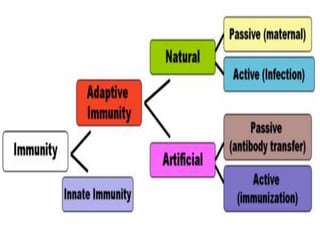
This document summarizes the different types of immunity. There are two main types: innate (non-specific) immunity, which is the body's first line of defense and does not depend on previous exposure; and acquired (adaptive/specific) immunity, which develops over time after exposure and retains memory to mount a stronger response next time. Innate immunity includes physical barriers and cellular barriers like phagocytes and cytokines. Acquired immunity consists of antibody-mediated (humoral) immunity and cell-mediated immunity, and can be actively or passively acquired through natural infection or vaccination.