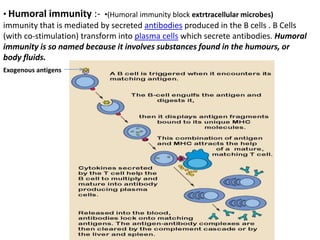
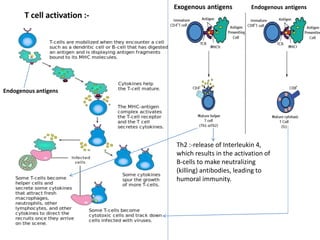
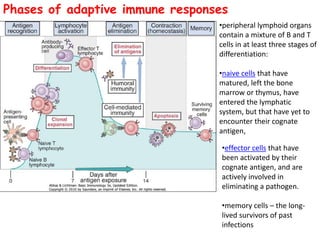
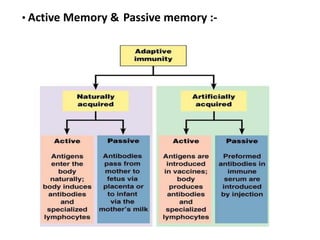
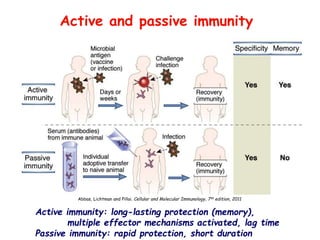
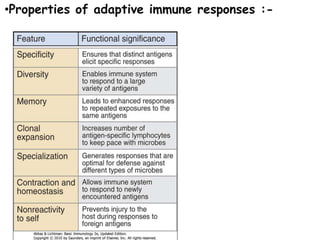
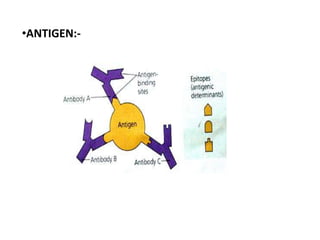
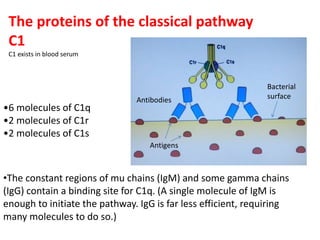
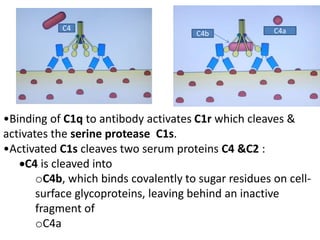
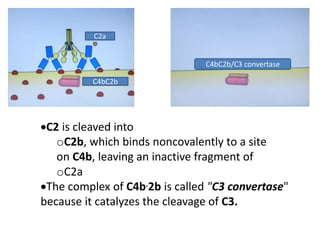
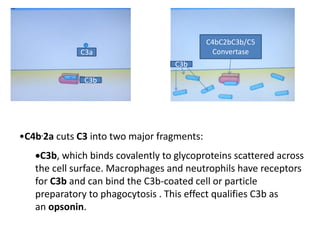
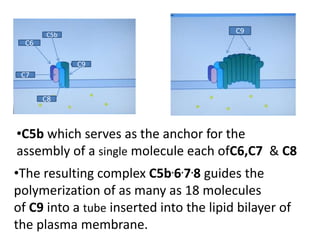
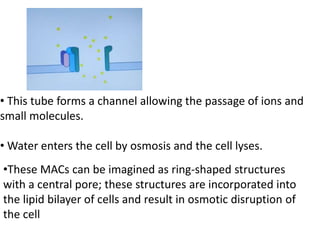
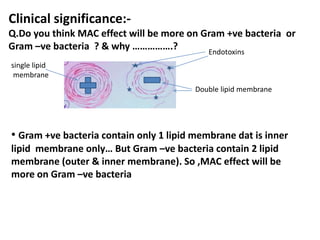
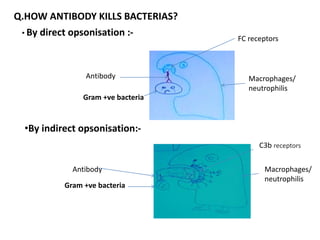
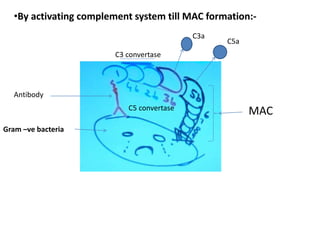
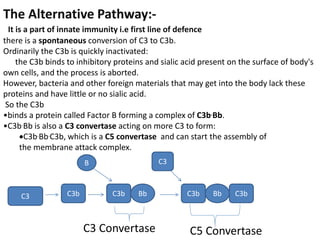
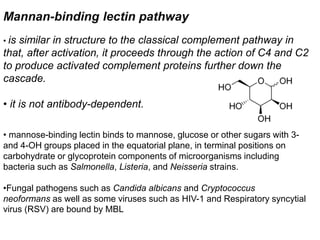
Adaptive immunity is induced in response to specific antigens after collaboration between phagocytic cells, T and B lymphocytes, and production of immunoglobulins and lymphokines. There are two types of adaptive immunity: humoral immunity mediated by secreted antibodies and cell-mediated immunity which activates phagocytes, natural killer cells, cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and cytokines without antibodies. Humoral immunity involves B cell transformation into plasma cells secreting antibodies, while cell-mediated immunity blocks intracellular microbes by activating macrophages or cytotoxic T cells killing infected cells.