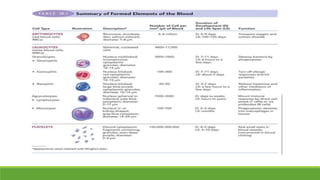
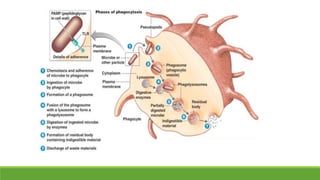
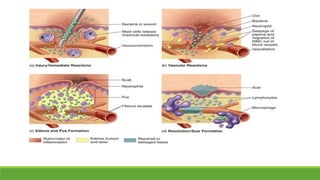
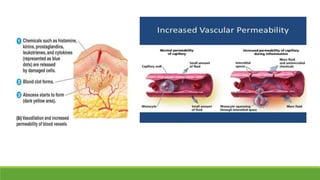
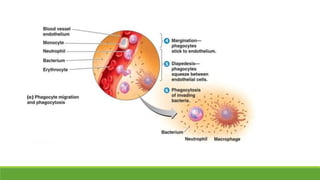
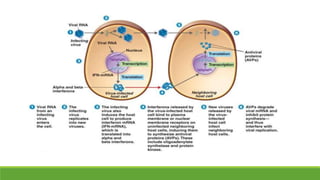
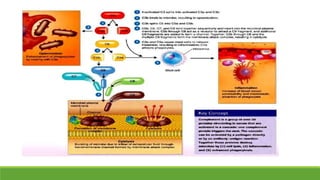
Immunity is the body's defense mechanism against foreign bodies like bacteria, viruses, and toxins. Innate immunity provides immediate protection through physical and chemical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, as well as white blood cells that phagocytose pathogens. The complement system and interferons are also part of innate immunity. When barriers are breached, inflammation occurs, attracting more immune cells to the site of infection to destroy pathogens and repair tissue damage.