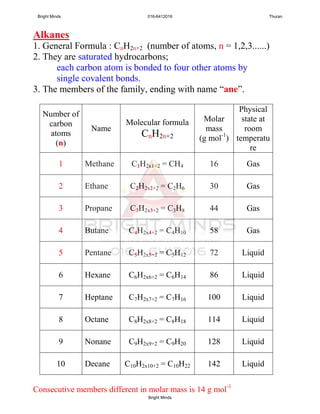
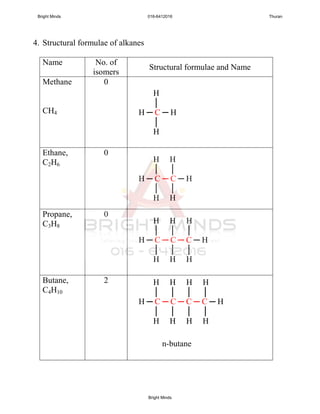
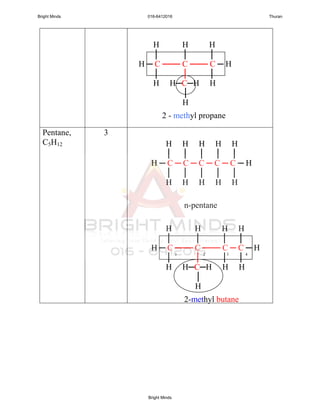
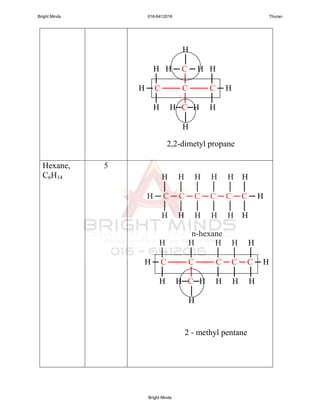
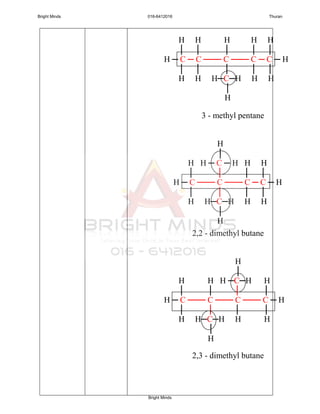
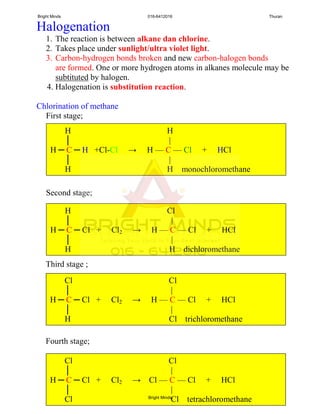
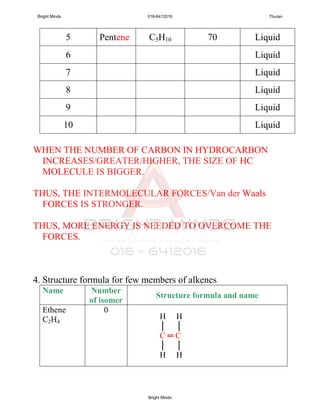
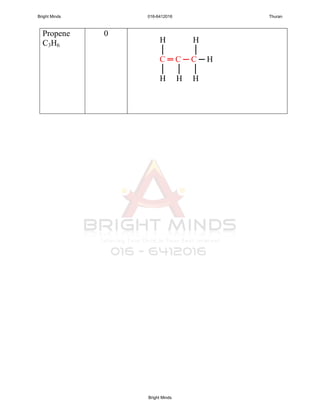
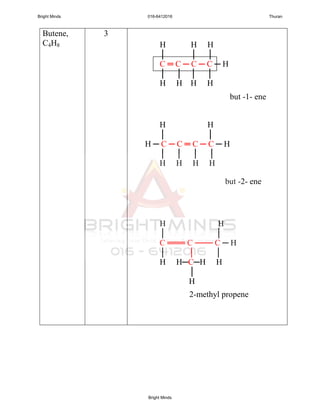
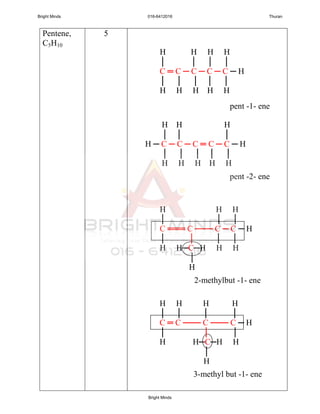
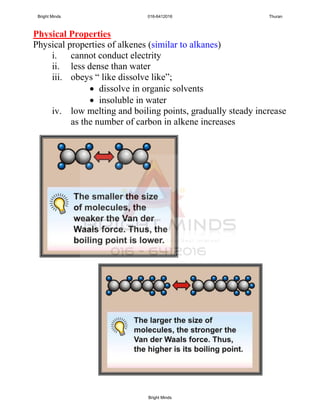
Alkanes are a family of saturated hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2. They contain only single bonds between carbon atoms. The physical and chemical properties of alkanes are determined by the strength of intermolecular forces between molecules which increase with increasing molecular size. Alkanes are generally nonpolar, insoluble in water, and do not readily undergo chemical reactions due to the stability of their single carbon-carbon bonds. Common reactions include combustion, halogenation, and substitution reactions.


