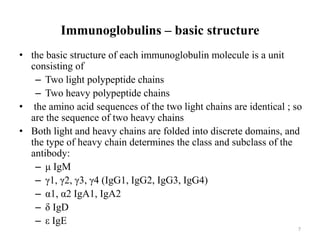
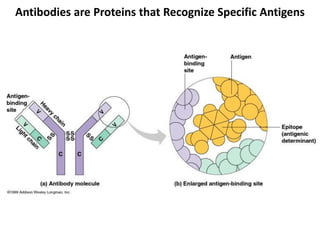
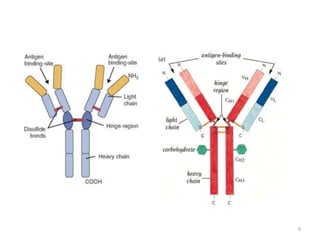
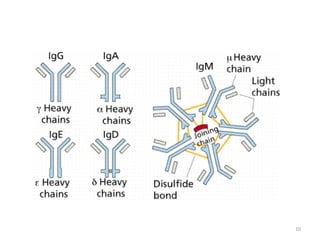
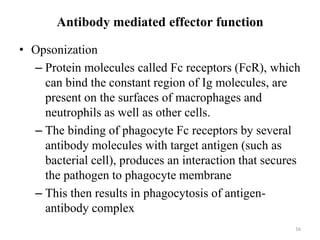
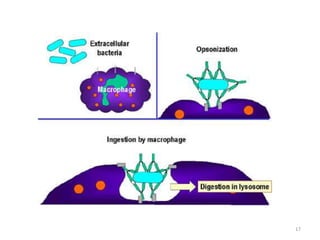
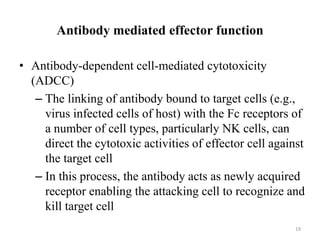
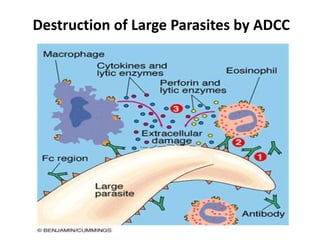
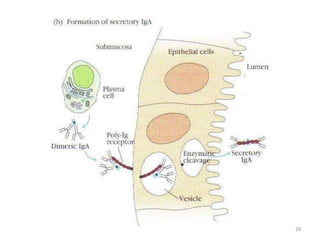
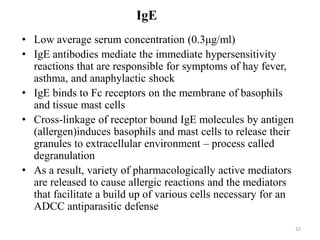
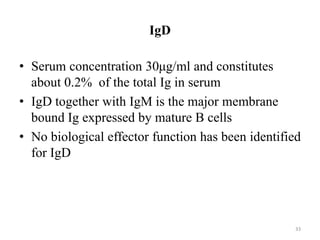
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are proteins produced by plasma cells that recognize and help eliminate antigens or microorganisms bearing those antigens. There are two main types of molecules involved in antigen recognition: antibodies and T cell antigen receptors. Antibodies exist in two forms - as membrane-bound receptors on B cells or as soluble proteins in serum and tissue fluids. The different classes of antibodies - IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE - have distinct structures and biological functions like opsonization, complement activation, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, and mediating allergic reactions. Secretory IgA plays an important role in mucosal immunity by preventing pathogen attachment and