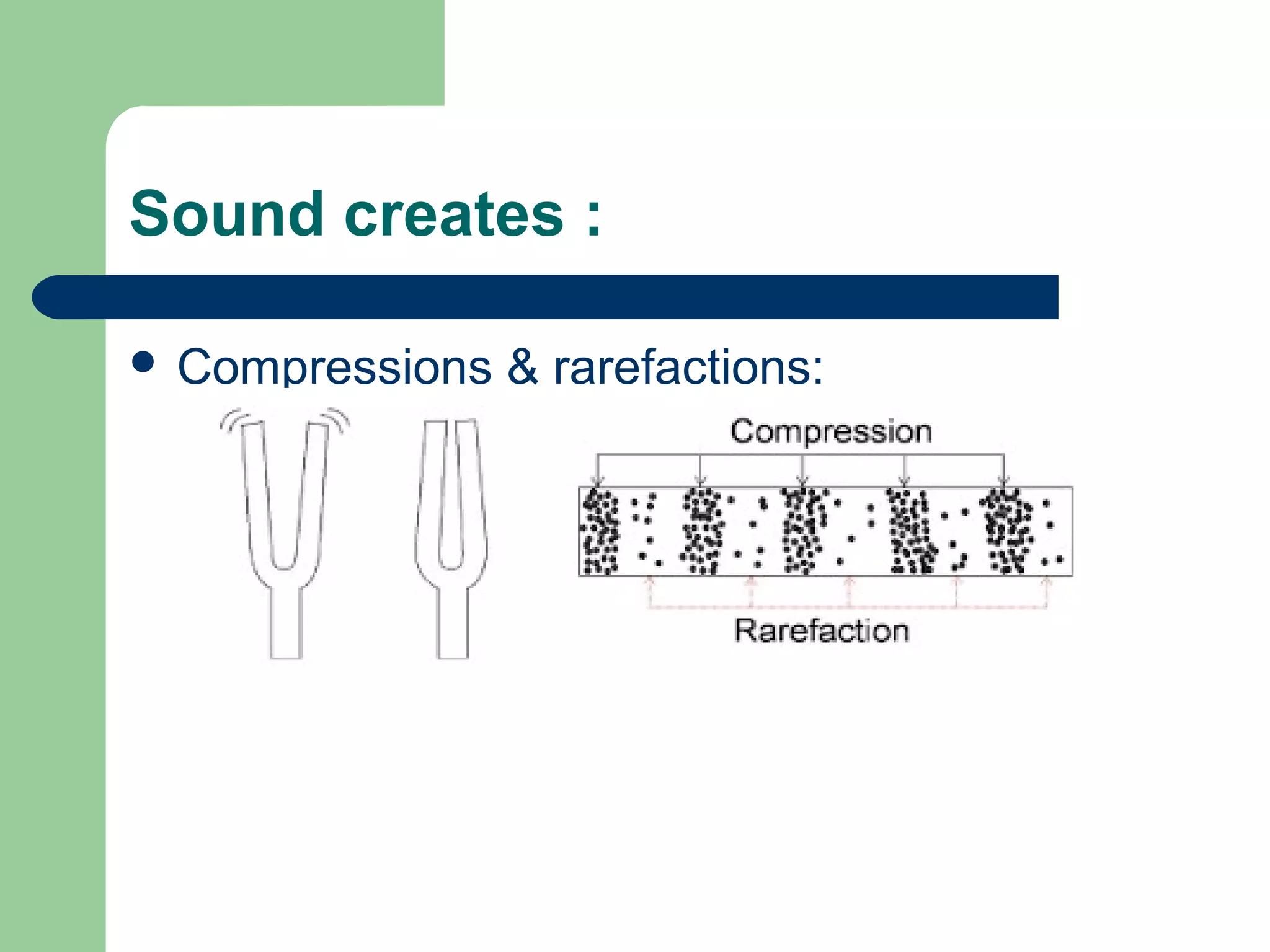
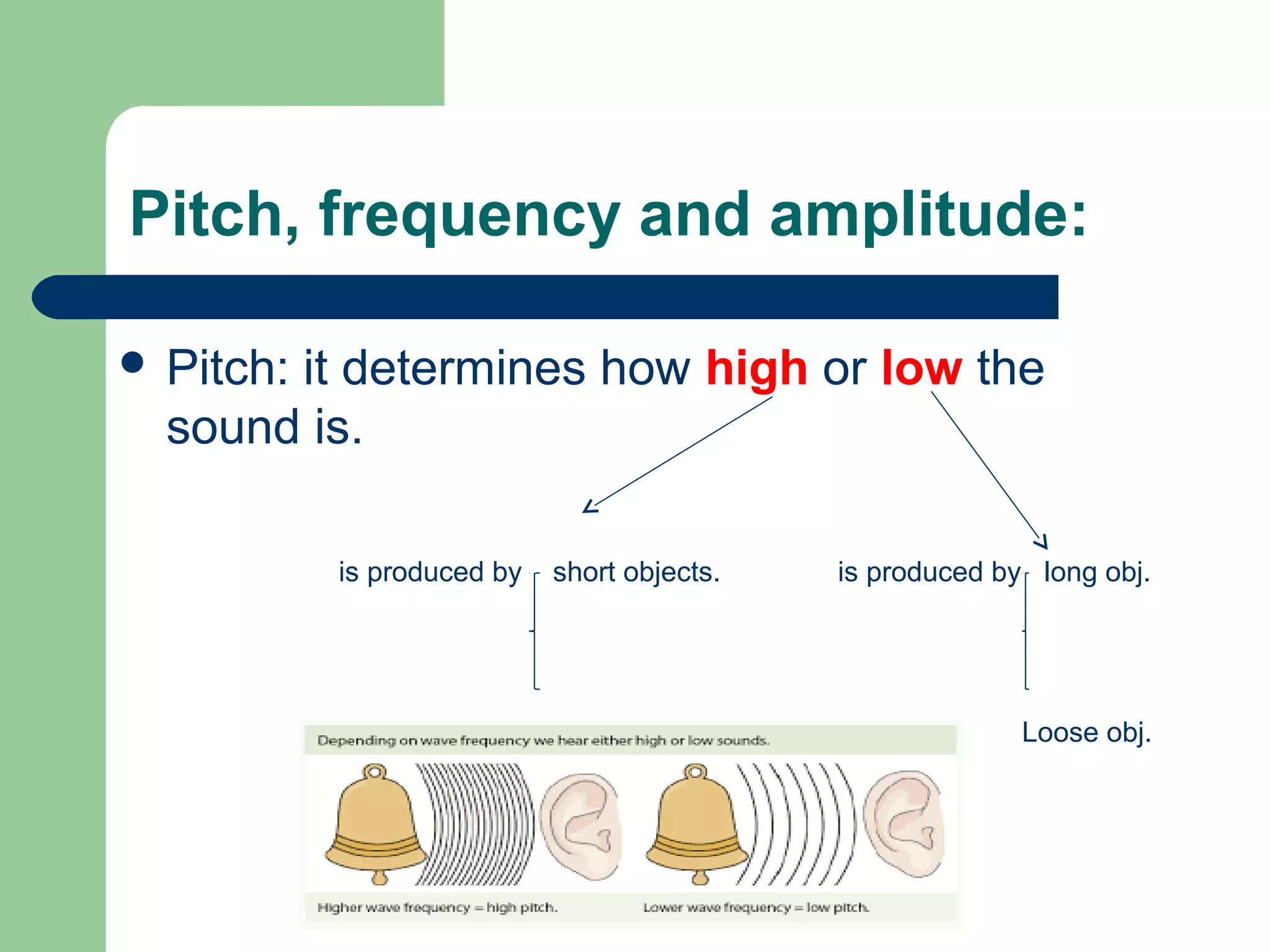
Sound is a form of energy created by vibrations that travel through matter as longitudinal waves. When an object vibrates, it causes the air particles around it to move in a compression and rarefaction pattern that transfers the sound energy. Sound travels through gases, liquids, and solids as a medium and cannot travel through a vacuum. The pitch and loudness of sound depends on the frequency and amplitude of its waves. Musical instruments create sound through vibration of strings, woodwinds, or percussion. The human ear detects sound waves through vibration of the ear drum and small bones, which are translated into nerve signals in the cochlea and perceived as sound by the brain.