![Alkenes
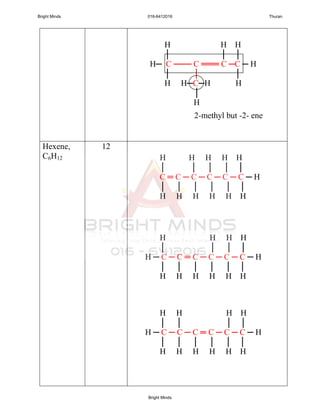
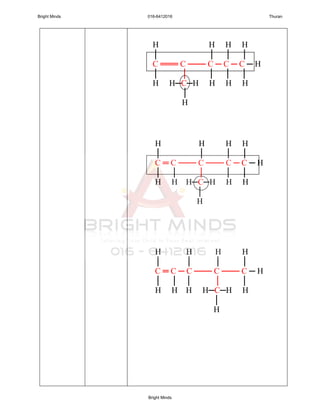
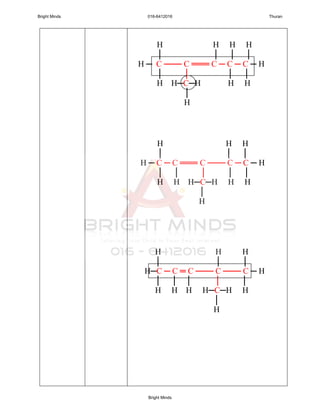
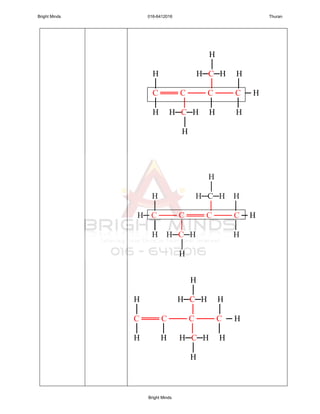
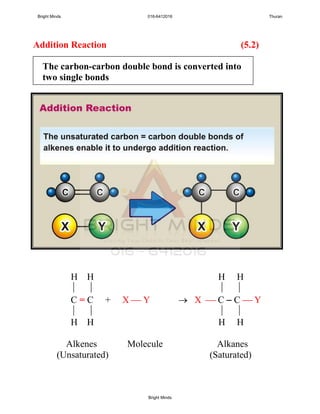
1. General formulae : CnH2n
[ no alkene corresponding to n = 1 as CH2 is not exist]
2. Alkenes is unsaturated hydrocarbon because the presence of the
double bond.
3. Name of each members end with “ene”.
No. of
carbon atom
Name
Molecular
formulae
Molar mass /
g mol-1
Physical
state at room
condition
1 None
2 Ethene C2H4 28 Gas
3 Propene C3H6 42 Gas
4 Butene C4H8 56 Gas
ethenes
Alkenes containing at least one carbon-carbon
double bond
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-11-320.jpg)


