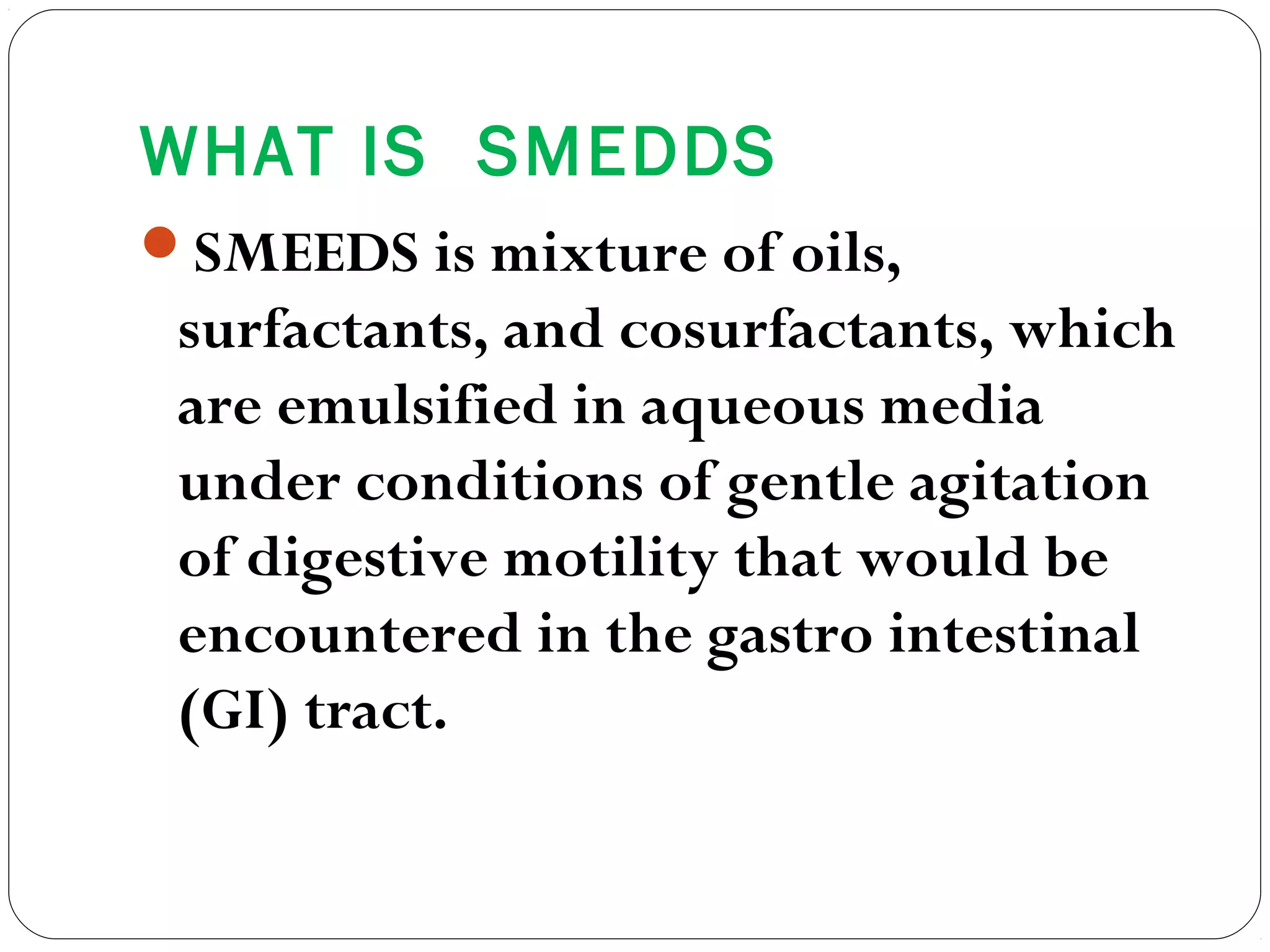
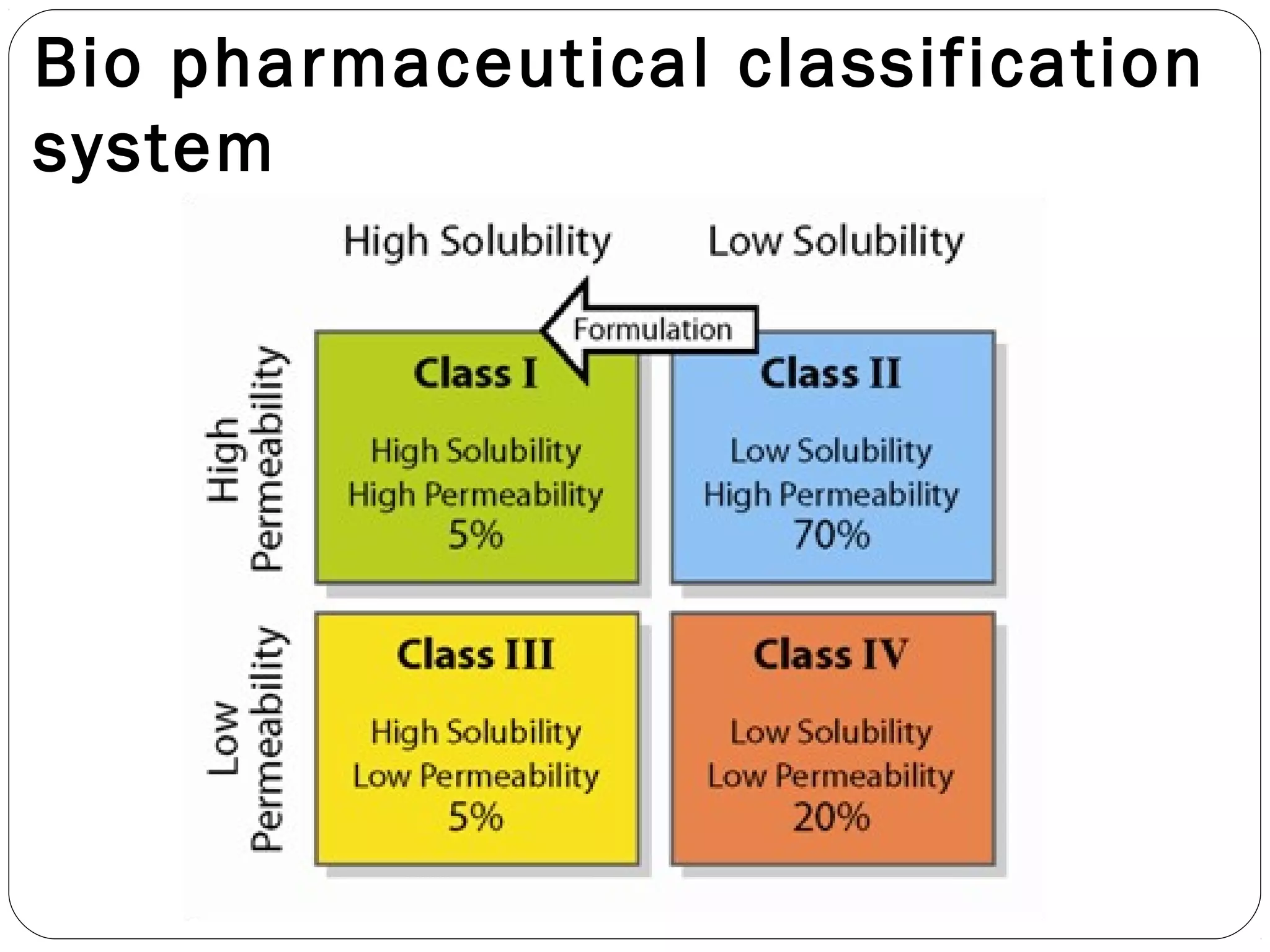
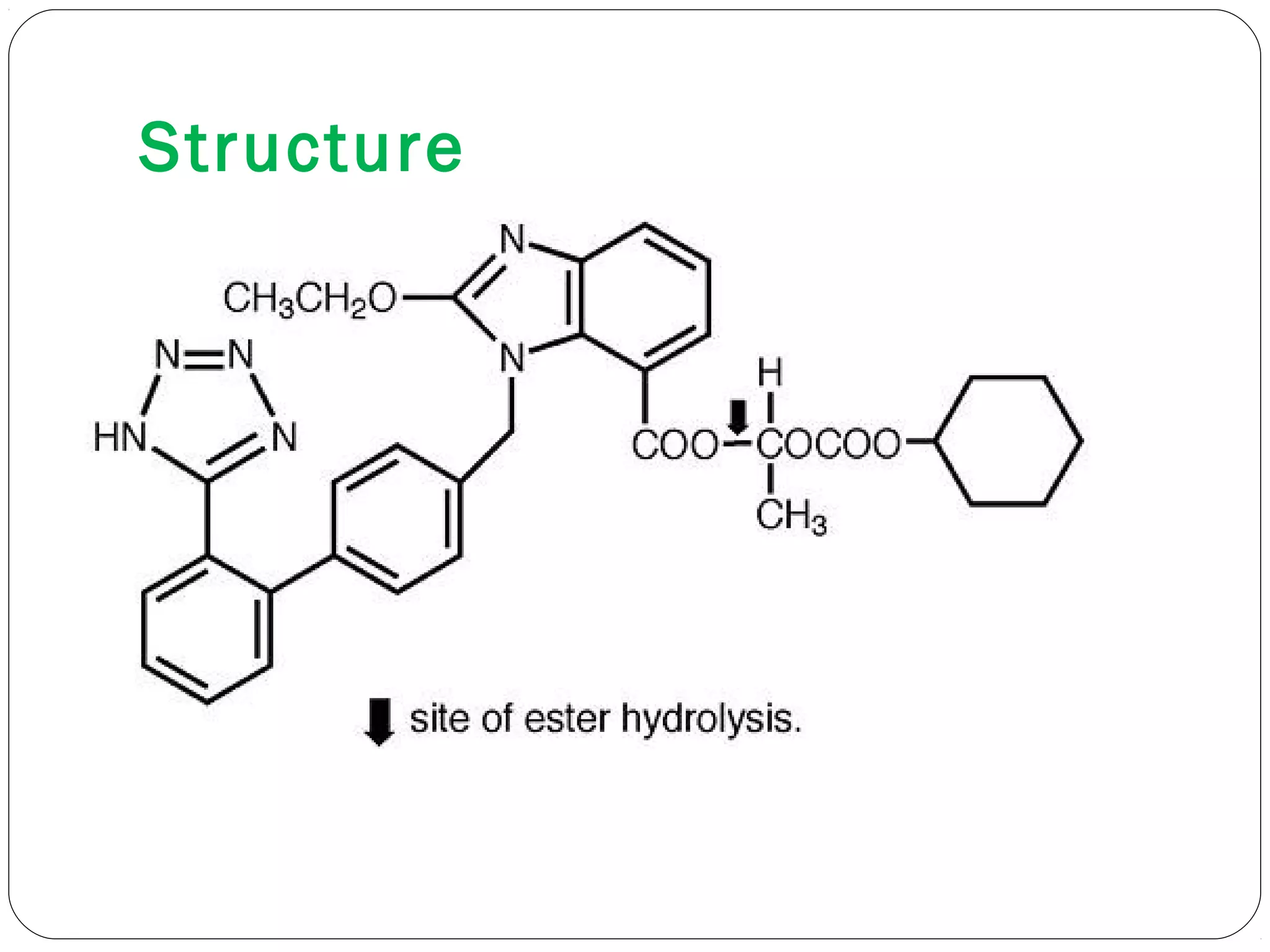
