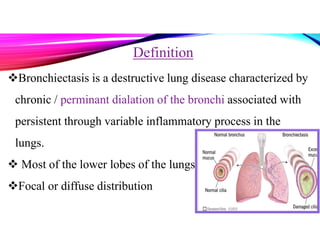
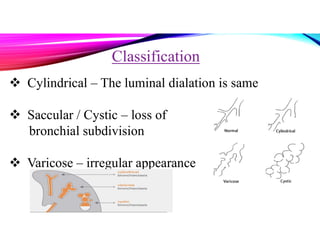
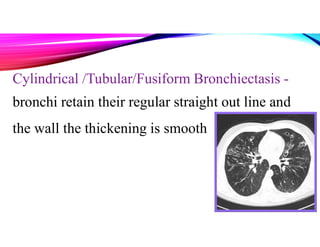
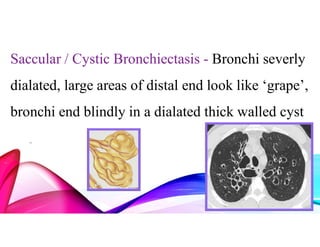
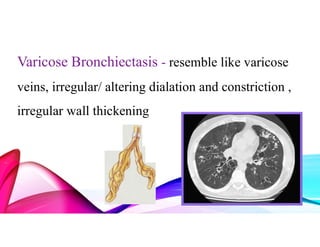
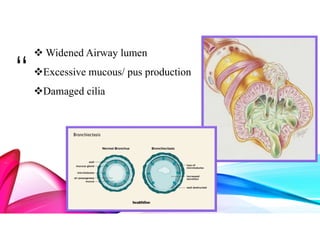
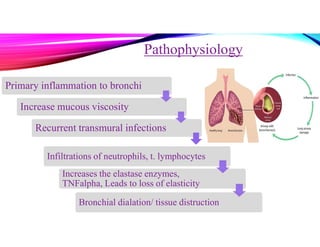
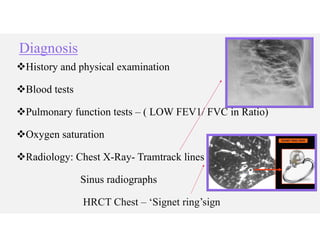
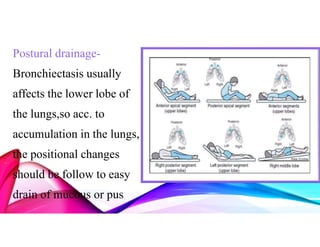
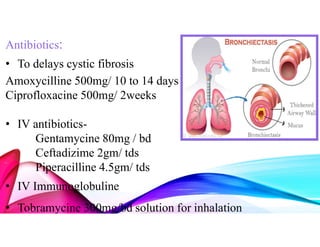
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung disease characterized by permanent dilation of the bronchi due to various causes such as infections and autoimmune disorders. It presents with symptoms like shortness of breath, chronic cough, and excessive sputum production, and requires diagnosis through clinical examination and radiological tests. Treatment focuses on eliminating causes, controlling infections, and may include antibiotics, bronchodilators, and in severe cases, surgical intervention.