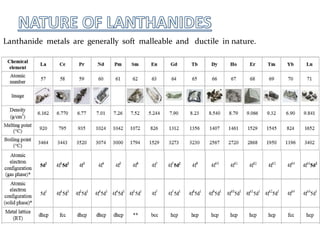
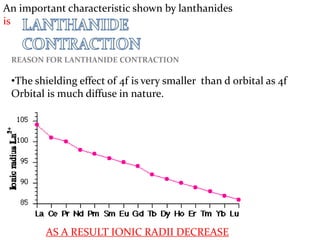
The lanthanide series includes fifteen elements from lanthanum to lutetium, characterized by their electronic configurations and position within the periodic table as inner transition metals. Lanthanides exhibit similar physical and chemical properties, resulting in challenges for their separation, and possess unique characteristics such as color variations, magnetic properties, and applications in metallurgy, ceramics, nuclear technology, and life sciences. The lanthanide contraction explains the decrease in ionic radii and related trends, with lanthanides commonly used in various industries despite their pure metals having limited applications.



![•In case of Ba 56 ,6s orbital is completely filled and in case of
•La 57 5d orbital is singly filled….
•But after crossing La57 ,
•The nuclear charge increases by one unit and 4f orbital which is
•Much in energy fall than fd is filled first.
•An exception is shown by GADOLINIUM.Its outermost
electronic
•Configuration s [Xe]4f7 5d1 6s2.though there is a huge energy gap
•Between 4f and 5d,Gd tends to remsin in 4f7 confg in order to
•Attain a half filled stability.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation12-170405210026/85/Lanthanide-Chemistry-5-320.jpg)

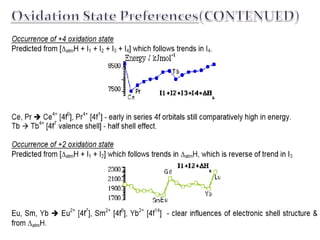
![Ionization For any given Lanthanide:
•™As successive electrons are removed from
neutral Ln the stabilizing effect on the
orbitals is related to their principal
quantum number, 4f > 5d > 6s. ™
•For Ln2+ (except for La & Gd) the
configuration is [Xe]4fn
•™For Ln3+ the configuration is always
[Xe]4fn ™The 4f binding energy is so great
that remaining 4f electrons are regarded as
"core-like" (i.e. incapable of modification
by chemical means), except Ce.
Therefore in almost all cases Ln3+
provides the best energetics:
Atomization ∆atmH follows the
inverse trend to I3, and therefore also
to (I1 + I2 + I3). Metallic bonding is
correlated with ease of ionization to
Ln3+ state. This trend is modified
slightly due to the different structures
of the Ln metals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation12-170405210026/85/Lanthanide-Chemistry-8-320.jpg)