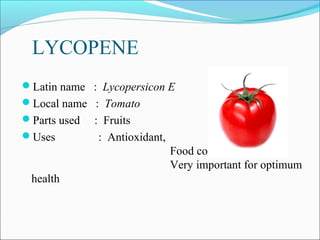
This document discusses nutraceuticals, which are foods or food components that provide health benefits. It defines nutraceuticals and outlines their classification based on beneficial ingredients or therapeutic uses. Some common nutraceuticals like lycopene, leutin, vitamins, minerals, herbs, and phytochemicals are described. The health benefits of different nutrients are highlighted. In conclusion, nutraceuticals are naturally present in many foods and consuming a diet rich in these can help maximize health and reduce disease risk.