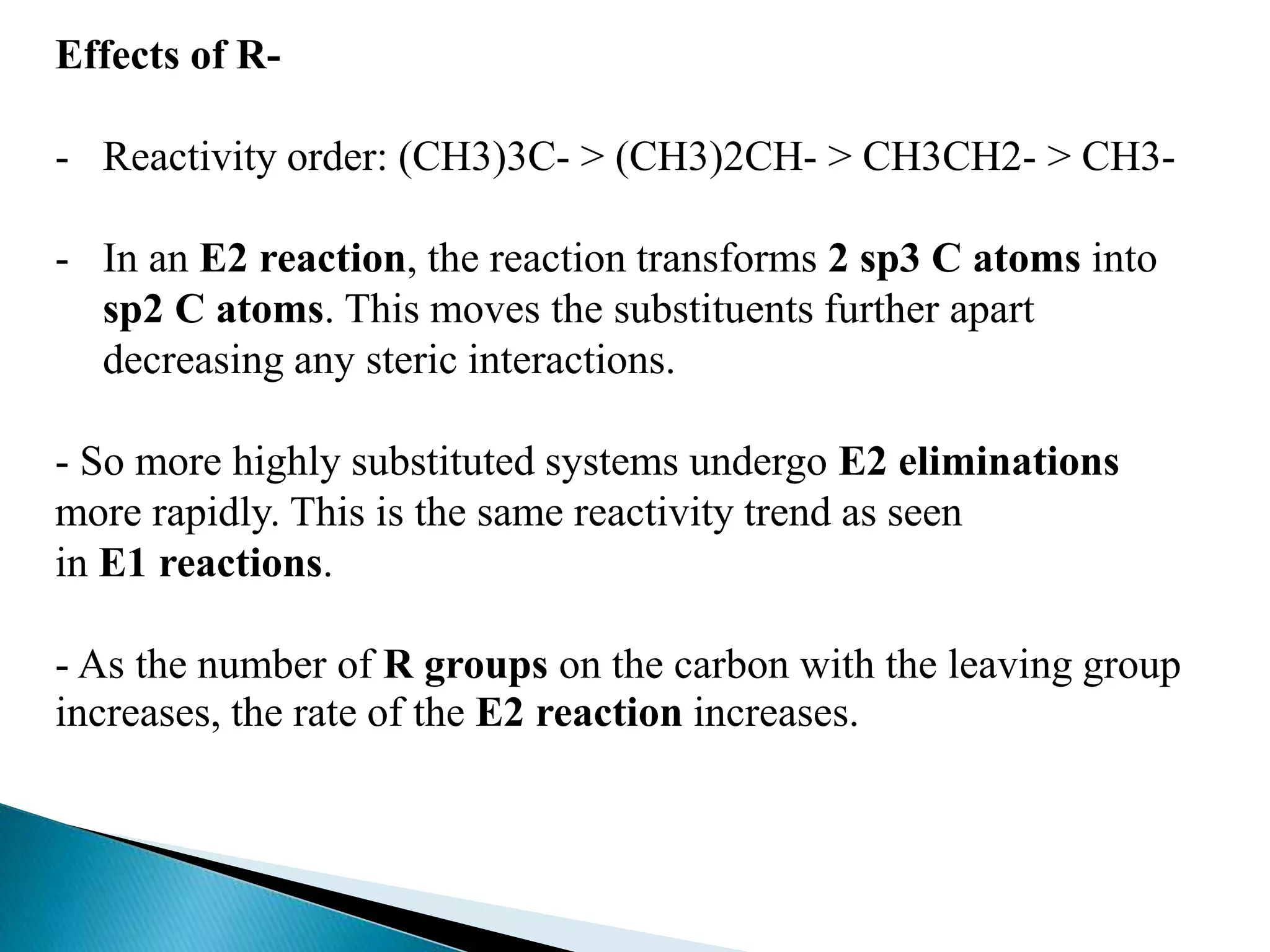
- Elimination reactions occur by either an E1 or E2 mechanism. E1 is a one-step reaction involving a carbocation intermediate, while E2 is a concerted, single-step reaction.
