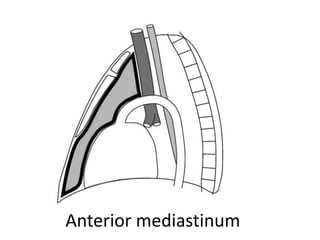
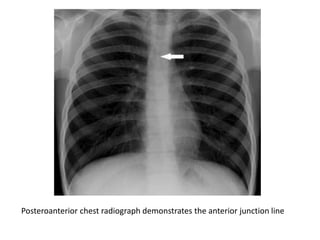
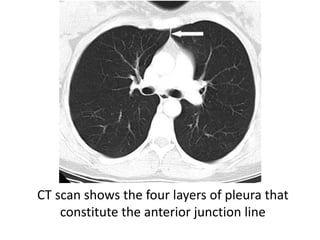
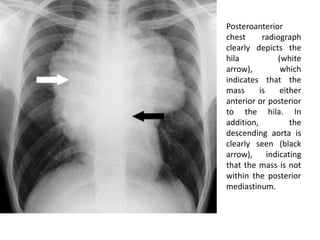
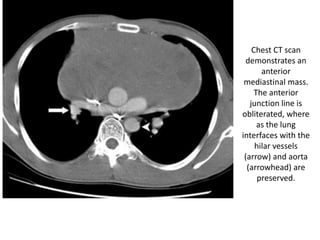
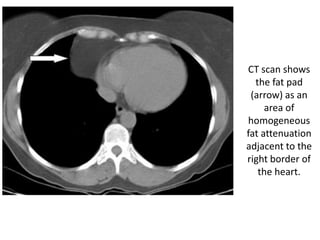
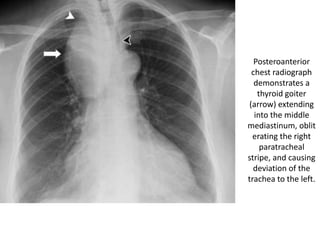
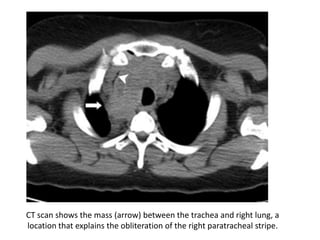
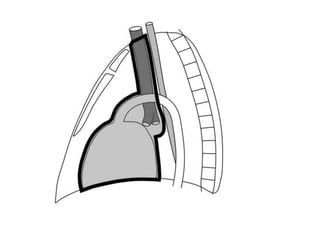
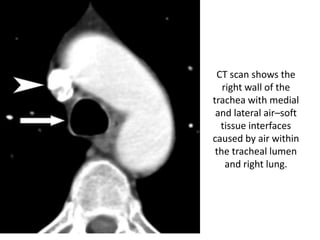
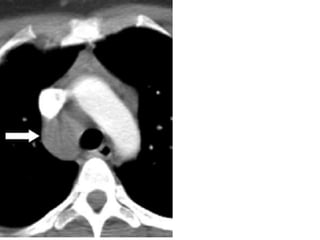
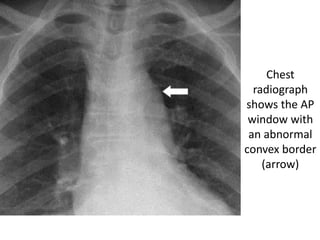
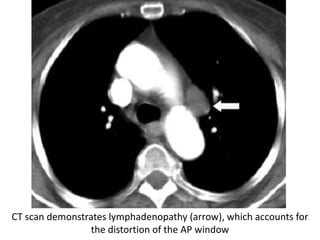
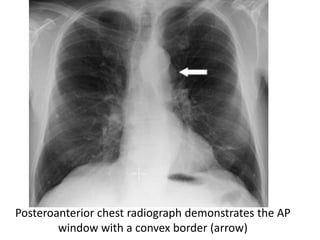
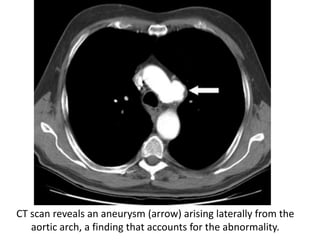
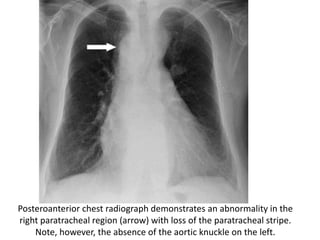
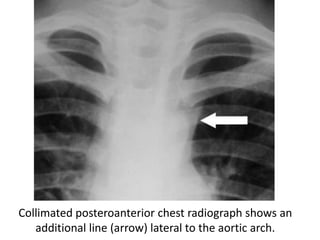
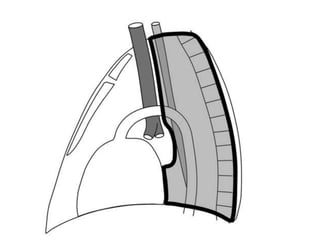
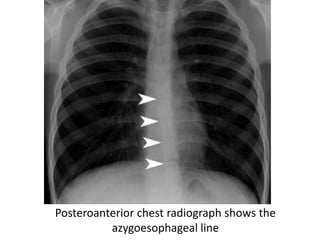
