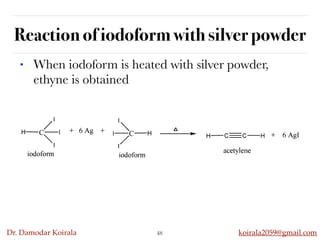
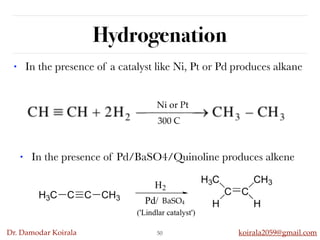
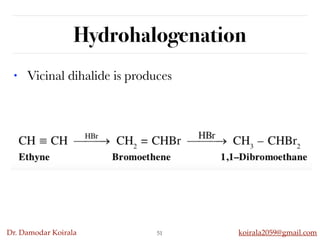
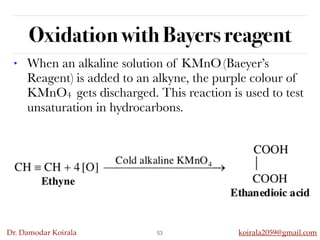
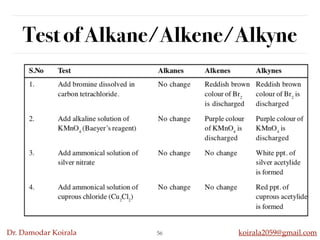
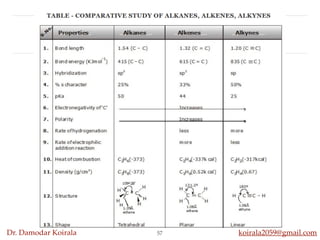
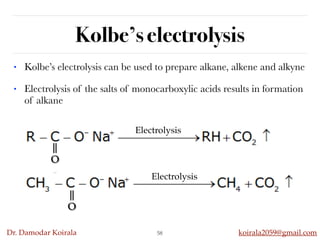
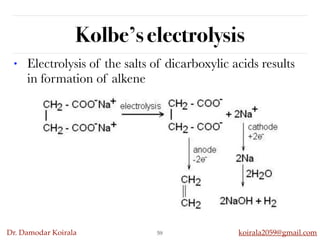
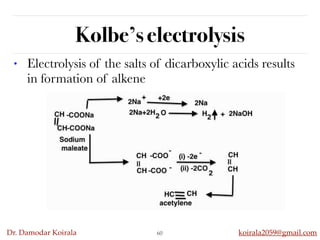
This document discusses organic hydrocarbons. It begins by defining hydrocarbons as organic compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen. It then discusses saturated hydrocarbons such as alkanes which contain only single carbon-carbon bonds. Unsaturated hydrocarbons like alkenes and alkynes contain double and triple bonds. The document provides information on the structures, properties, nomenclature and reactions of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. It also describes methods of preparing these compounds, including hydrogenation, dehydrohalogenation, and dehydration reactions.