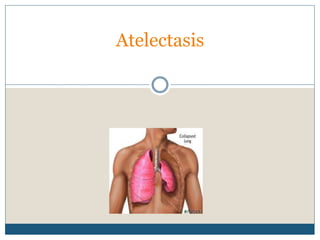
Atelectasis is the collapse or closure of the lungs caused by the absence of air in parts of the lung. It develops when alveoli become airless and collapse. Common causes include obstruction of the airways, diminished lung expansion, retained secretions, altered breathing patterns during anesthesia or sedation, and compression of the lungs. Symptoms may include cough, difficulty breathing, and low oxygen levels. Treatment focuses on removing obstructions and secretions through techniques like suctioning, chest physiotherapy, and bronchodilators to reinflate the lungs. More severe cases may require procedures like bronchoscopy or mechanical ventilation.