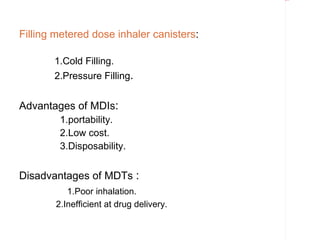
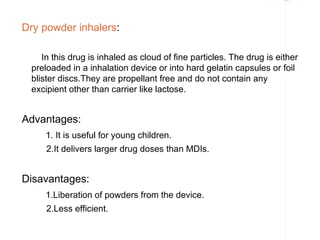
Pharmaceutical aerosols are pressurized dosage forms that emit a fine dispersion of active ingredients in a gaseous or liquid medium upon actuation. They are commonly used to treat asthma and COPD by delivering drugs directly to the lungs. Aerosols consist of a propellant that expels the formulation through a metering valve. Common propellants include hydrocarbons and chlorofluorocarbons. Aerosols can be manufactured via cold or pressure filling processes. Quality control tests evaluate the containers, valves, and drug delivery performance of aerosol products.