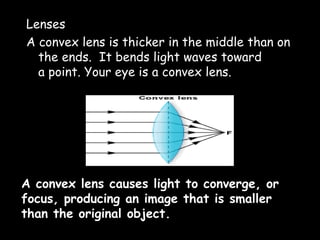
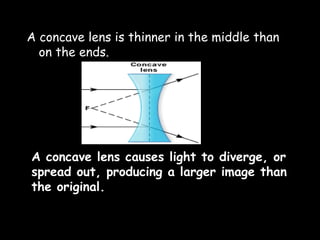
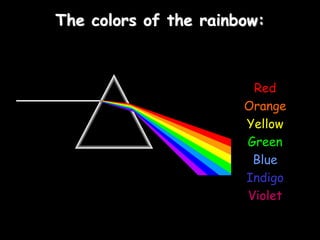
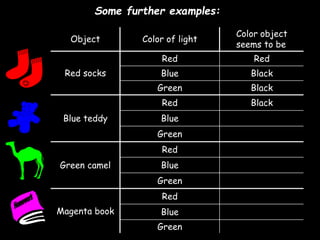
This document provides an overview of light and optics. It covers:
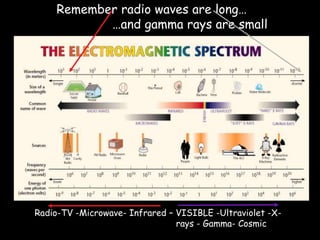
1) The electromagnetic spectrum and different types of electromagnetic waves like radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
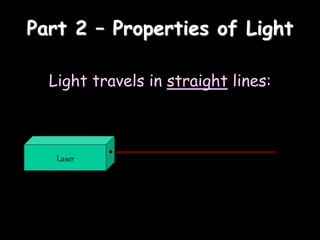
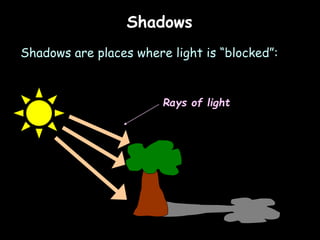
2) Properties of light including that it travels in straight lines at high speed, and how shadows are formed when light is blocked.
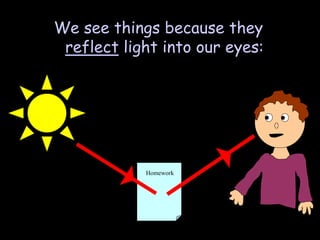
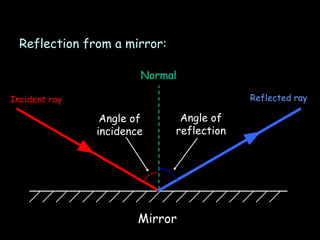
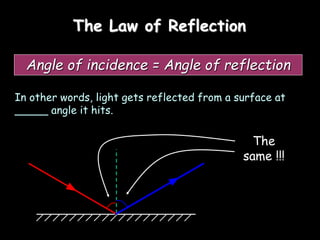
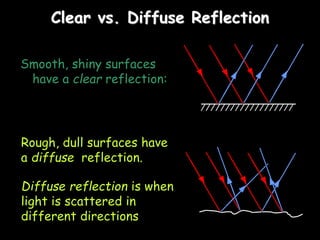
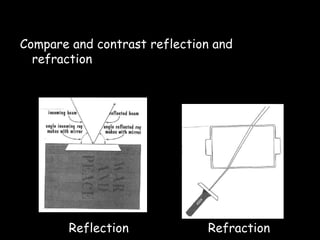
3) Reflection - how light bounces off surfaces at the same angle it hits based on the law of reflection, and the differences between clear and diffuse reflection.
4) Colors - how white light is made up of the visible light spectrum, the primary colors, how objects get their color, and using colored light and