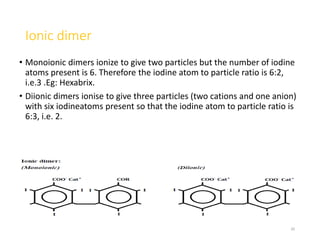
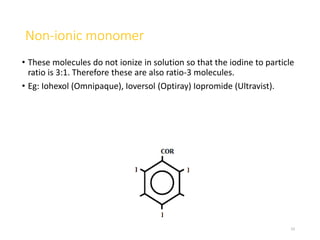
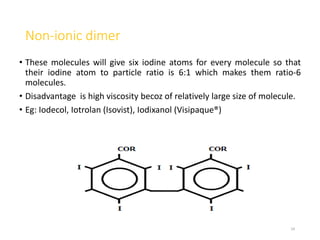
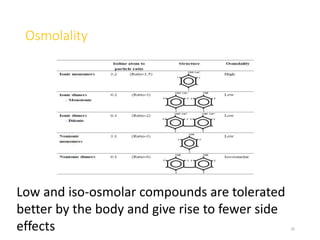
1. Contrast agents are substances that have different atomic numbers or electron densities than surrounding tissues, allowing visualization of internal organs on imaging.
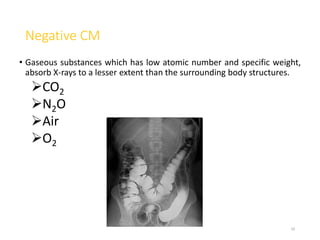
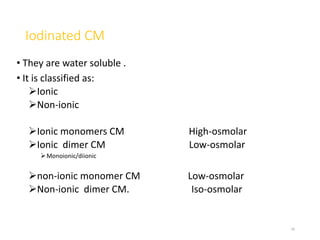
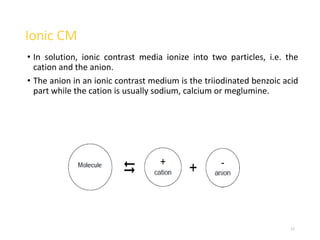
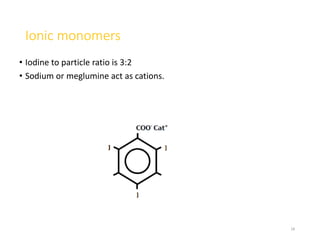
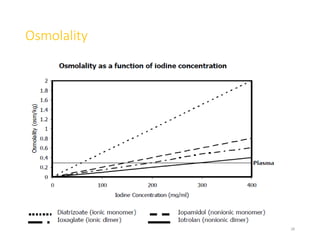
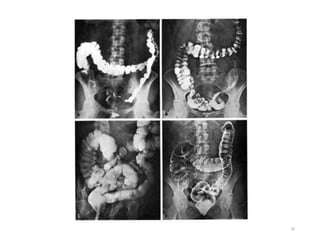
2. Early contrast agents included barium sulfate, iodinated compounds, and air or CO2. Modern agents are classified as ionic or non-ionic monomers and dimers with varying osmolalities and viscosities.
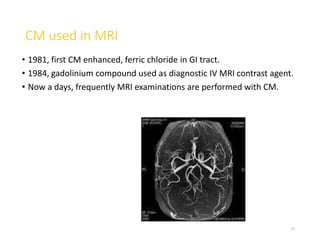
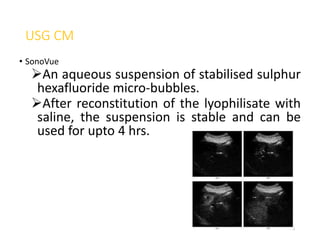
3. Contrast agents are used with multiple imaging modalities like CT, MRI, ultrasound, and fluoroscopy. They are administered orally, intravenously, or directly into structures. The choice depends on the physical properties and safety of the specific agent and the anatomy being imaged.