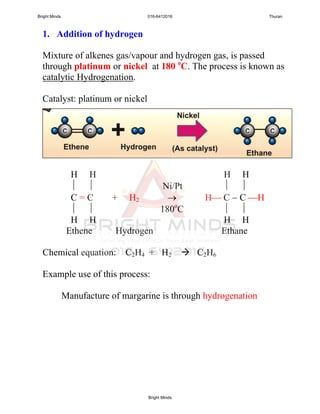
![2. Addition of halogens
The process is known as halogenation
H H H H
C = C + Br Br Br C C Br
H H H H
Ethenes Bromine 1,2-dibromoethanes
(unsaturated) (saturated)
Chemical equation: C2H4 + Br2 C2H4Br2
[HW-notes book]
Q1: Write a chemical equation reaction between but-1-ene with
bromine water. Show the structural formula as well.
[HW-exercises book]
Q2: Halogenation process is best used to differentiate between
alkanes and alkenes. Explain how it can be done?
[notes: refer to SAB]
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-25-320.jpg)
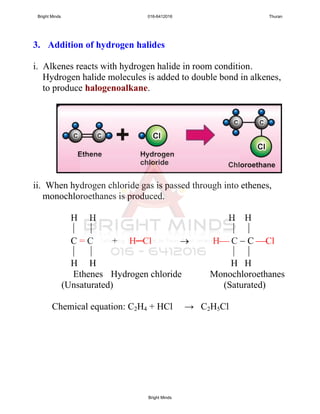
![4. Addition of acidified potassium manganate(VII)
1. When alkenes is mixed with acidified potassium manganate(VII),
its purple colour is decolourised.
2. This is because addition process occurred, a group of
hydroxyl (--OH) is added to the molecules of alkenes to form a
molecule of –diol (type of alcohol) which is saturated and
colourless.
C = C + H2O C C
OH OH
Alkenes alkanes-diol compound
(Unsaturated) (Saturated)
[O]
[from acidified KMnO4]
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-27-320.jpg)
![Example;
H H H H
C = C + H2O + [O] H C C H
H H OH OH
Ethene Ethane-1,2-diol
(Unsaturated) (Saturated)
Q: Use propene as example.
H H H H H
│
H— C —C = C + H2O + [O] H C−C C H
│ │
H H H H OH OH
Propene, C3H6 Propane-1,2-diol
C3H6 + H2O + [O] C3H8O2
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-28-320.jpg)
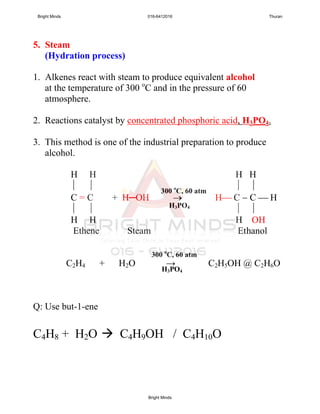

![2
ESSAY;
HOW TO DIFFERENTIATE THE ALKANE and
ALKENE IN THE BOTTLES?
Solutions: i. Procedure
ii. Observations
iii. Inference
[8marks]
Sample answer
Aim: To investigate the liquid in bottle A and B
Test tube A Test tube B
Dropper
Test tube
BA
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-34-320.jpg)

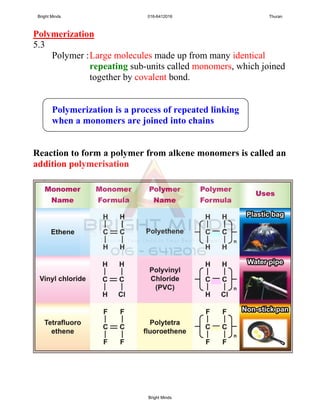
![1
ALCOHOL
The Alcohol Family
1. One of member of homologous series which contain carbon,
hydrogen and oxygen.
2. General formula for alcohol is CnH2n+1OH. [n=1,2,3..]
3. Alcohol contains the hydroxyl group, -OH as their functional
group. [notes: not hydroxide ion, OH-
, alcohol not is alkaly ]
4. Alcohol is neutral compound.
5. Alcohol are named by replacing -e for alkane with –ol.
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-36-320.jpg)
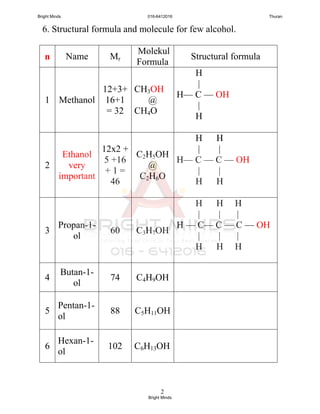