- The E1 mechanism is favored by good leaving groups, stable carbocations, and weak bases. It is non-stereospecific and does not occur with primary alkyl halides. The E2 mechanism is favored by strong bases and polar aprotic solvents. It is stereospecific and proceeds through an anti-periplanar transition state.
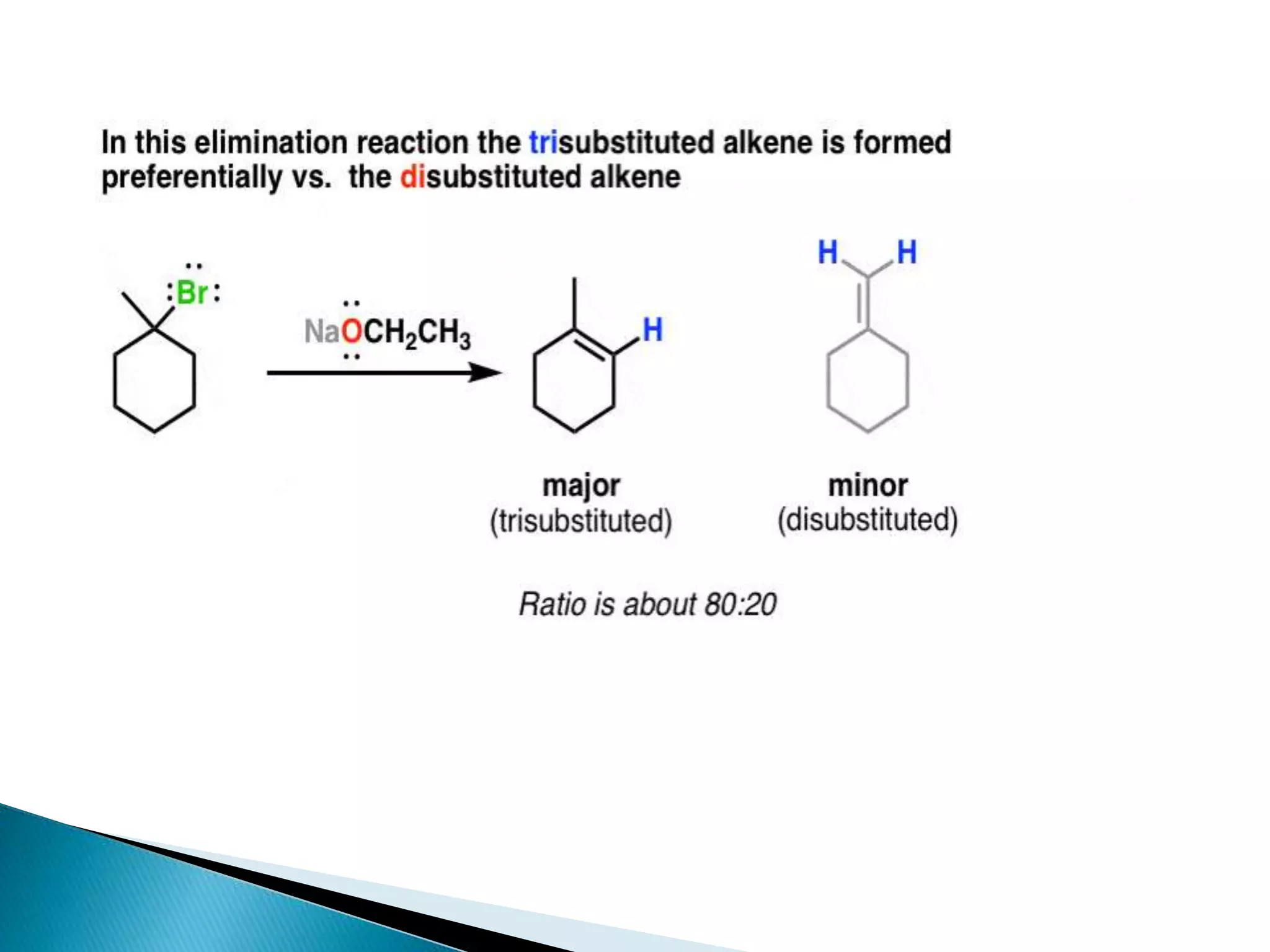