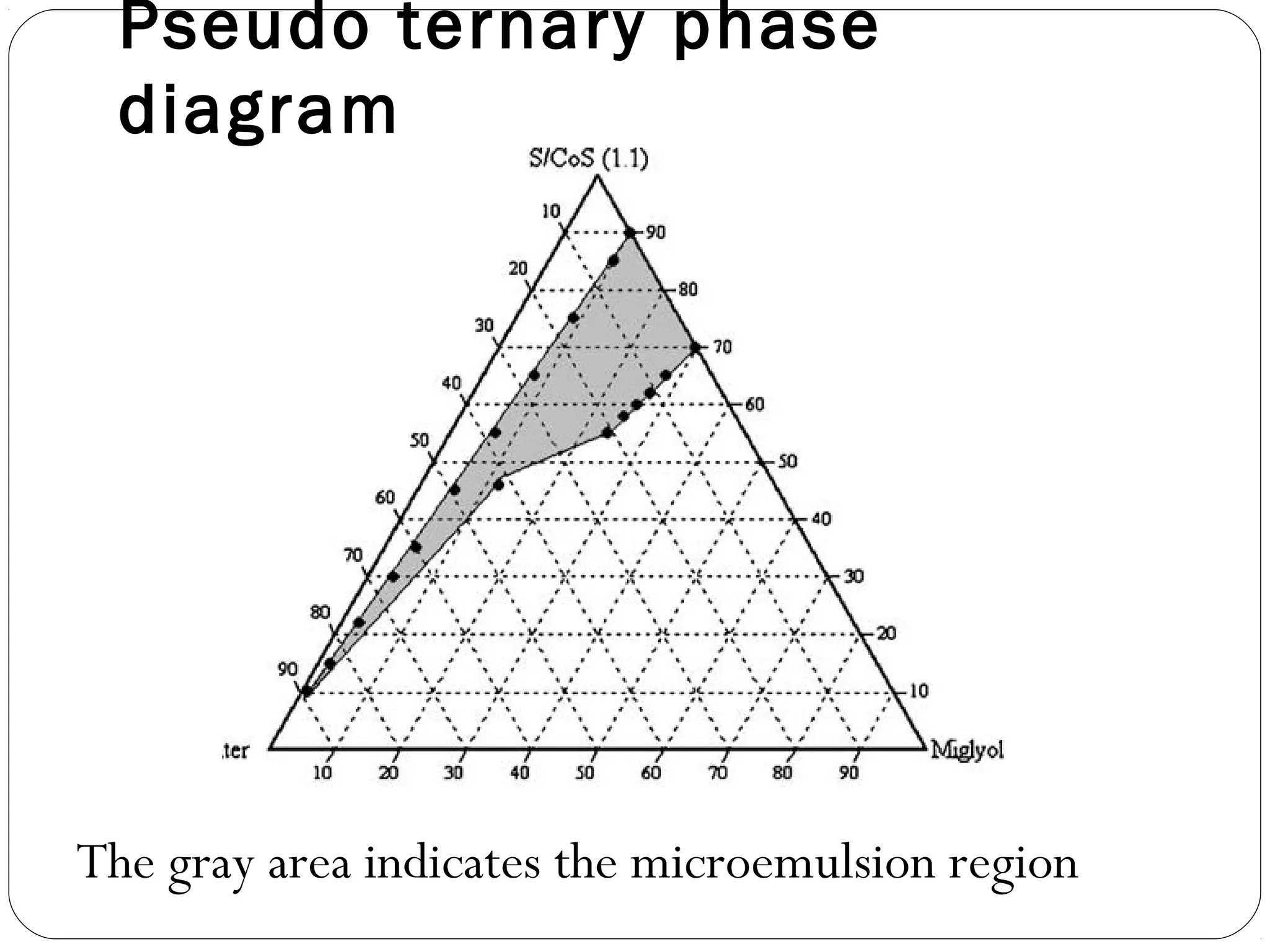
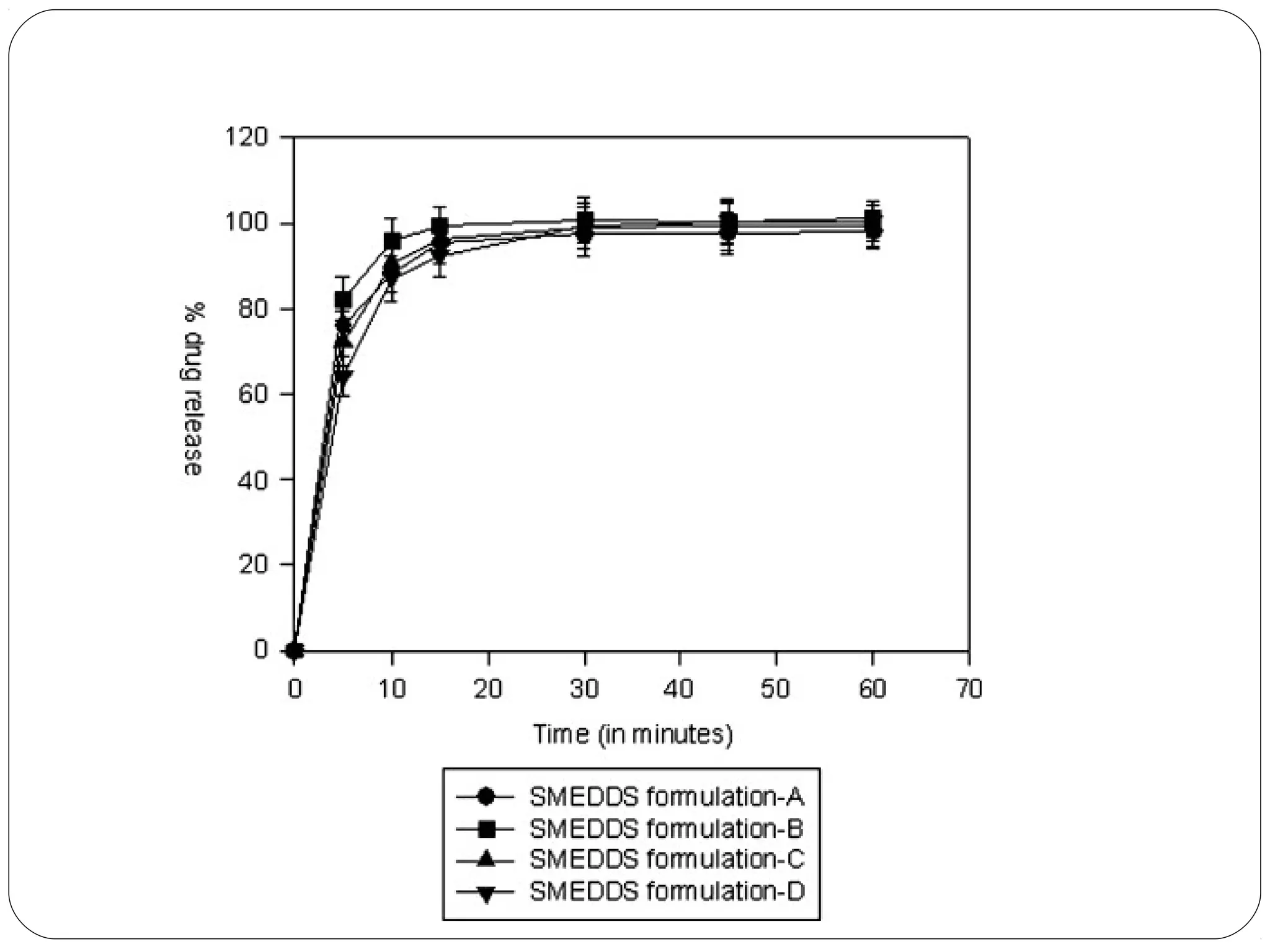
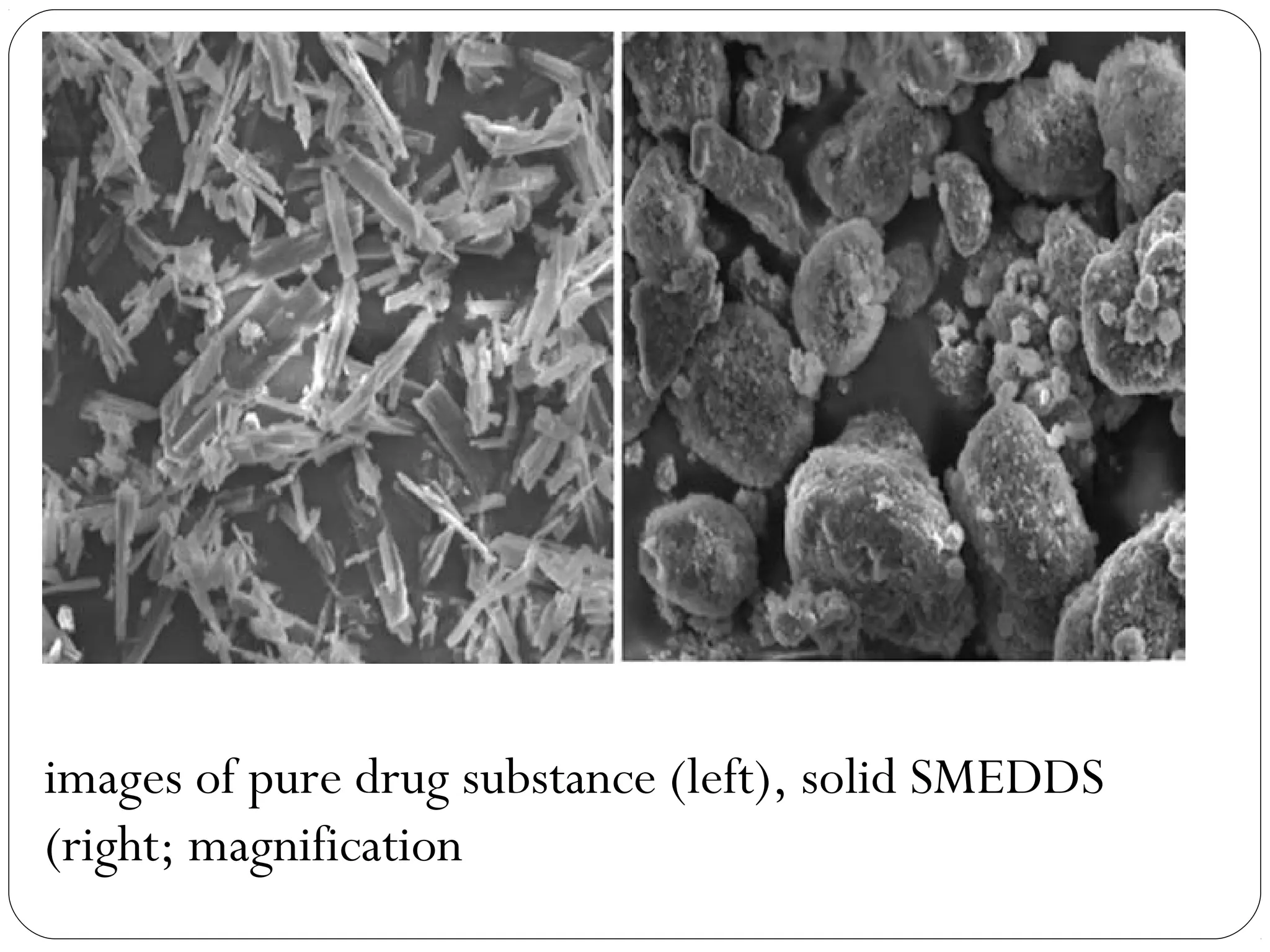