![6
(iv)
C2H5 OH
CH3 CH2 CH CH2 CH CH2 ─ CH3
Formula : C9H19OH
Name : 5-ethyl heptan-3-ol
Physical Properties
1. Liquid at room temperature. (pg. 62) [ no gas]
2. Simple alcohol are very soluble in water, infinite solubility.
Methanol, ethanol dan propan-1-ol is miscible in all proportions
(terlarut campur dengan air dalam semua kadaran).
The rest of the alcohol less soluble or insoluble.
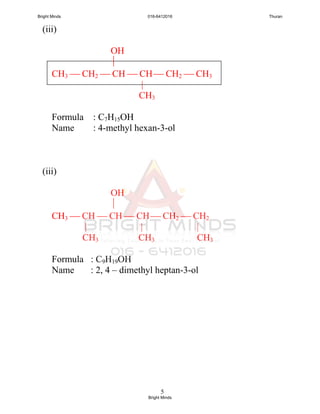
Isomerism
Similar to alkenes, isomerism in alcohol results from the
branching of the carbon chain and the different location of the
hydroxyl group.
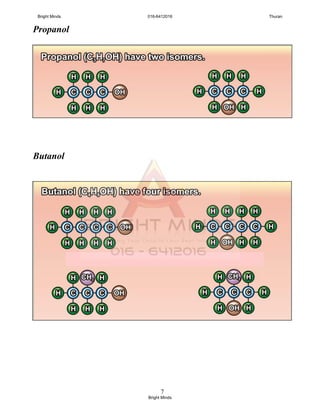
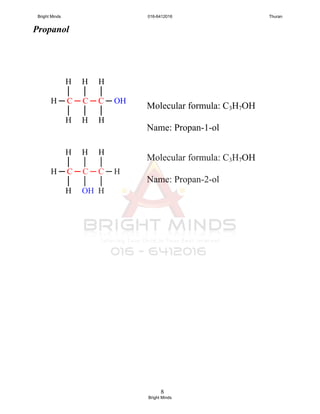
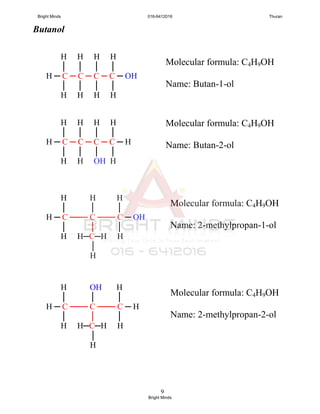
You only have to know the isomerism in propanol dan butanol.
Q : Draw 2 isomers for propanol and 4 isomers for butanol,
and dan named the isomers.
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-41-320.jpg)


![15
Chemical Properties
1. Combustion
i. Alcohol are very flammable sustances.
ii. Ethanol burns with non-smoky and blue flame and releases
lot of heat. Suitable for use as fuel, described as clean fuel.
Q: Write combustion equation for hexanol
2. Oxidation
i. Ethanol can be oxidised into ethanoic acid by an oxidising agent.
[Ethanoic acid is a family of carboxilic acids]
C2H5OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 3H2O
Ethanol Oxygen Carbon Water
dioxide
C6H13OH + 9O2 6CO2 + 7H2O
hexanol Oxygen Carbon Water
dioxide
CH3CH2OH + 2[O] CH3COOH + H2O
Etanol Ethanoic acid
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-50-320.jpg)
![16
Q: Show the structural formula for the equation above.
Q: Named 2 solutions are commonly used as oxidising agent.
(i) Acidified potassium manganate(VII), KMnO4
(purple to colourless / decolourised)
(ii) Acidified potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7
(orange to green)
Q: Draw a labeled diagram for the process.
H H H O
| | | ║
H — C — C — OH + 2[O] → H — C — C — OH + H2O
| | |
H H H
Heat
Ethanol +
potassium dikromat(VI) +
dilute sulfuric acid
Cold
water
Distillate
(ethanoic acid)
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-51-320.jpg)

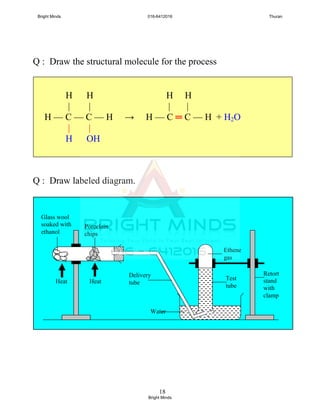
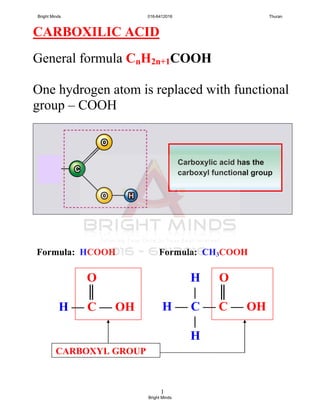

