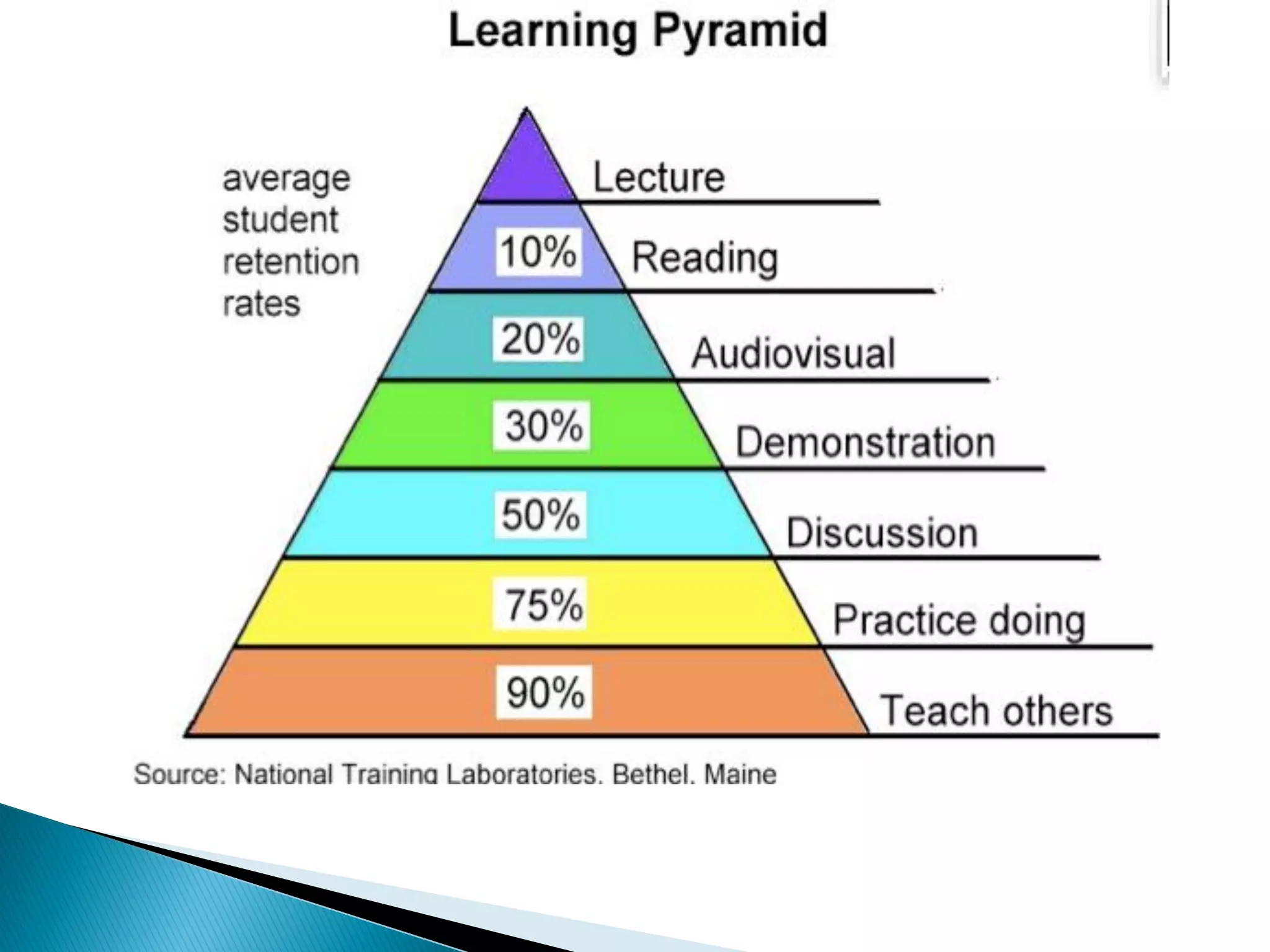
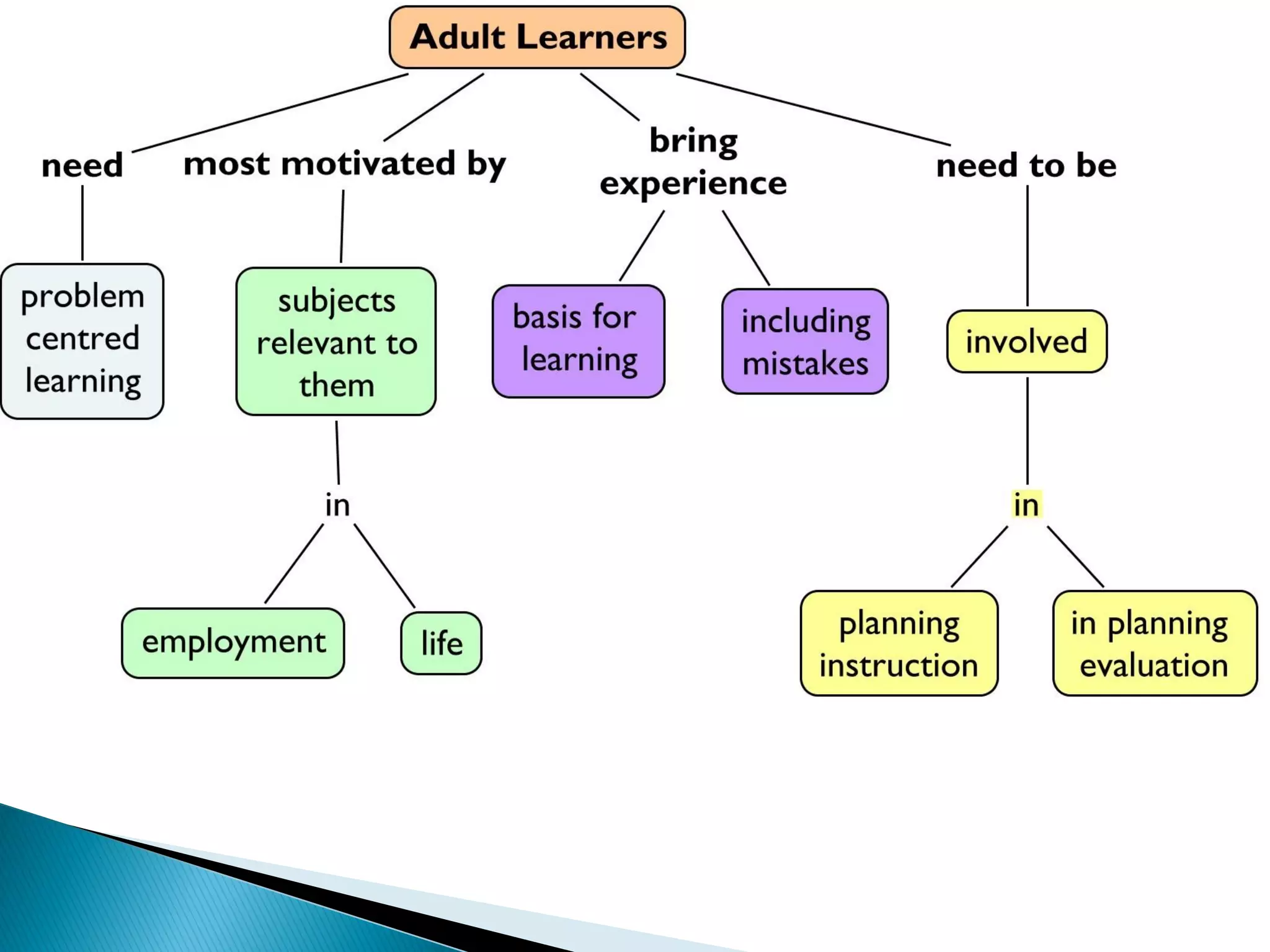
This document discusses adult learning principles and effective training methods for adult learners. It begins by introducing Dr. Charles Ware and his credentials in health education. It then outlines key differences between how children and adults learn, such as adults being self-directed and needing immediate application of knowledge. The document also discusses Malcolm Knowles' theory