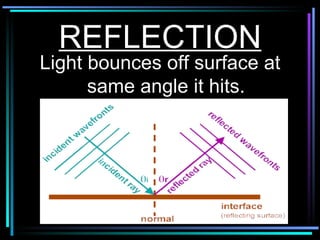
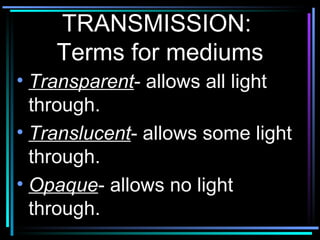
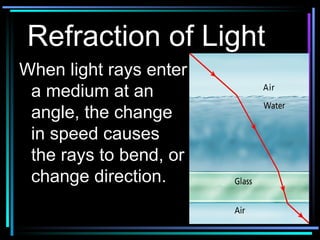
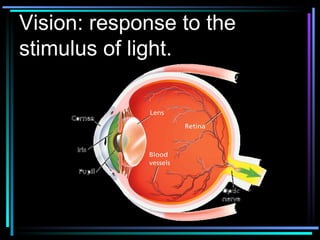
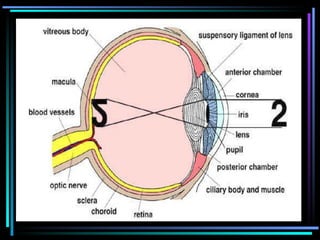
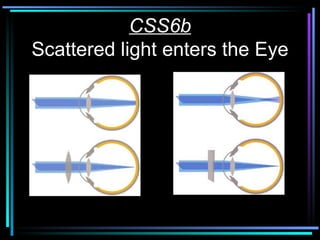
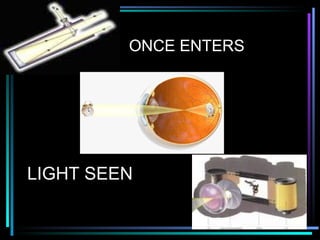
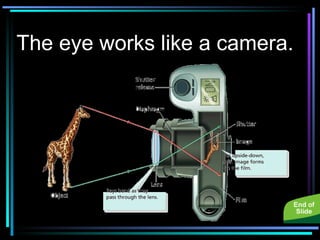
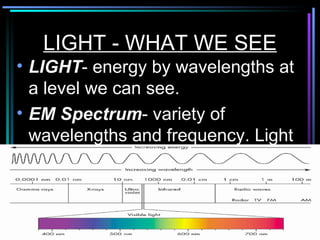
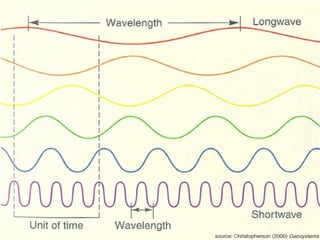
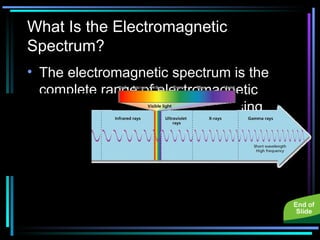
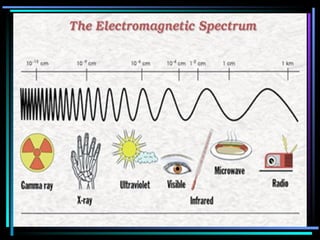
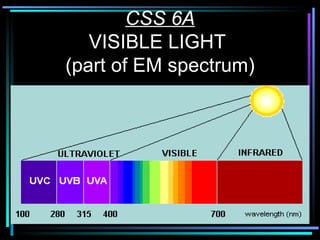
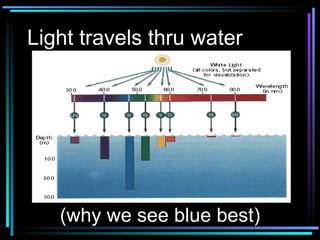
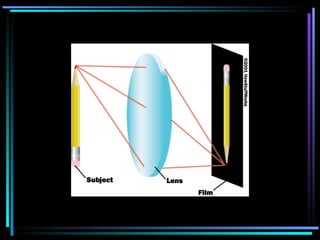
Light travels in straight lines until interacting with objects. It can scatter, reflect, refract, or be absorbed. Reflection causes light to bounce off a surface at the same angle. Refraction causes light to change speed and direction when passing from one medium to another, such as from water to air. Absorption occurs when light is taken in by an object and its energy is transferred to heat.