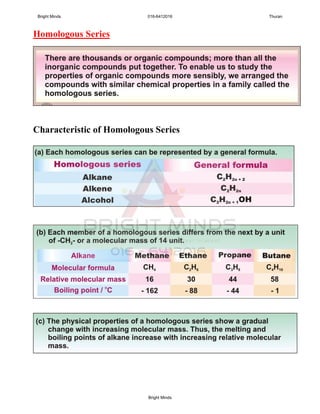
![3
Molecular and Structural Formula
n Name
Molecular
formula
Mr
Structural
formula
0
Methanoic
acid
C0H2(0)+1COOH
= HCOOH
46
O
║
H — C — OH
1
Ethanoic
acid
C1H2(1)+1COOH
= CH3COOH
[C2H4O2]
60
H O
| ║
H — C — C — OH
|
H
2
Propanoic
acid
C2H2(2)+1COOH
= C2H5COOH
74
H H O
| | ║
H — C — C — C — OH
| |
H H
3
Butanoic
acid
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-56-320.jpg)
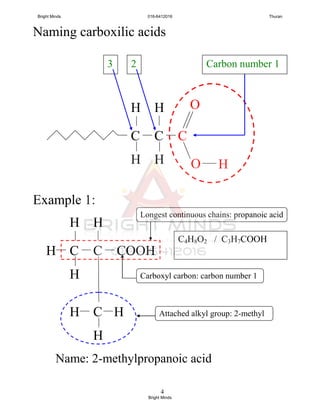
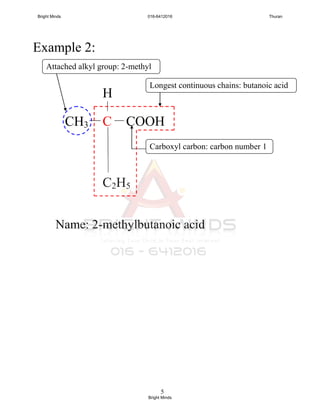
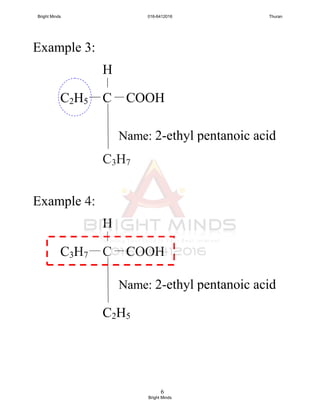
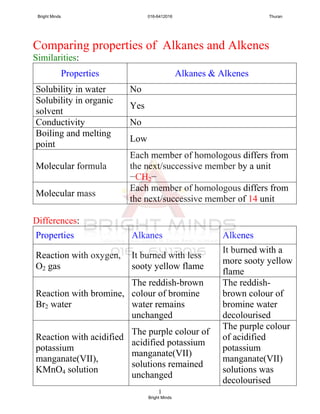
![7
Ethanoic Asid
Can be prepared through oxidation of an
ethanol.
Chemical equation:
This is carried out by refluxing ethanol with
an oxidising agent such as acidified potassium
dichromate(VI) or potassium manganate(VII)
solution.
H H
│ │
H — C — C — OH
│ │
H H
H O
│ ║
H — C — C — OH
│
H
+ 2[O] + H2O
K2Cr2O7 solutions
+
dilute H2SO4
reflux
CH3CH2OH + 2[O] CH3COOH + H2O
Etanol ethanoic acid
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-60-320.jpg)
![9
Physical Properties
- pH less than 7
- sharp or unpleasant smell
- turn moist blue litmus paper to red
- colourless liquid
Chemical Properties
Acid Properties
- Only hydrogen atom in the carboxyl group,
[-COOH] can ionize in water to produce
hydrogen ions, H+
.
Ethanoic acid is a weak acid. Why?
- it dissociates in water partially, most of
the molecules remain unchanged.
CH3COOH CH3COO-
+ H+
CH3COO-
Ethanoic
acid
Hydrogen
ion
Ethanoate
ion
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-62-320.jpg)

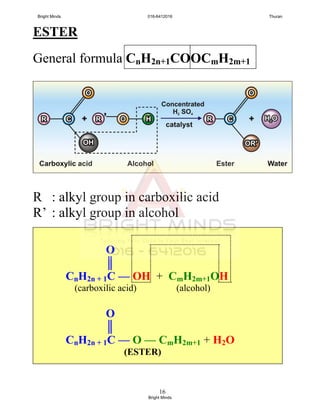
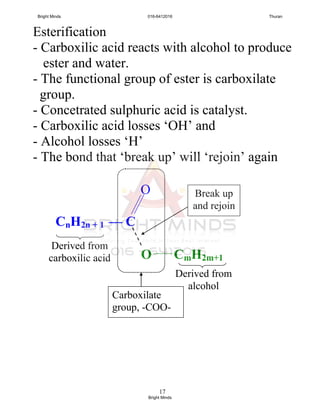
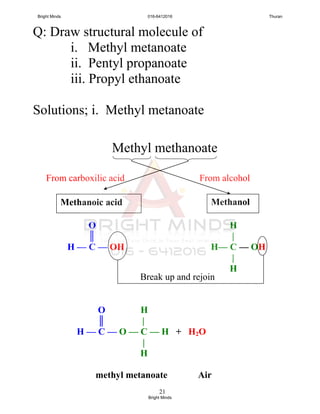
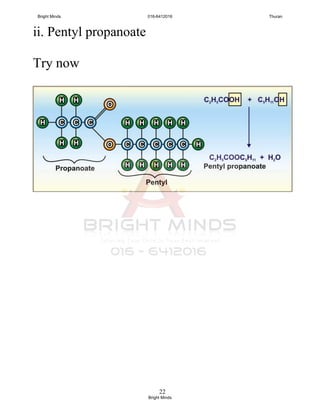
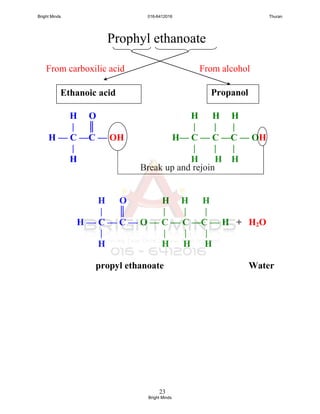
![13
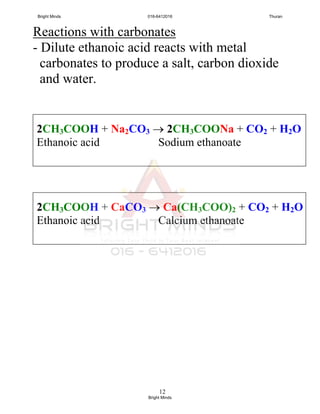
Reactions with alcohols [Esterification]
Esterification:
Carboxilic acid reacts with alcohol to
produce an ester and water.
Concentrated H2SO4 : catalyst
[will discuss more in next chapter]
Concentrated
H2SO4
Carboxilic acid + Alcohol ——— Ester + Water
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-66-320.jpg)

