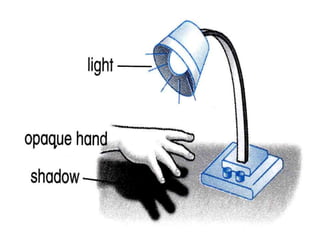
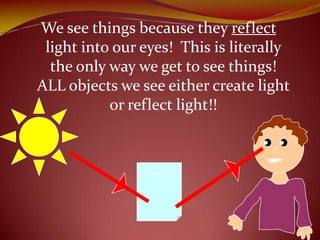
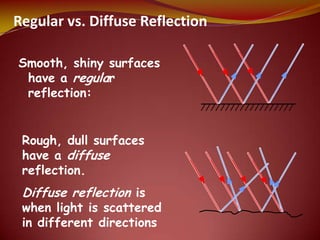
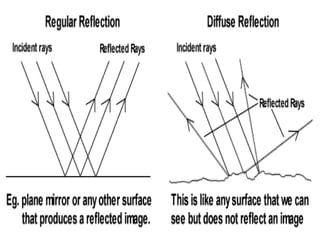
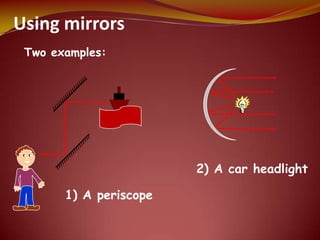
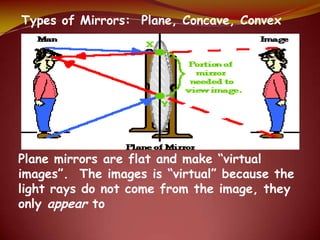
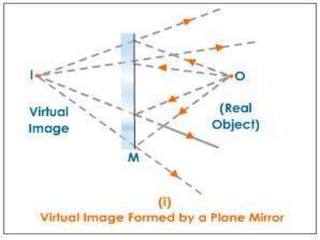
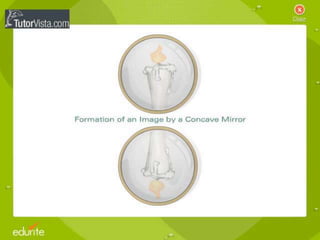
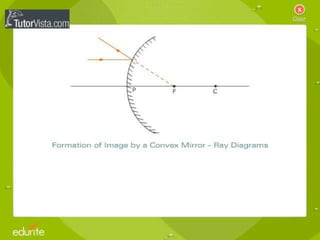
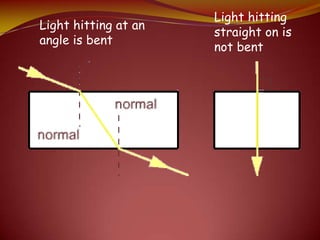
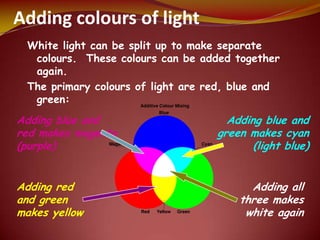
This document discusses the properties of light through a PowerPoint presentation. It covers topics like light traveling in straight lines at very fast speeds, how we see objects based on light reflection, the formation of shadows, and the electromagnetic spectrum. It also discusses reflection off mirrors, the three types of mirrors, and refraction through lenses. The document finishes by covering the topics of color, how white light is made up of the colors of the rainbow, the primary colors of light, and how objects appear different colors based on which wavelengths of light they reflect or absorb.