of andragogy and six assumptions about adult learners - that they have a self-concept of being responsible for their own decisions, a need to know why they need to learn something, valuable prior experiences to contribute, readiness to learn, orientation to learning focused on real-world problems, and intrinsic motivation. It concludes by evaluating several training methods and their advantages/disadvantages for adult learners



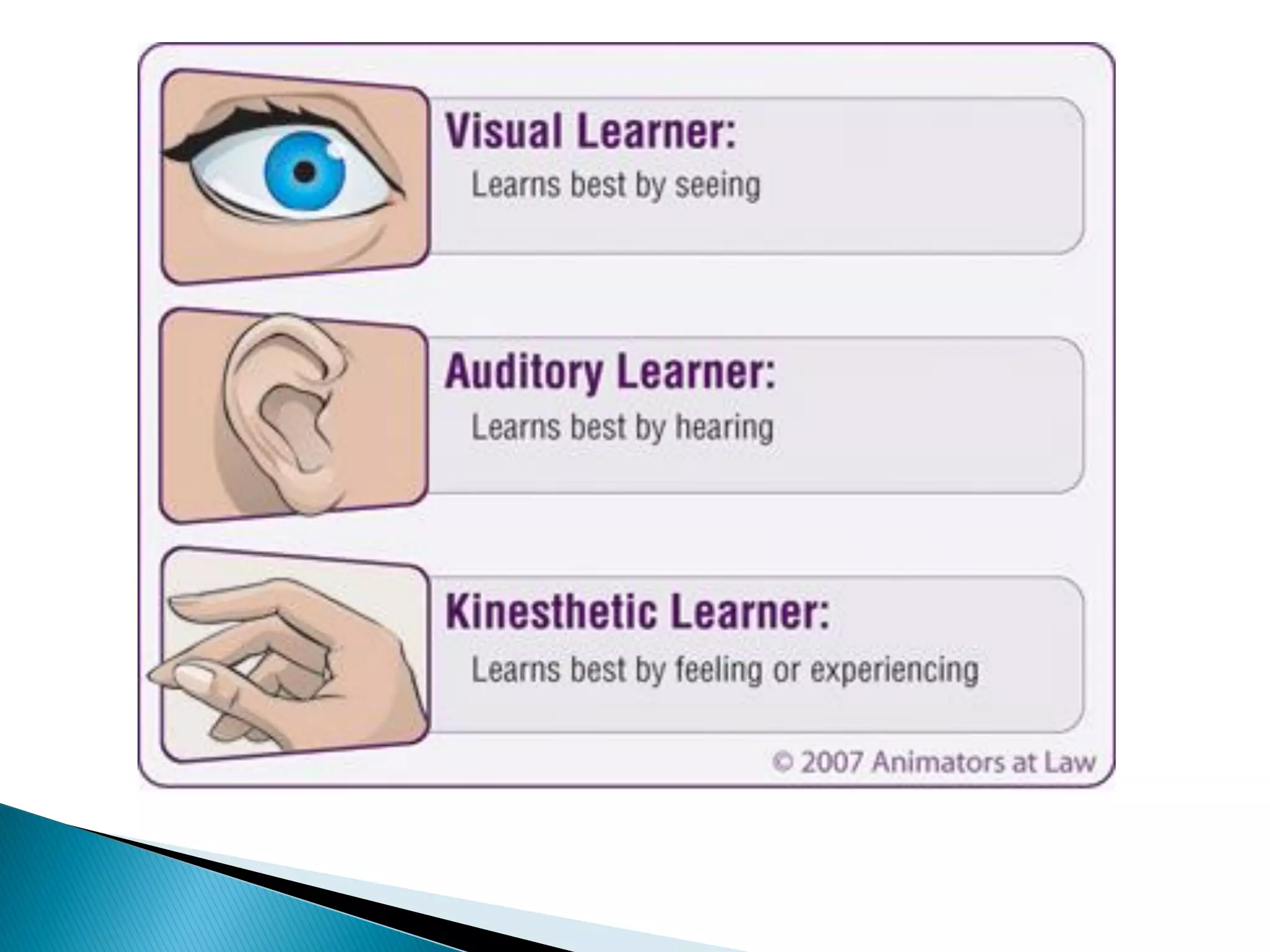























![ Presentation/Lecture
◦ Advantages
Keeps group together and on the same point
Time control is easier
Useful for large group size (20 or more]
◦ Drawbacks
Can be dull if used to long without learner participation
Difficult to gauge if people are learning
Retention is limited.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adultlearningstylesandtrainingmethods-150724211723-lva1-app6891/75/Adult-Learning-Styles-and-Training-Methods-28-2048.jpg)