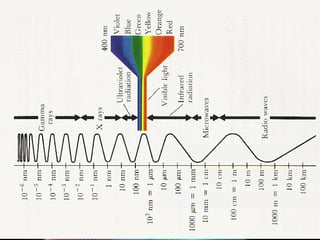
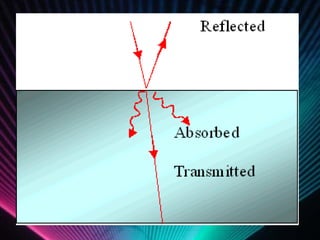
Light energy is electromagnetic radiation consisting of electrical and magnetic energy. It is emitted by electrons in objects and travels in waves across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption occurs when light is not reflected or transmitted by an object, with different colors absorbed and reflected. Reflection is when light bounces off a surface, like in mirrors. Transmission is when light passes through a medium without being absorbed or scattered. Refraction is the bending of light waves changing direction as they pass between substances. Scattering causes light to bounce off objects in many directions, as seen with the blue sky and halos around the sun.