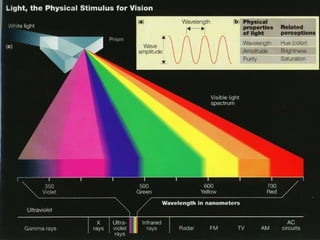
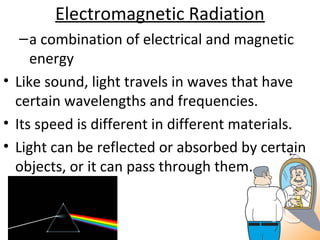
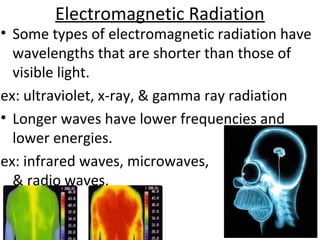
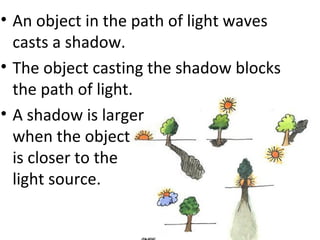
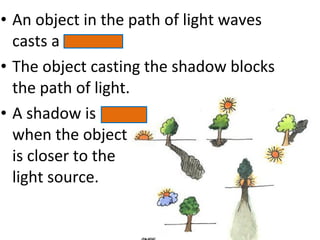
The document discusses properties of electromagnetic radiation including light. It explains that light travels in waves at different speeds in different materials and can be reflected, refracted, or absorbed. Shorter wavelengths like ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma rays have more energy than longer wavelengths like infrared, microwaves, and radio waves. The document also describes how light travels in straight lines and is bent by lenses, forming shadows and rainbows.