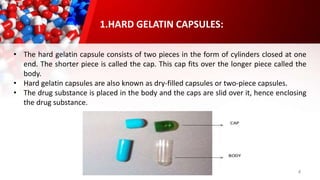
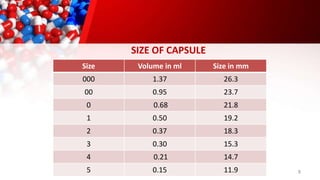
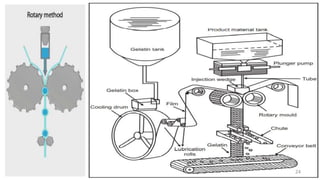
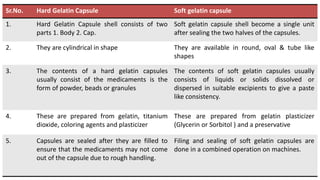
The document provides an overview of solid unit dosage forms, specifically focusing on hard and soft gelatin capsules, their manufacturing processes, advantages, disadvantages, and quality control tests. It details the composition, preparation methods, and sealing techniques for both types of capsules, as well as outlines key quality control measures to ensure product integrity. Additionally, the document differentiates hard gelatin capsules from soft gelatin capsules in terms of structure, contents, and manufacturing processes.