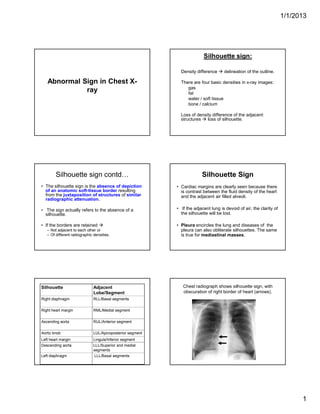
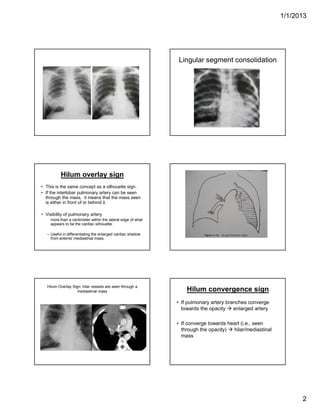
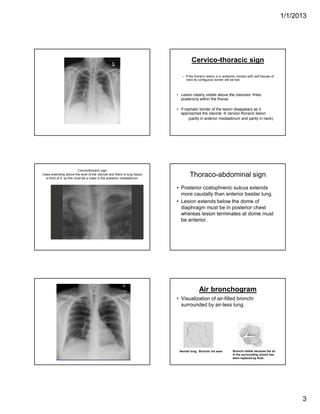
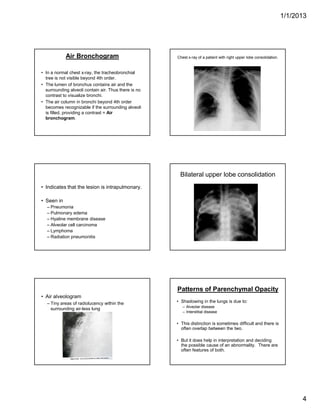
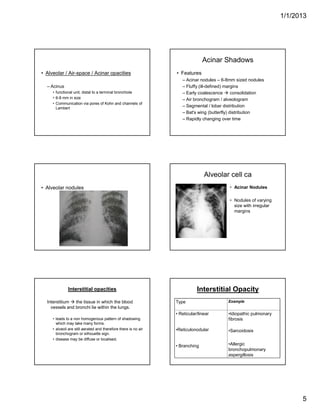
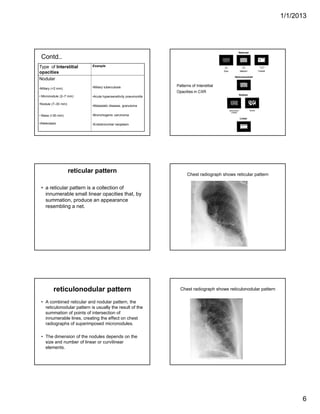
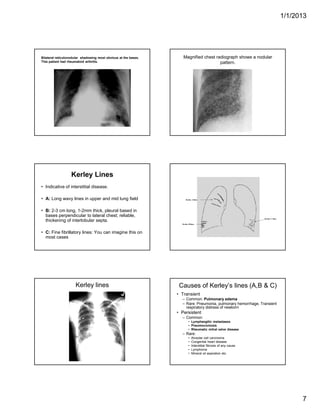
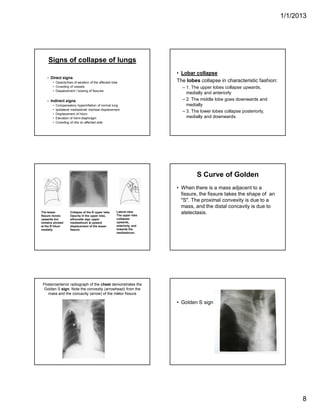
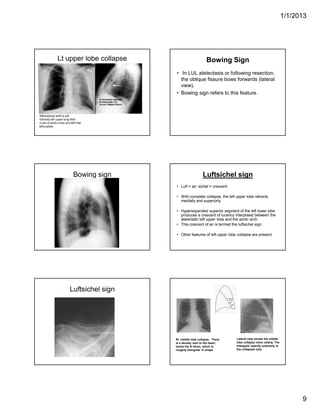
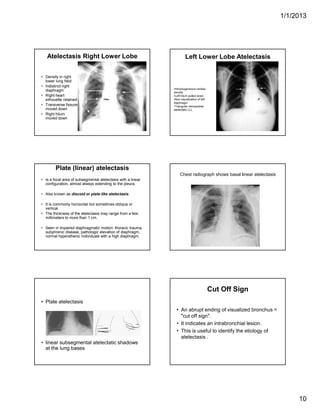
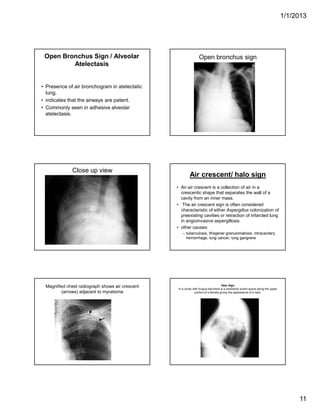
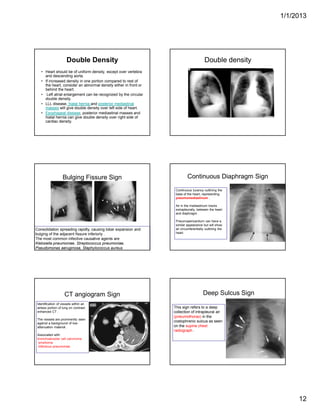
The document discusses various abnormal signs seen on chest x-rays. It describes the silhouette sign as the loss of depiction of an anatomic border due to similar radiographic densities of adjacent structures. The hilum overlay sign refers to visibility of pulmonary arteries through a mediastinal mass. An air bronchogram is visualization of air-filled bronchi surrounded by airless lung. Patterns of parenchymal opacities include alveolar/interstitial opacities which can appear as reticular, reticulonodular or nodular patterns. Kerley lines are indicative of interstitial disease and can have transient or persistent causes such as edema, metastases or fibrosis. Signs of lung collapse include opacification