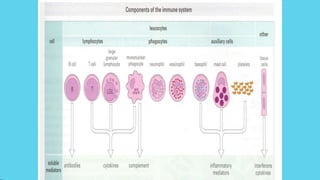
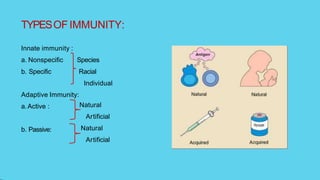
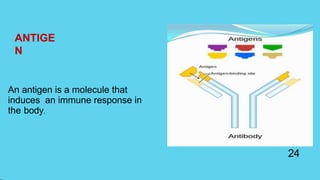
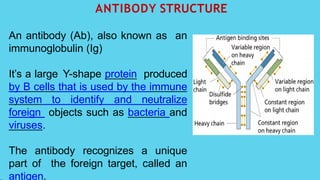
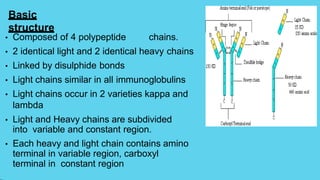
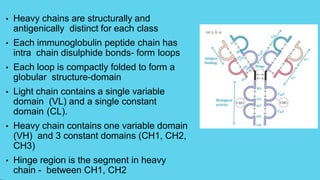
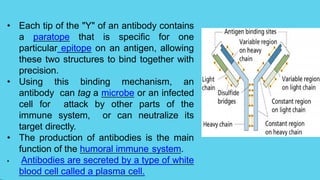
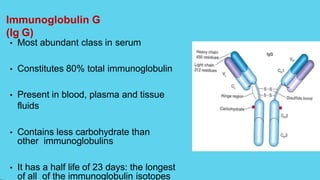
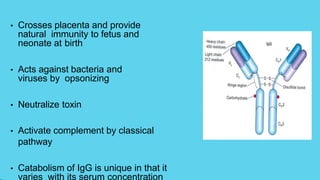
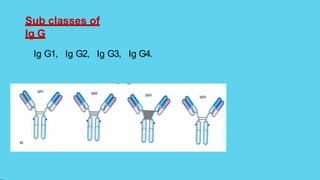
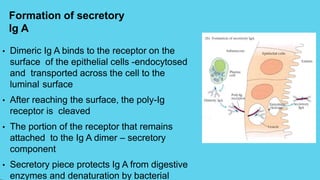
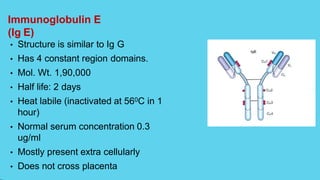
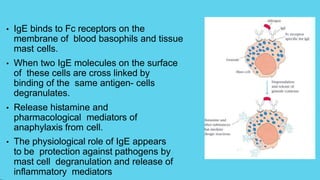
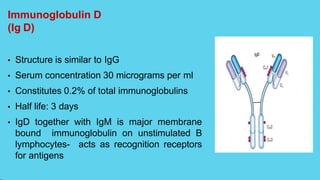
Innate immunity provides non-specific protection against pathogens and involves physical and chemical barriers as well as cellular responses. Adaptive immunity provides pathogen-specific protection through antibodies and T-cells, develops over time, and results in immunological memory. Innate immunity forms the first line of defense through mechanisms like epithelial surfaces, antimicrobial proteins, inflammation, and phagocytosis. Adaptive immunity is subdivided into active and passive immunity and involves both humoral and cell-mediated responses that are stimulated by antigens.