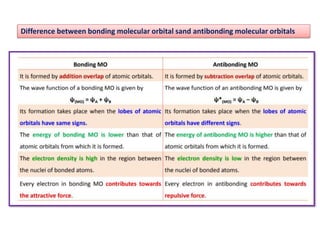
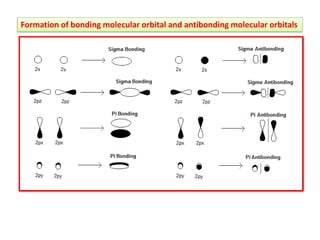
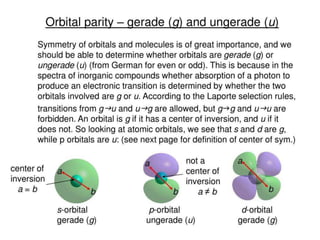
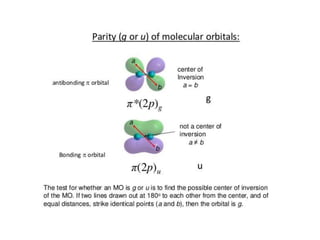
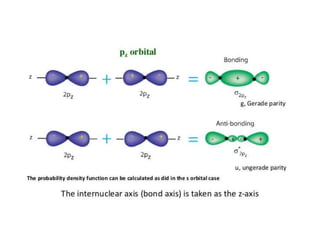
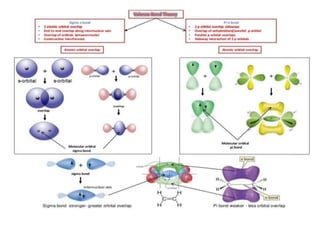
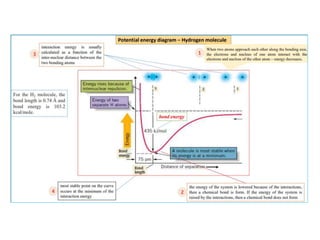
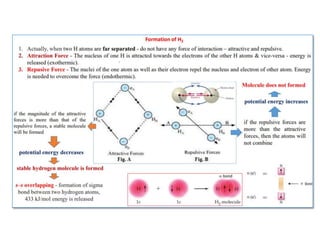
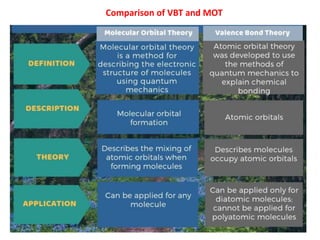
- The document discusses molecular orbital theory, which describes chemical bonding through the combination of atomic orbitals into molecular orbitals.
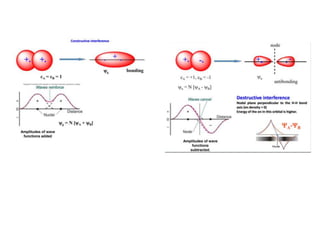
- Key features include molecular orbitals being formed from linear combinations of atomic orbitals, with bonding, antibonding, and nonbonding molecular orbitals resulting. Electrons fill these orbitals based on orbital energy.
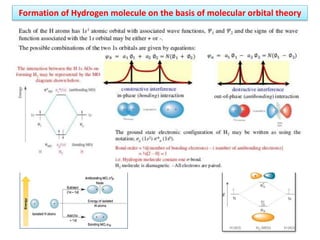
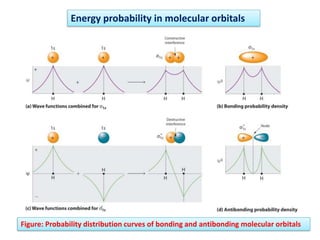
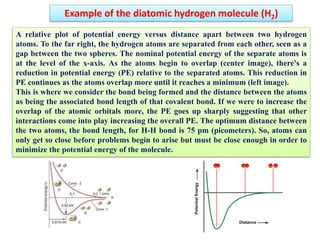
- The formation of molecular orbitals from atomic orbitals of hydrogen is used as an example, with bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals illustrated.