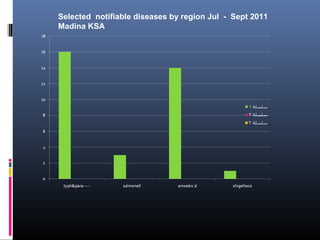
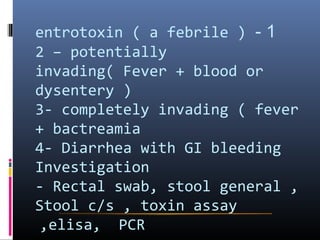
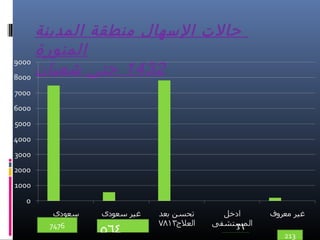
This document discusses acute infectious diarrhea. It defines it as an alteration of normal gastrointestinal function caused by ingested microorganisms or their toxins. The mechanisms of disease include osmotic load, intestinal secretion, malabsorption, and altered motility. Common causes are discussed such as ETEC, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Shigella, and viruses. Symptoms, diagnostic testing, treatment, and prevention are covered. Management involves rehydration and use of antimicrobials in some cases.