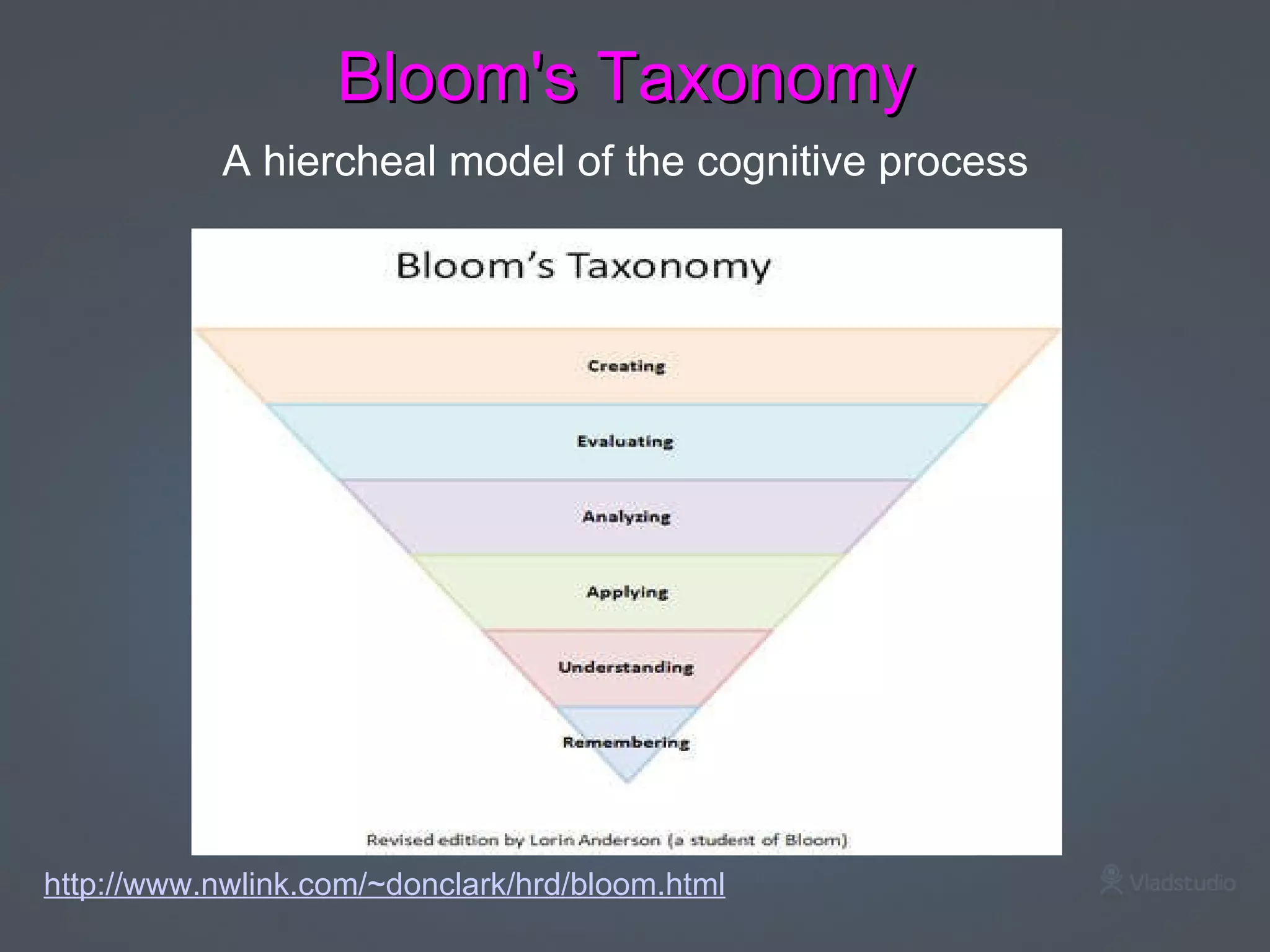
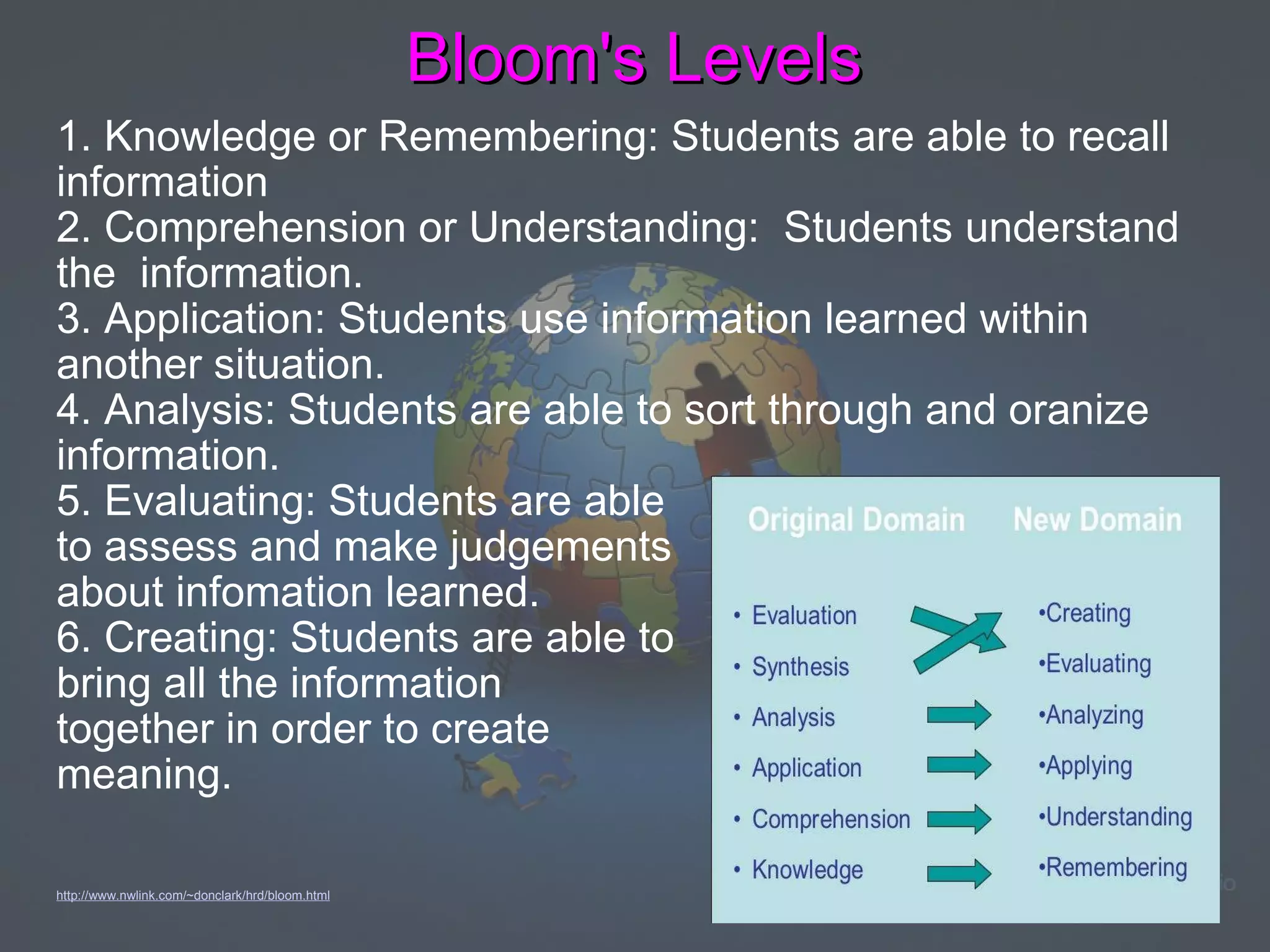
Constructivism is a theory of learning that states that individuals create their own understanding and knowledge from their experiences. According to constructivism, learning occurs as learners are actively engaged in making meaning by connecting new information to prior knowledge through hands-on exploration and discovery. Key principles of constructivism include linking new concepts to existing knowledge, using real-world problems and experiments to promote understanding, and placing emphasis on meaningful learning activities rather than rote memorization. In the classroom, constructivist teaching strategies include collaborative and project-based learning to encourage critical thinking skills based on Bloom's Taxonomy. Differentiating instruction to accommodate different learning styles and providing a creative learning environment also support the constructivist approach.