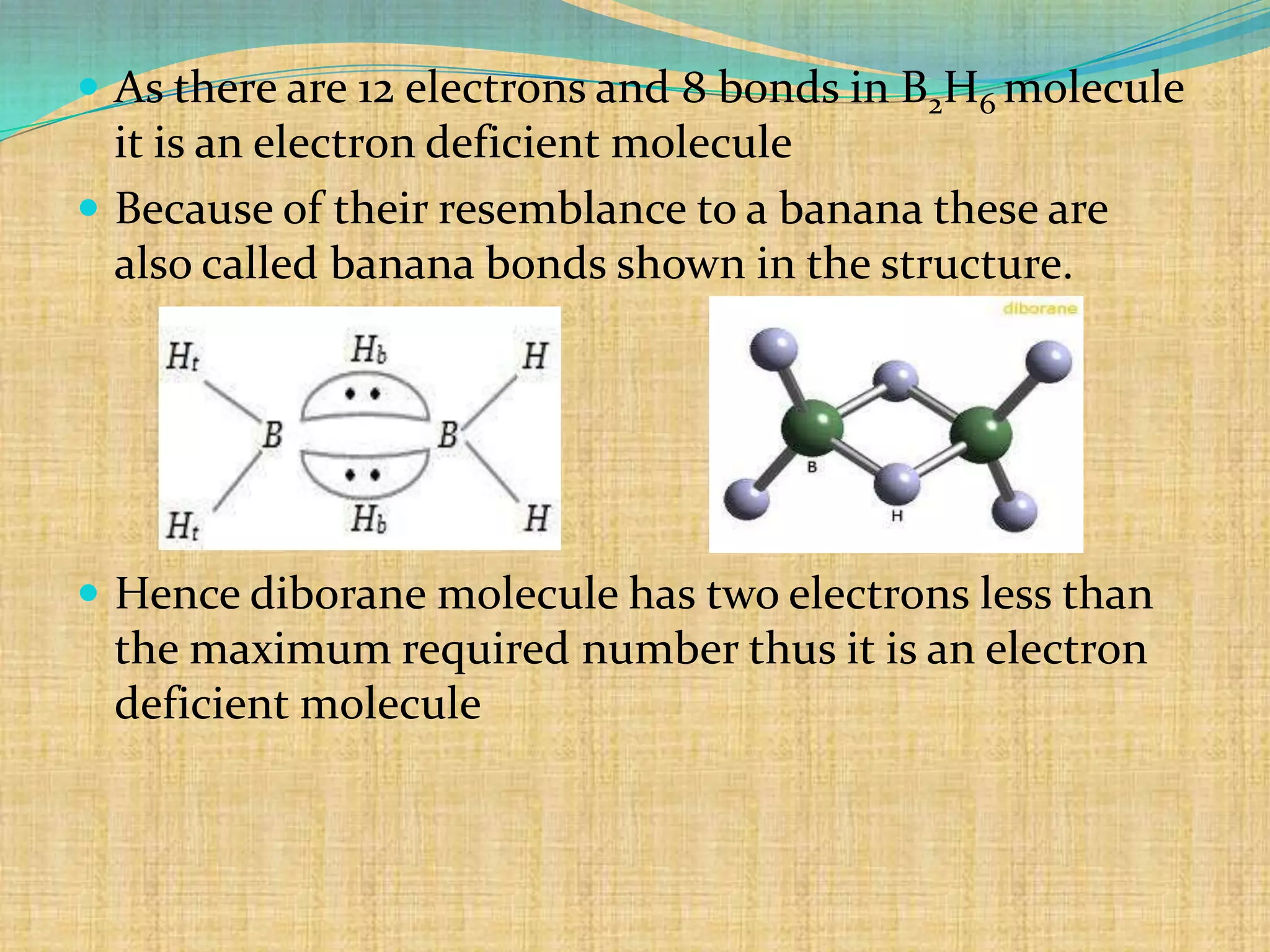
Diborane is prepared through several methods including reacting boron trifluoride with lithium aluminum hydride or oxidizing sodium borohydride with iodine. It is a colorless, toxic gas that spontaneously burns in air and is readily hydrolyzed by water. Diborane has a structure with two bridging hydrogen atoms between two boron atoms in a banana-like bond configuration, making it an electron deficient molecule. It has potential uses as a rocket propellant or in vulcanization and hydrocarbon polymerization processes.


