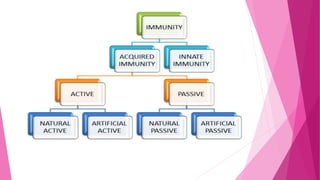
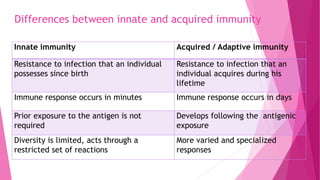
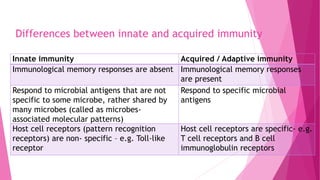
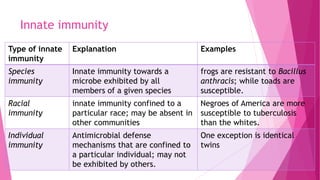
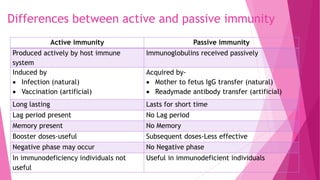
This document defines and compares innate and acquired immunity. Innate immunity is present from birth and provides non-specific resistance to pathogens. It involves anatomical barriers, inflammatory responses, complement pathways, and cytokines. Acquired immunity develops during a person's lifetime through active or passive transfer of antibodies or immune cells. Active immunity results from infection or vaccination and is long-lasting, while passive immunity provides short-term protection through antibody transfer from mother to fetus or through immunoglobulin treatments.