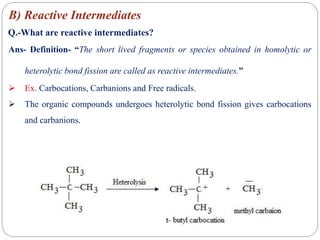
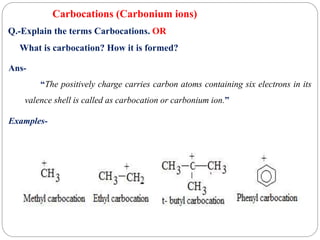
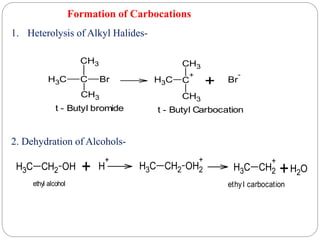
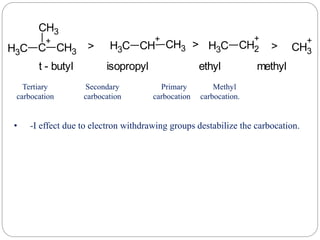
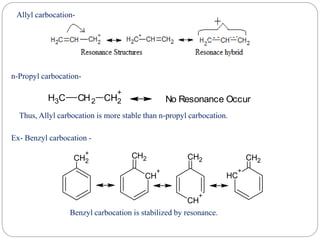
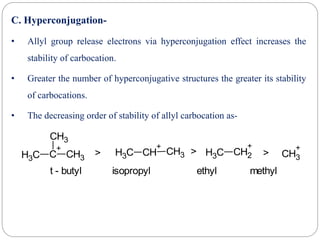
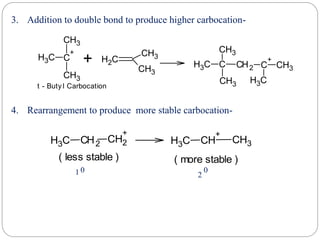
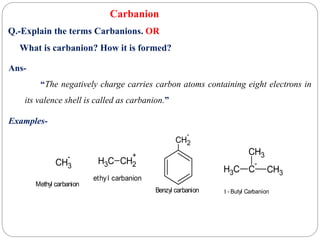
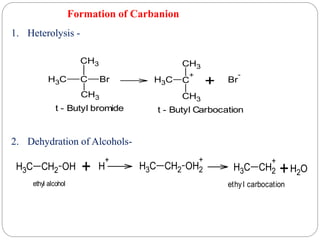
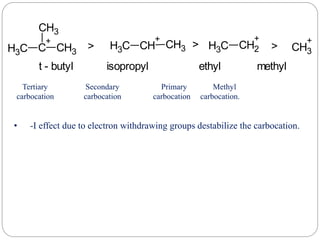
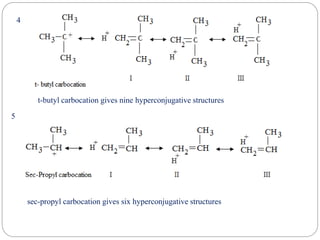
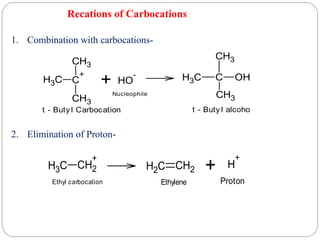
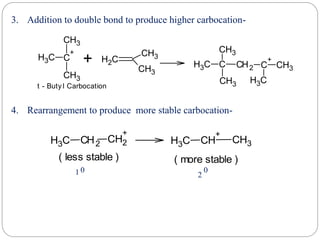
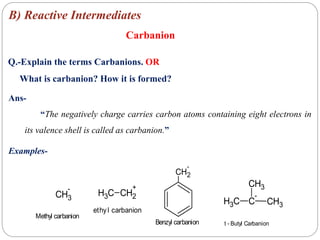
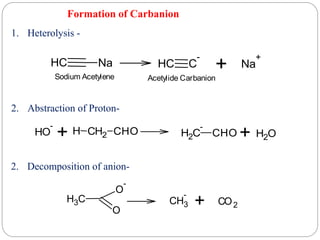
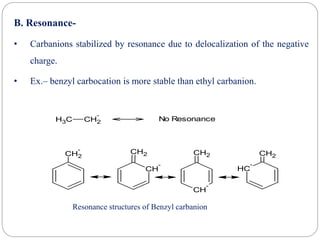
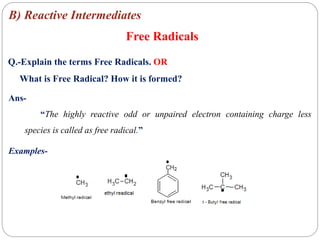
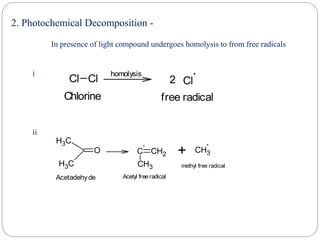
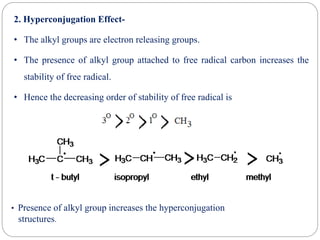
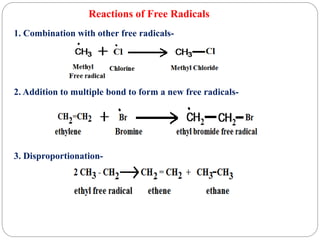
The document discusses reactive intermediates in organic chemistry, focusing on carbocations, carbanions, and free radicals. It describes their characteristics, stability, formation, and reactions, emphasizing factors like hybridization, inductive effects, resonance, and hyperconjugation in determining stability. The stability order for carbocations is tertiary > secondary > primary, while for carbanions it is methyl > primary > secondary > tertiary, and for free radicals it is tertiary > secondary > primary.