Embed presentation
Downloaded 113 times


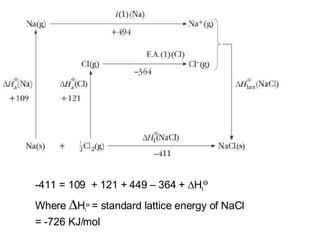

The Born-Haber cycle summarizes the standard enthalpy changes that occur during the formation of an ionic crystal from its gaseous constituent elements. It relates the standard enthalpy of sublimation, bond dissociation, electron affinity, and lattice energy to the standard enthalpy of atomization through Hess's law. For example, in forming NaCl, the standard enthalpy of atomization for sodium and chlorine contributes -411 kJ, which is balanced by the energy absorbed in ion formation, bond breaking, and crystal lattice formation.



