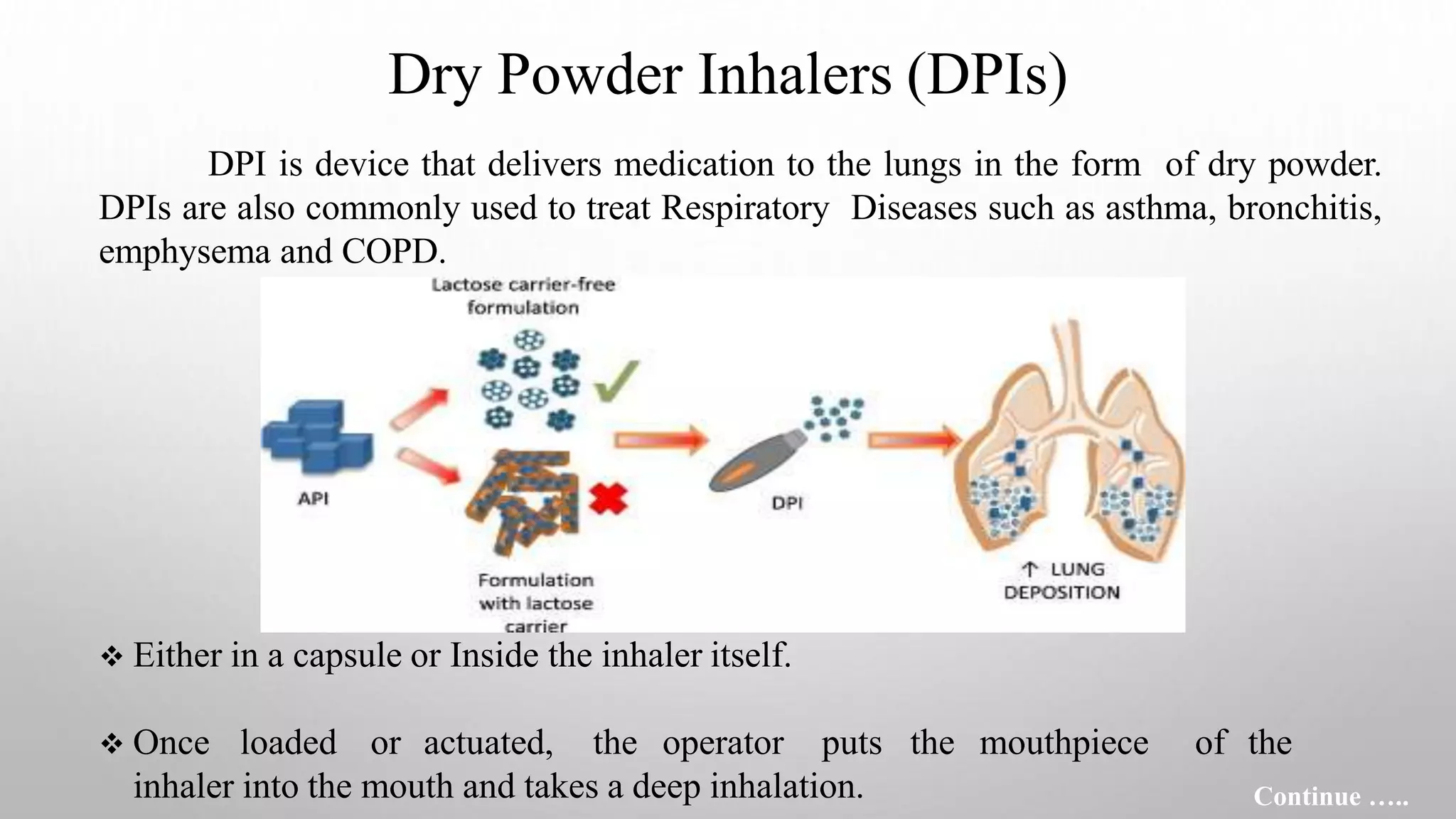
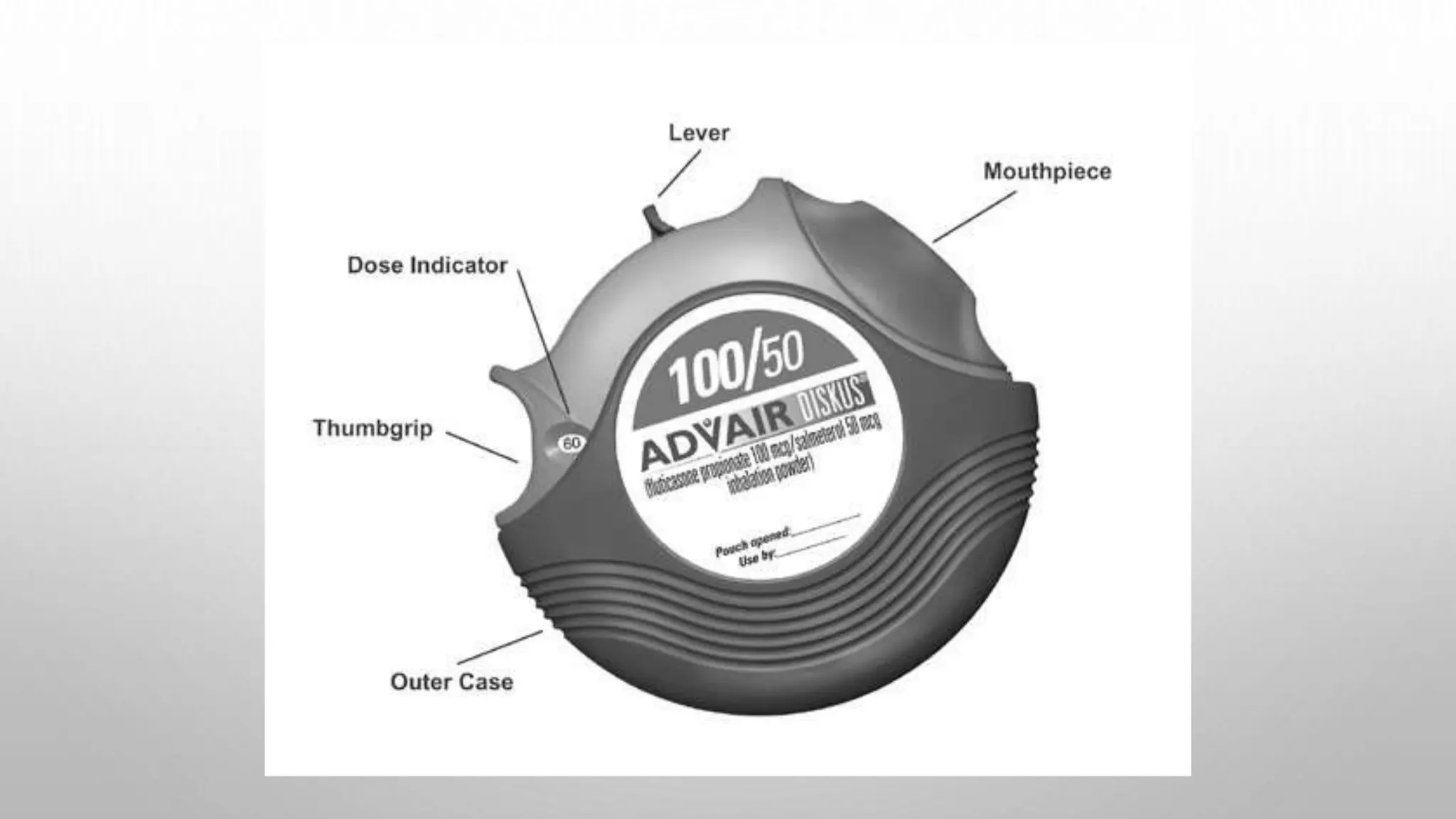
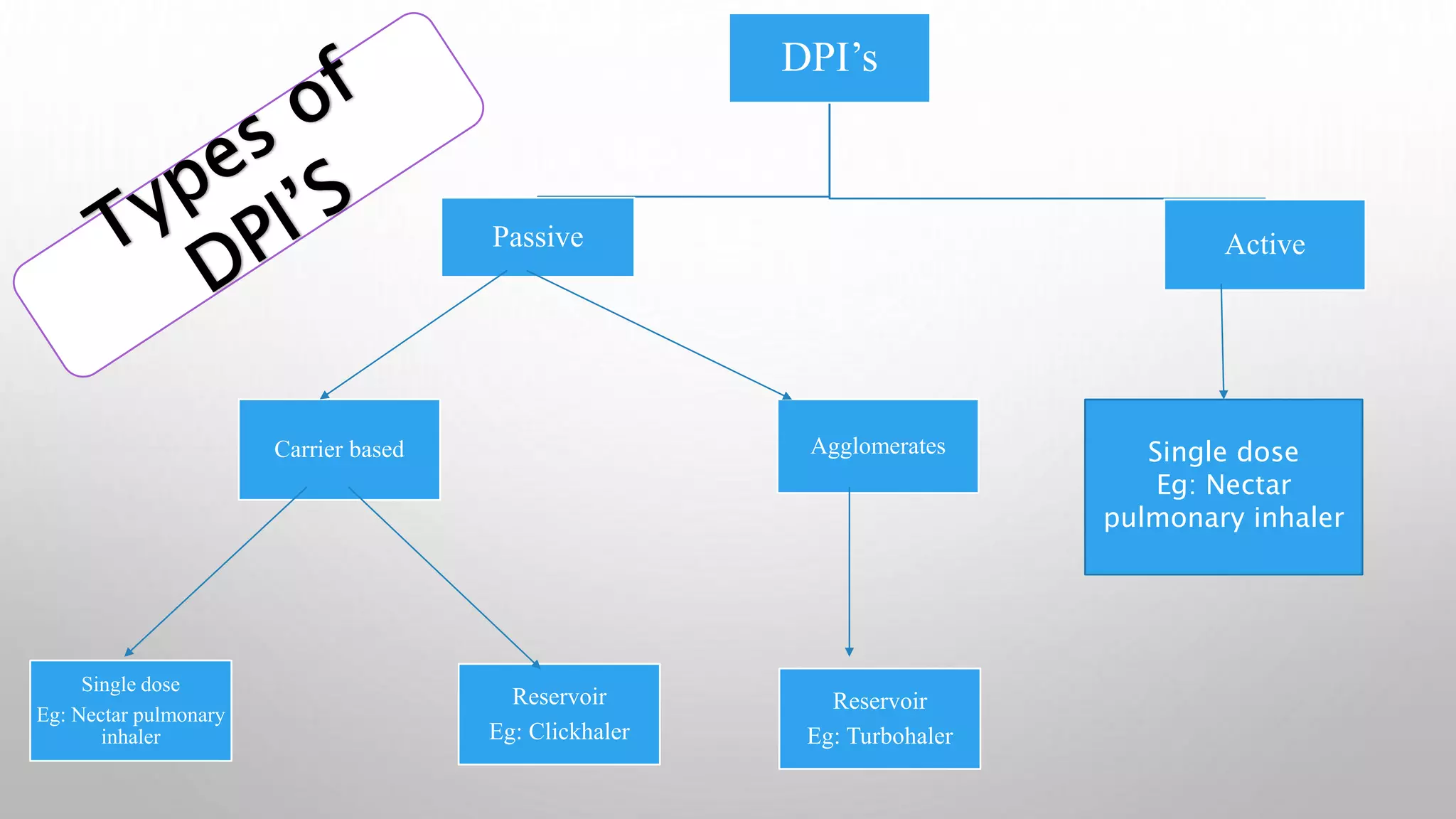
This document provides an overview of dry powder inhalers (DPIs), including their definition, types, characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, formulation considerations, common carriers used, manufacturing techniques, and characterization methods. DPIs deliver medication to the lungs in dry powder form and are commonly used to treat respiratory diseases like asthma. They have advantages over metered dose inhalers like not requiring breath holding and being propellant-free. Key aspects in developing effective DPIs include achieving targeted deposition, optimized aerosol generation, and operation at low inhalation flow rates. Common carriers in DPI formulations include lactose for its stability and compatibility. Micronization is often used to reduce drug particle size.