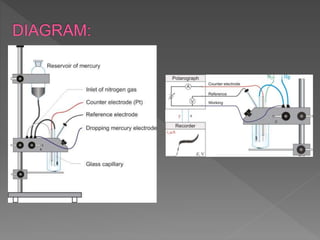
Polarographic analysis is a voltammetry technique that uses a dropping mercury electrode (DME) or static mercury drop electrode (SMDE) to measure the current resulting from the electrolysis of electroactive species at controlled potentials. It involves applying a potential between a mercury working electrode and a reference electrode, like a saturated calomel electrode, while measuring the current. The current-voltage curve, or polarogram, reveals information about the species present in solution, including qualitative and quantitative analysis through measurements of diffusion current and half-wave potential. Polarography takes advantage of mercury's wide cathodic potential range and its ability to renew its surface between drops.