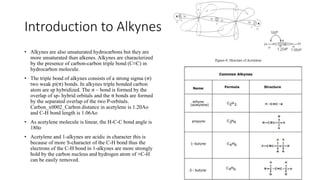
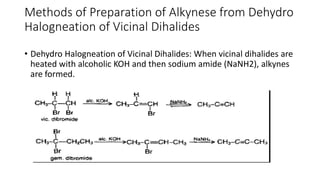
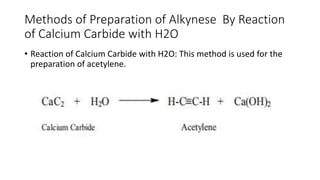
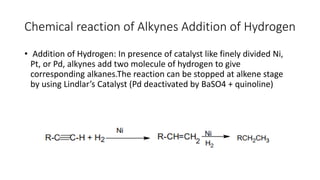
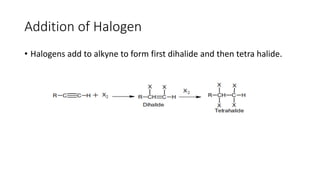
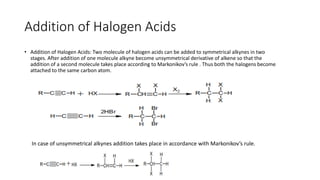
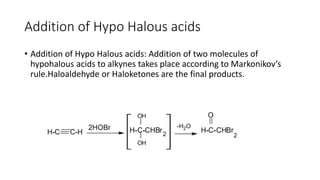
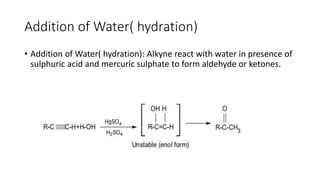
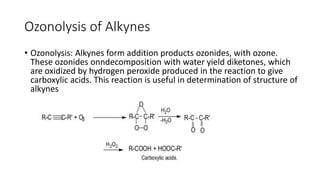
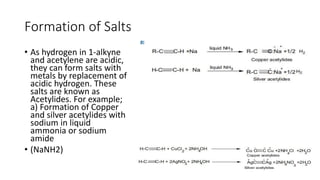
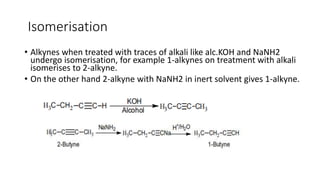
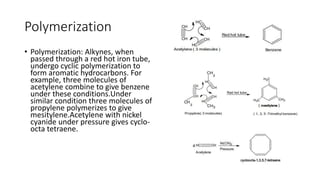
Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing a carbon-carbon triple bond. They are more unsaturated than alkenes. Alkynes undergo characteristic reactions including addition reactions, oxidation, hydration, and polymerization. They can be prepared through methods such as the dehydrogenation of tetrahalides, dehydrohalogenation of vicinal dihalides, and the reaction of sodium acetylides with primary alkyl halides.