- Key factors that determine the mechanism include the stability of carbocation intermediates, the strength of the leaving group and base, and steric



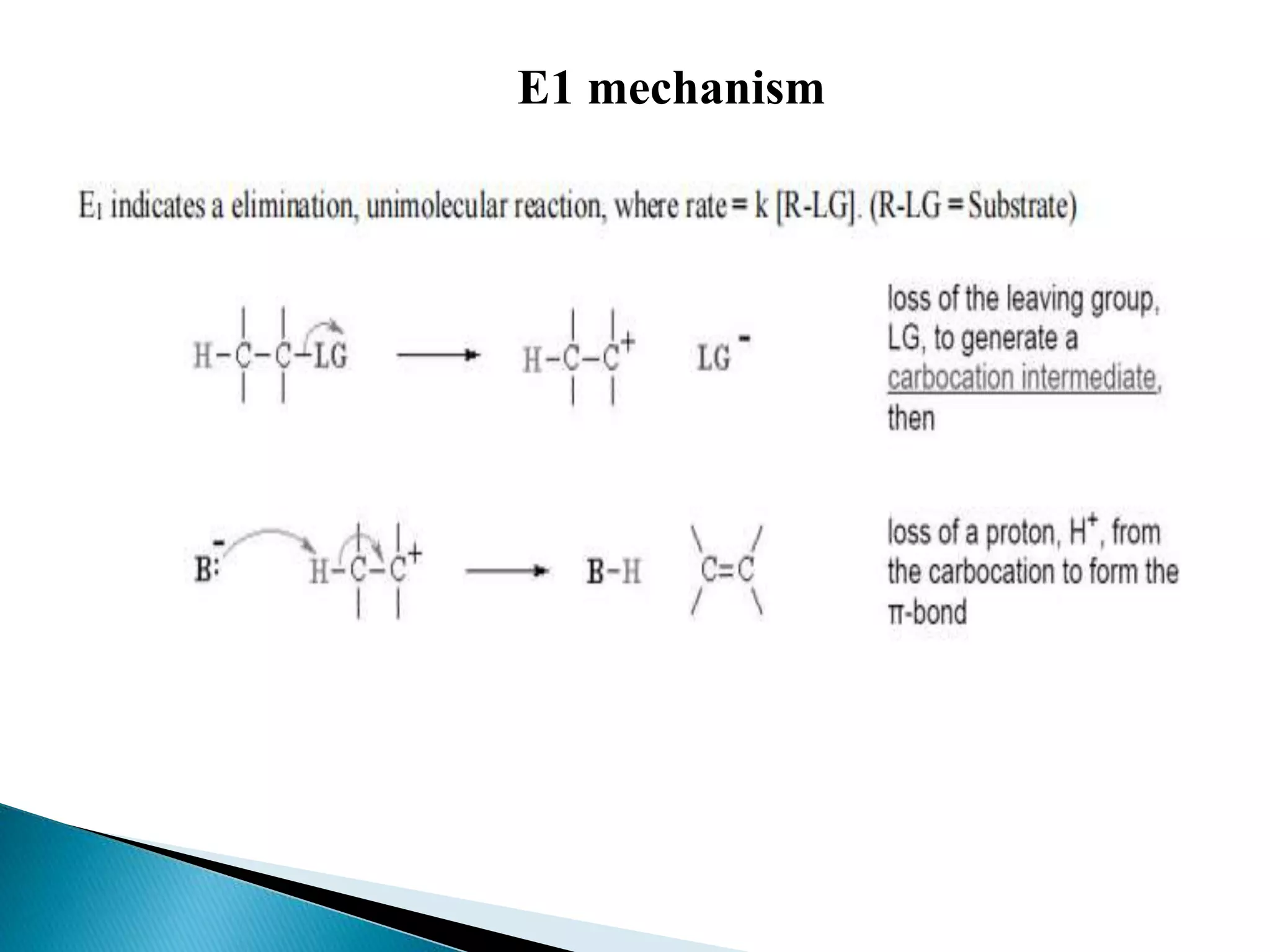












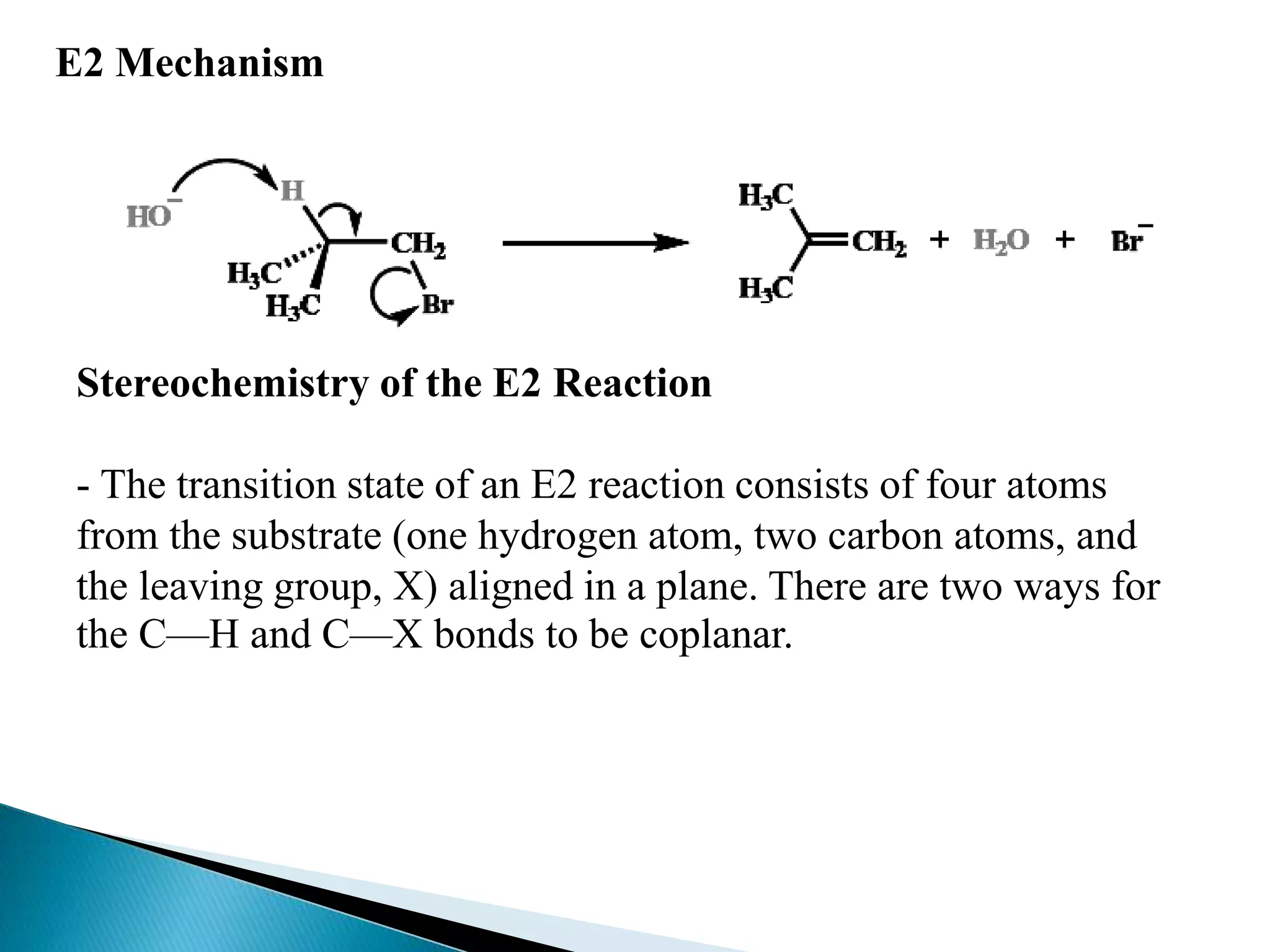
![E2 mechanism
1. E2 indicates an elimination, bimolecular reaction, where rate = k
[B][R-LG].
2. This implies that the rate determining step involves an interaction
between these two species, the base B, and the organic substrate,
R-LG
Removal of the proton, H+, by the base, loss of the leaving
group, LG, and formation of the π-bond](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eliminationreaction-220204005214/75/Elimination-reaction-18-2048.jpg)