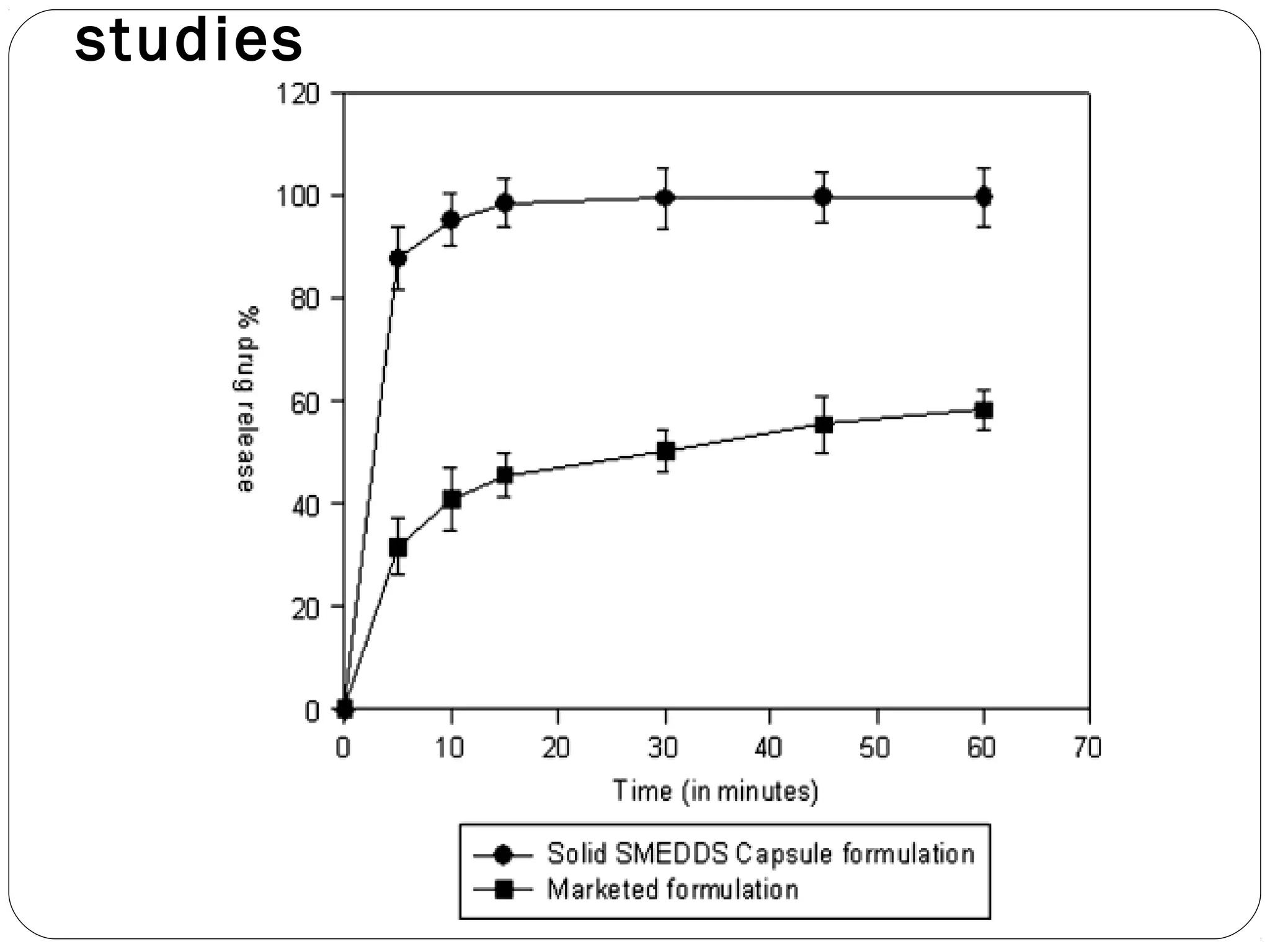
The document summarizes a study on developing a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) to enhance the solubility and dissolution of the poorly water-soluble drug candesartan cilexetil. SMEDDS were formulated using oils, surfactants, and cosurfactants. Pseudo ternary phase diagrams were used to optimize the formulations. Solid SMEDDS were developed and showed comparable drug dissolution to liquid SMEDDS. The solid SMEDDS formulations demonstrated enhanced drug release compared to commercial tablets, indicating their potential for improving bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs like candesartan cilexetil.