Here are the answers to your questions:
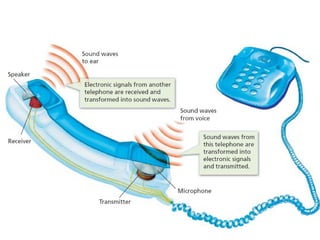
1. The three main parts of a phone are the transmitter, receiver, and dialing mechanism.
2. During a phone call, sound waves cause a metal disk in the transmitter to vibrate, transforming sound into an electronic signal. The receiver uses a speaker to transform the electronic signal back into sound.
3. Electromagnetic waves consist of changing electric and magnetic fields that can carry signals over long distances. A changing magnetic field produces a changing electric field and vice versa.
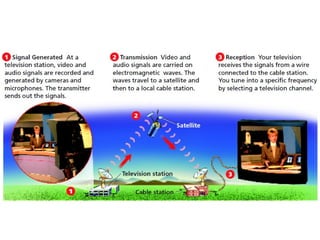
4. For radios, an audio signal is combined with a carrier wave and transmitted via electromagnetic waves to antennas. The radio separates the signal from the carrier wave. For TV, video and audio signals