![15
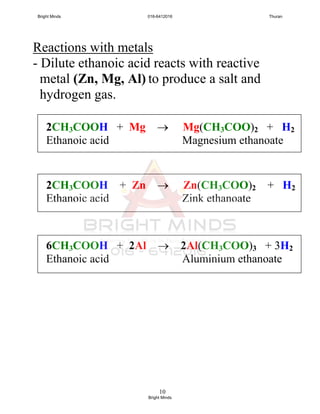
Conclusion on chemical reaction;
Carboxilic acid + reactive metal
carboxylate salt + hydrogen
Carboxilic acid + base
carboxylate salt + water
Carboxylate acid + metal carbonate
carboxylate salt + carbon dioxide +
Water
Carboxilic acid + alcohol
ester + water
1. Learning task 2.9 Summarizing pg 75
[notes book]
2. Effective Practise pg 75
1, 2, 3
[exercise book]
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-68-320.jpg)
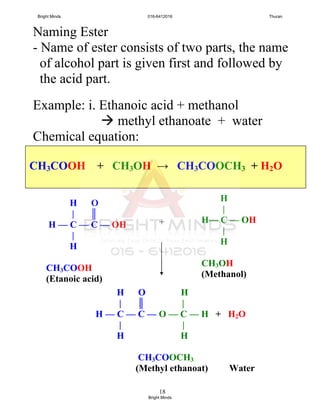
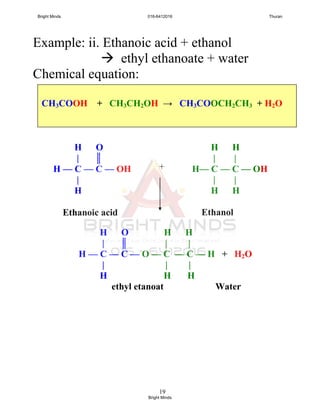
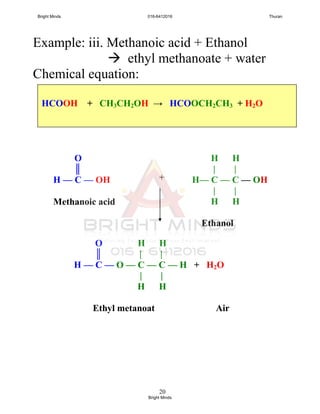
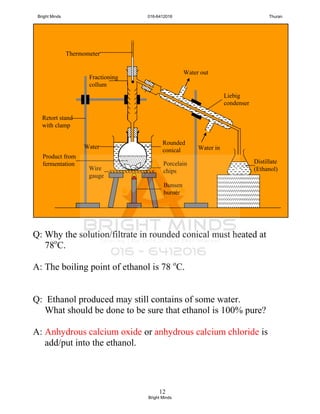
![24
Preparation of ester through reflux
How to carry out this process?
[Success pg 378]
After boiling, Liebig condenser is rearranged
To carry out the fractional distillation at
74o
C – 78o
C to collect ethyl ethanoate.
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Tissel tube
Liebig
condenser
Ethanol +
ethanoic acid +
concentrated
sulphuric acid
Porcelain chip
Water
bath
Water
in
Water
out
To prevent
bumping and
ensure smooth
boiling
To cold the
ethanol and
ethanoic acid
Uniform
heating
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-77-320.jpg)

