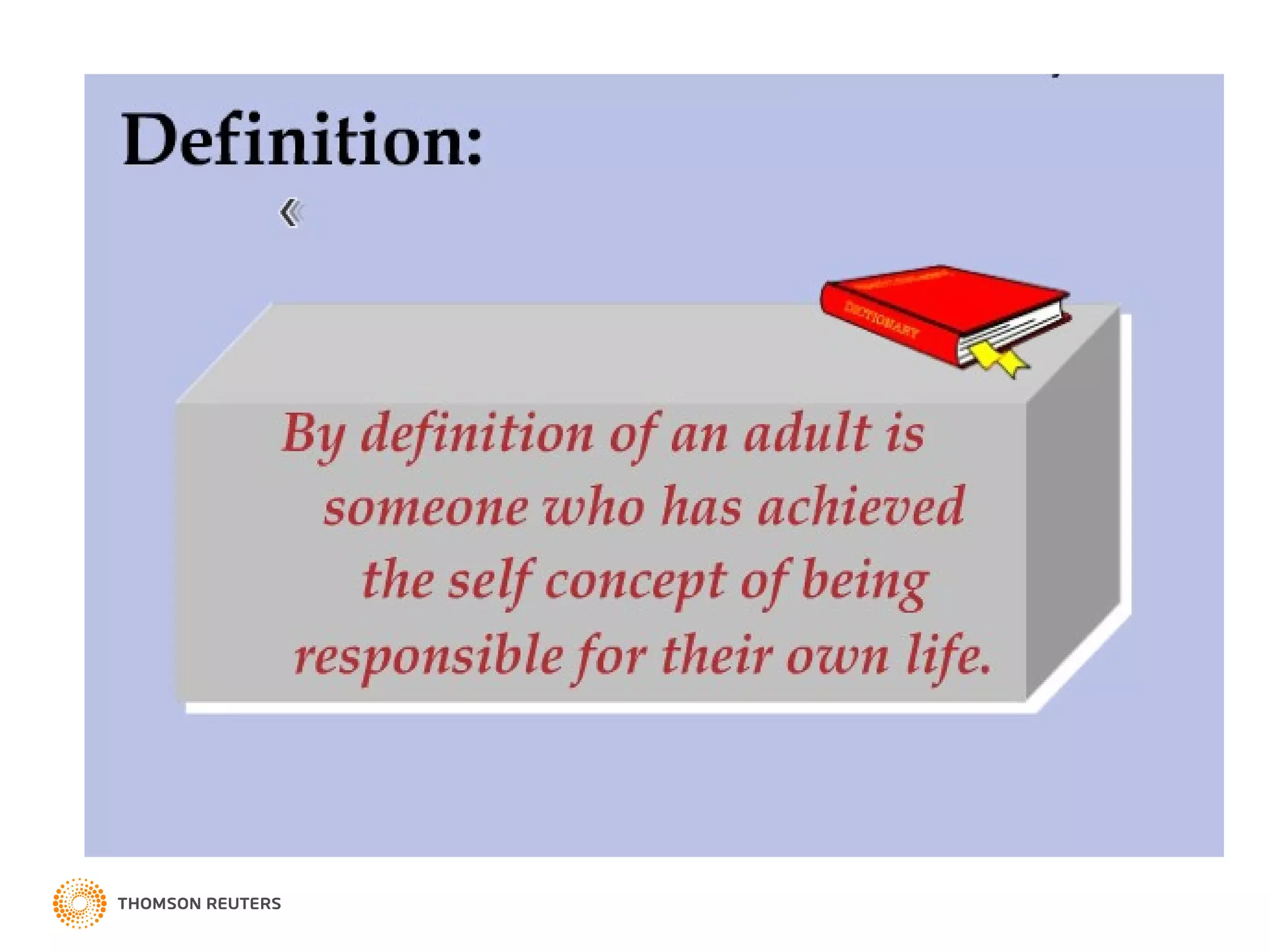
The document discusses adult learning theory and instructional design for training adult learners. It defines andragogy as the art and science of adult learning, which focuses on self-directed, experience-based, problem-centered, and socially motivated learning. Malcolm Knowles' assumptions about adult learners and his theory of andragogy are explained. Heutagogy, a more self-determined form of learning, is also introduced. The document then provides Thomson Reuters' 10-step model for instructional design when training adult learners.