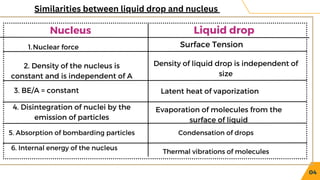
The document presents an overview of nuclear models, particularly the liquid drop model proposed by Niels Bohr and F. Kalcar in 1937, which compares the nucleus to a liquid drop based on similarities such as surface tension and internal energy. It outlines the model's assumptions, the semi-empirical mass formula, and its successes in predicting atomic masses and decay processes, while also noting its limitations in explaining the stability of certain nuclei and excited states. Overall, the document discusses key aspects and challenges of understanding nuclear structure through various models.