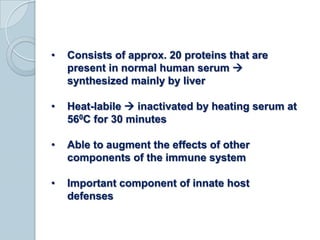
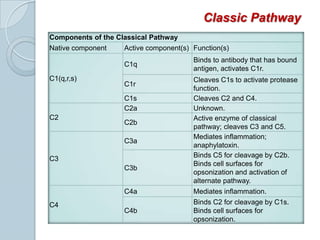
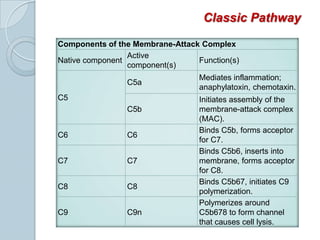
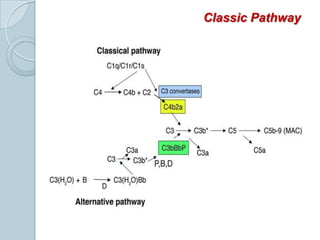
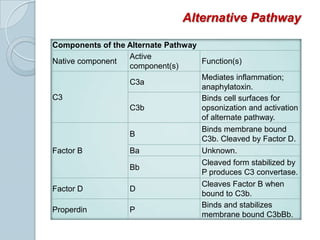
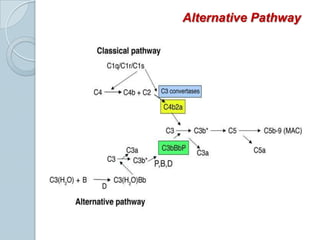
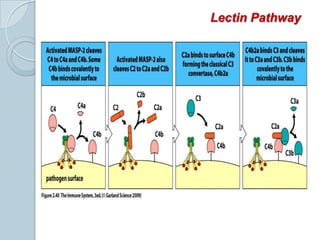
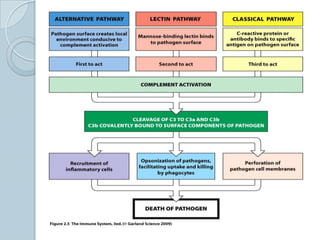
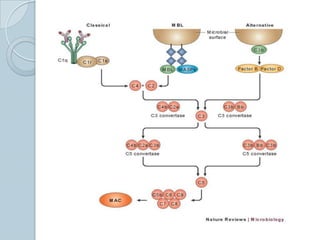
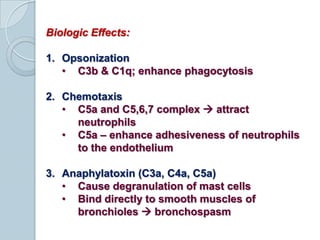
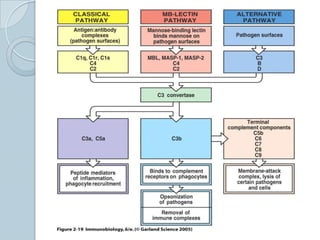
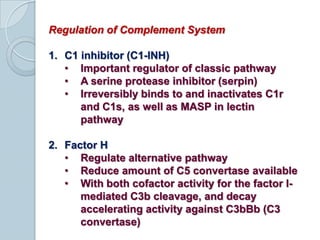
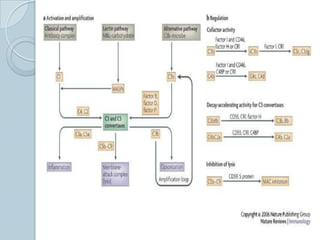
The complement system consists of approximately 20 proteins that are mainly synthesized by the liver and play an important role in innate immunity. It has three main effects: lysis of cells, generation of inflammatory mediators, and enhancement of phagocytosis. There are three pathways of complement activation: the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways. The classical pathway is part of acquired immunity and requires antigen-antibody complexes, while the lectin and alternative pathways are part of innate immunity and activate in response to microbial surfaces. Complement activation leads to opsonization and lysis of pathogens as well as inflammatory responses. The system is tightly regulated to prevent damage to host cells. Deficiencies in complement proteins predispose individuals to certain infections