![26
Uses of ester
- to make perfume, cosmetics
- to make artificial food flavoring
[Text Book: Table 2.8 pg 81]
- used as organic solvents
eg. ethyl ethanoate used in sunburn
lotion, polish removers, glues.
- to make synthetic polymers/fabrics
- to make aspirin (pain reliever)
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-79-320.jpg)


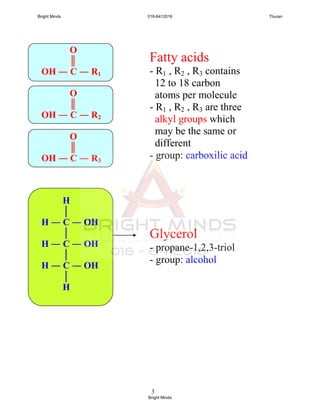
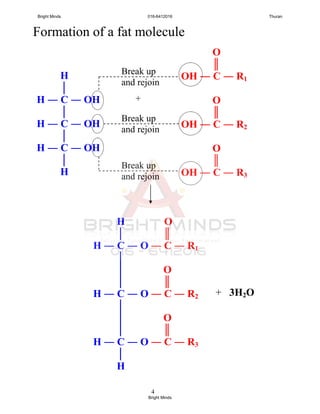
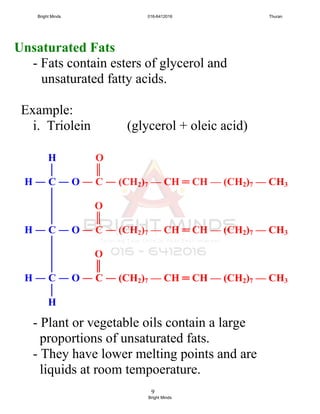
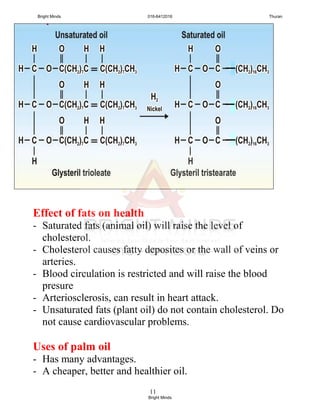
![5
Importance of fats and oils
- energy
- nutrients
- thermal insulation
- protection to internal organ
[Text book: Figure 2.34 pg. 86]
Saturated and unsaturated fats
- Fat or oil molecules is affected by parent fatty
acids.
- Fatty acids can be differentiated in two ways;
i. the length of the carbon chains
(12 to 18 carbon atoms)
ii. saturated or unsaturated
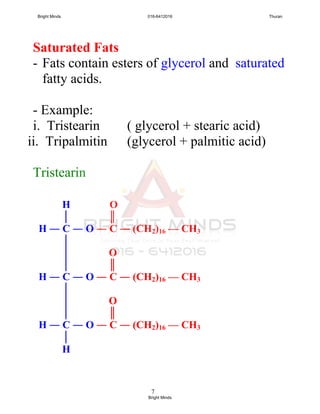
Saturated fatty acid
- All carbon atoms joined together by
carbon-carbon single covalent bond.
- example:
Lauric acid (12 carbon atoms)
Palmitic acid (16 carbon atoms)
Stearic acid (18 carbon atoms)
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-84-320.jpg)
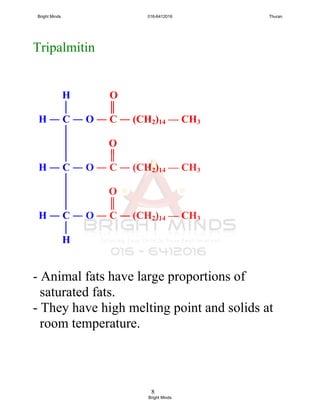
![6
Unsaturated fatty acid
- The carbon chain has one or more
carbon-carbon double covalent bond.
Example:
i. Oleic acid: monounsaturated fatty acid
(one carbon-carbon double bond)-
[no of C = 18, DB = 9&10]
ii. Linoleic acid: polyunsaturated fatty acid
(two carbon-carbon double bond)
[no. of C = 18, DB = 9&10, 12&13]
iii. Linolenic acid: polyunsaturated fatty acid
(three carbon-carbon dauble bond)
[no. of C = 18, DB = 9&10, 12&13,
15&16]
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-85-320.jpg)


