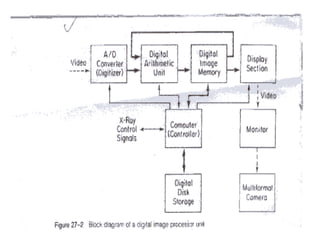
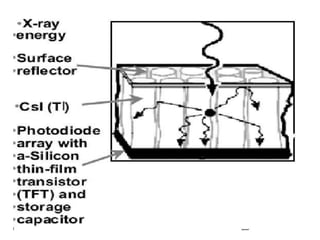
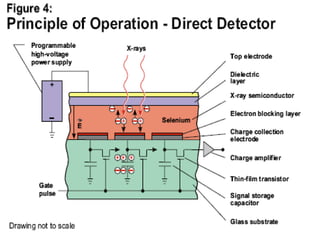
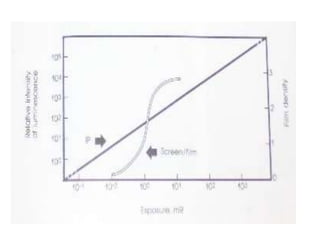
The document discusses digital radiography, including computed radiography (CR) and direct radiography using flat panel detectors. It summarizes the limitations of conventional film-based radiography and then describes the key components and workings of CR and direct digital radiography systems. Some advantages include improved image quality, ability to manipulate images digitally, faster processing, and reduced need for retakes compared to conventional methods.







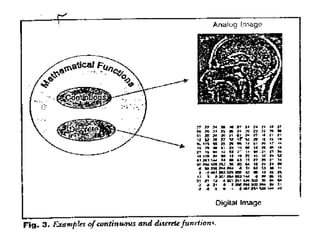
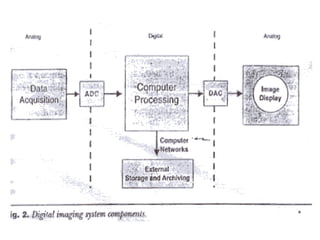
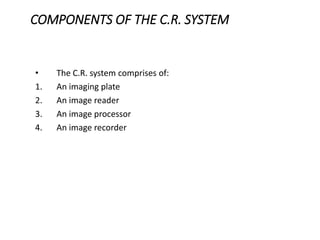
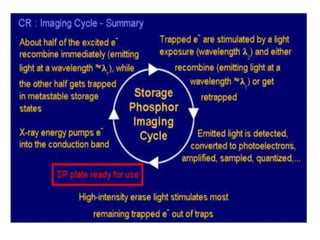
![COMPUTED RADIOGRAPHY
•PRINCIPLE:
•In the C.R. system we use an imaging plate made of
a photostimulable phosphor.
•The cassette is exposed to x-rays in a similar
fashion as the conventional cassette.
•The latent image is produced in the phosphor layer
of the imaging plate.
•Then the cassette is transferred to the reader
system where the imaging plate is scanned with a
red helium-neon [633mm] beam.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalradiography-190304082852/85/Digital-Radiography-10-320.jpg)

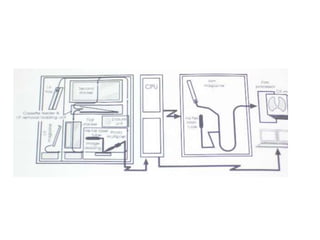
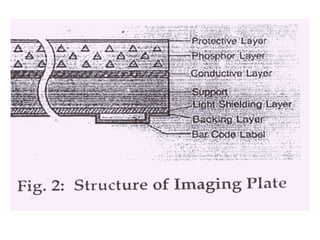
![THE IMAGING PLATE
•It consists of a polyester base over which a layer of
photostimulable phosphor [europium doped
barium fluoro bromide crystals- BaFBr:Eu 2] is
coated.
•A protective layer composed of fluorinated
polymer material is applied over it. A supporting
layer which prevents the reflection if light is also
applied.
•Next is the backing layer. This prevents the
scratching on the imaging plates during storage
and transfer. Therefore it has a protective action.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalradiography-190304082852/85/Digital-Radiography-14-320.jpg)




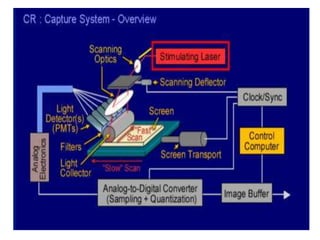


![THE IMAGE READER
•The image reader converts the continuous analog
information [latent image] into a digital format.
•In the reader the imaging plate is scanned
sequentially by a red helium-neon [633mm] laser
beam.
•The laser beam induces photostimulable
luminescence from the phosphor. The intensity of the
emitted luminescence is proportional to the amount
of x-ray energy absorbed in the crystal layer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalradiography-190304082852/85/Digital-Radiography-25-320.jpg)