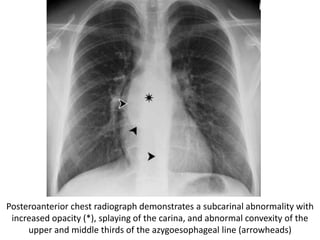
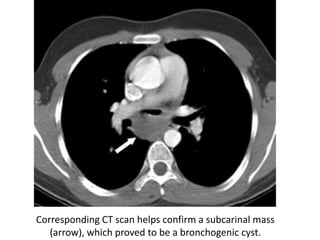
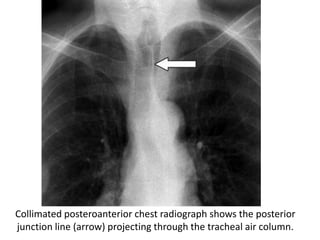
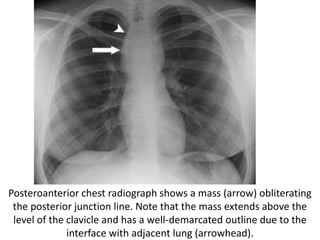
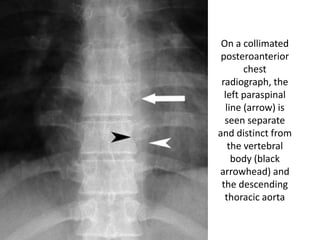
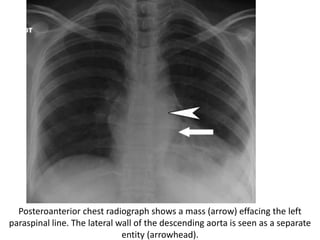
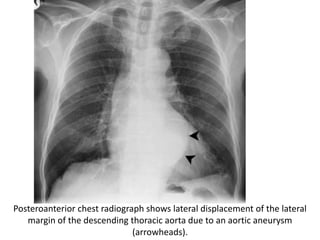
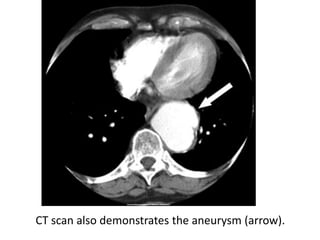
This document summarizes the anatomy and radiographic appearance of structures in the mediastinum. It describes the boundaries and contents of the anterior, middle, and posterior mediastinum. Key structures discussed include the anterior and posterior junction lines, right paratracheal stripe, azygoesophageal recess, and paraspinal lines. Common masses and abnormalities that can involve each mediastinal compartment are also reviewed.