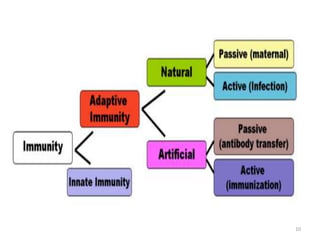
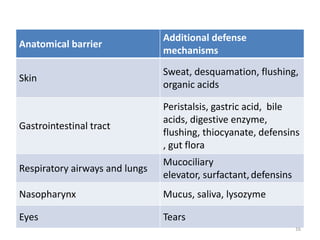
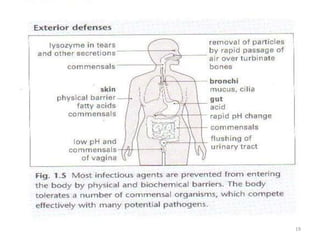
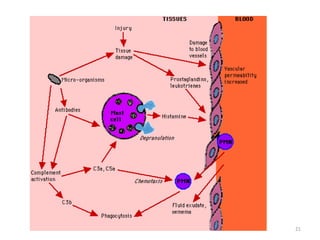
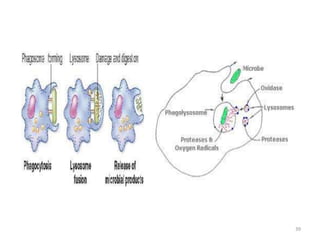
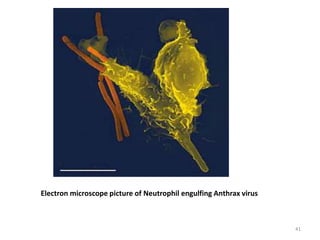
- Innate immunity refers to nonspecific defense mechanisms present from birth that provide immediate resistance to pathogens. It includes physical and chemical barriers as well as cellular responses like phagocytosis.
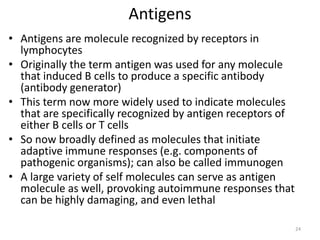
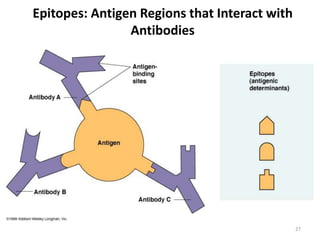
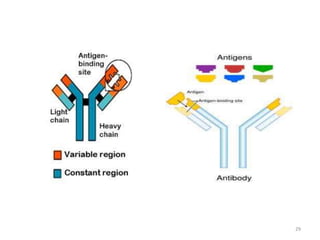
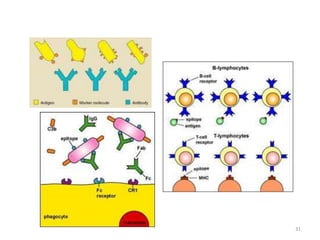
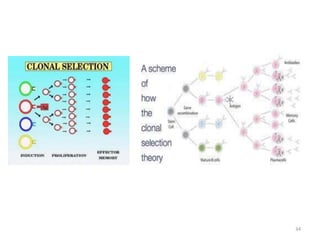
- Adaptive immunity develops later in life and involves antigen-specific immune responses mediated by lymphocytes. It is more complex than innate immunity and includes immunological memory.
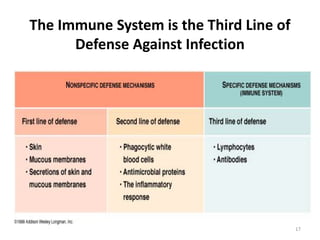
- The immune system consists of both innate and adaptive immunity. Innate responses provide initial defense against infection while adaptive responses provide acquired, antigen-specific immunity. Memory cells generated during adaptive responses enable faster responses upon reexposure.