![4) With Lewis bases, diborane first undergoes cleavage
(breaking) to form borane (BH3) which then reacts to
form adducts
B2H6 + 2NMe 2BH3 . NMe
B2H6 + 2CO 2BH3 . CO
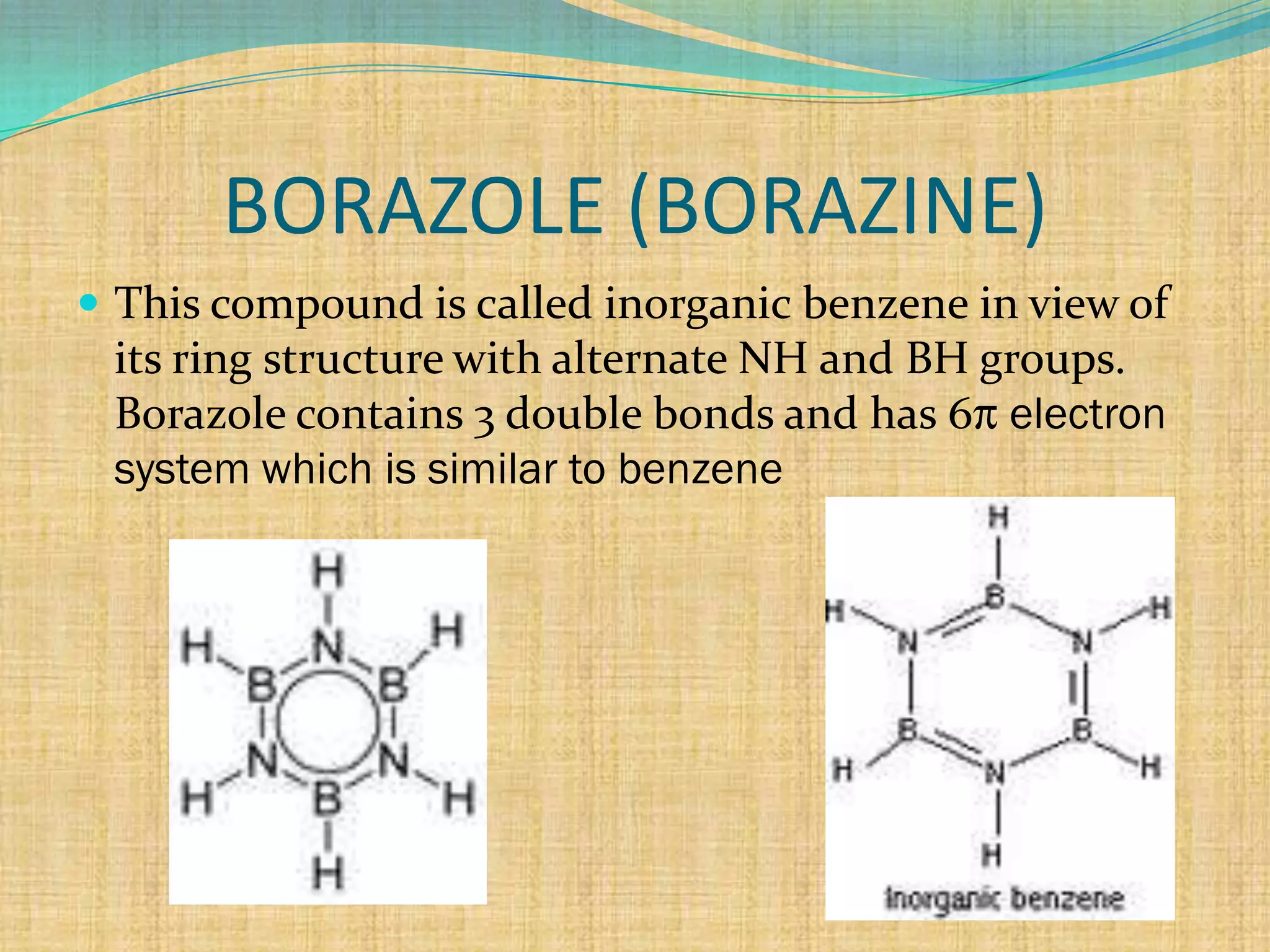
5) with ammonia an addition product B2H6.NH3formulated
as [ BH2(NH3)2]+ [BH4]- is formed which then
decomposes on heating at 473K to give a volatile
compound called borazole (Borazine)
3 B2H6 + 6NH3 [ BH2(NH3)2]+ [BH4]- 473K
2B3N3H6 + 12H2
( borazole)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diborane-130130093240-phpapp02/75/Diborane-4-2048.jpg)
![6)Many metal hydrides react with diborane to form
tetrahydridoborate which contain [BH4]- tetrahedral
ion.
2MH + B2H6 2M+ [BH4]-
Where (M=Li or Na), for ex:
2LiH + B2H6 2Li+ [BH4]-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diborane-130130093240-phpapp02/75/Diborane-6-2048.jpg)