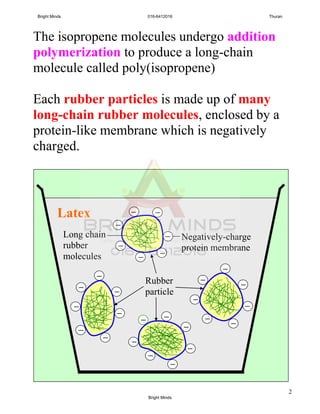
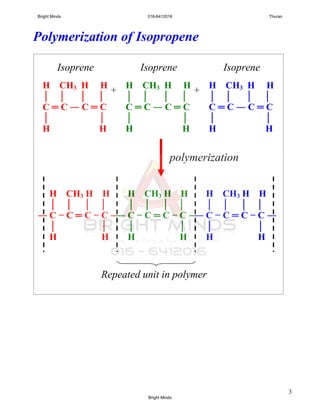
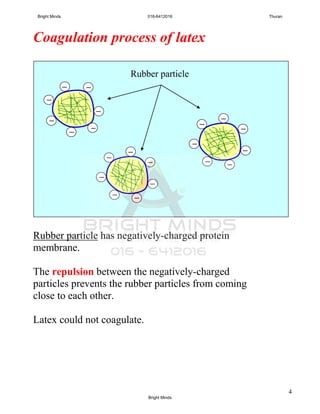
![5
Q: So what causes the latex to coagulate?
When an acid is added, the hydrogen ions, H+
neutralize the
negative charges on the protein membrane.
Q: Can you named the acid that usually used to coagulated
the latex in rubber industry?
A: Ethanoic acid also known as acetic acid.
[notes: all acid solutions can make latex coagulate]
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
─
+
+
+
++
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-95-320.jpg)
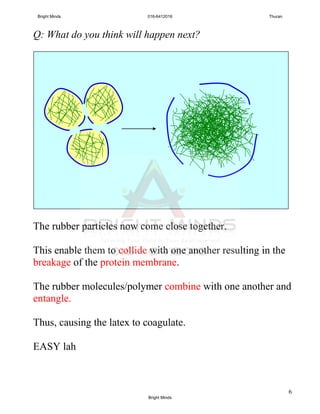
![7
Q: The coagulation of latex will also occur if latex is exposed
to air. Why?
A: Bacteria from air can enter latex. The growth and spread
of bacteria produce lactic acid that causes the process
above.
Q: Named the substance can be used to preserve latex in
liquid state? Explain.
A: Ammonia, NH3.
NH3 solutions contains hydroxide ions, OH-
that
neutralised the acid/hydrogen ions, H+
produced by the
bacteria. The rubber particles remain negatively charged
and the coagulation is prevented.
[notes: all alkaly solutions also can be used]
Properties of natural rubber
- Soft
- Elasticity decreases over time.
- Easily oxidized by air.
- Sensitive to heat. When heated, it becomes sticky.
When cooled, it becomes hard and brittle.
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-97-320.jpg)

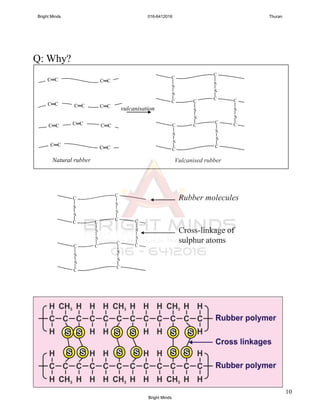
![9
Q: Compare and contrast the properties of vulcanised and
unvulcanised rubber.
Similarities
Vulcanised and unvulcanised rubber is elastic, and
heat and electrical insulator
Differences [notes: draw a table]
Properties
Vulcanised
rubber
Unvulcanised
rubber
Elasticity More elastic Less elastic
Hardness Harder Softer
Tensile strength Stronger Weaker
Resistance to
heat
Can withstand
higher
temperature
Cannot withstand
temperature
Resistance to
oxidation
Less easily
oxidized
Easily oxidized
Effect of organic
solvent
Does not
become soft and
sticky easily
Become soft and
sticky easily
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-99-320.jpg)


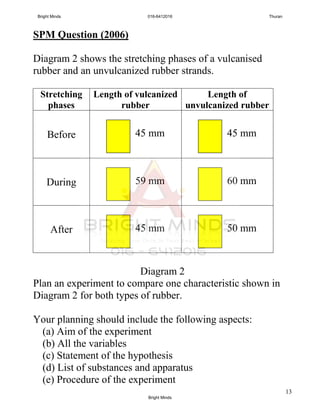
![14
(f ) Tabulation of data [17 marks]
Vulcanized
rubber
45 59 14 45
unvulcanized
rubber
45 60 15 50
Bright Minds 016-6412016 Thuran
Bright Minds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2hydrocarbon-140519232359-phpapp01/85/SPM-CHEMISTRY-Chapter-2-hydrocarbon-104-320.jpg)