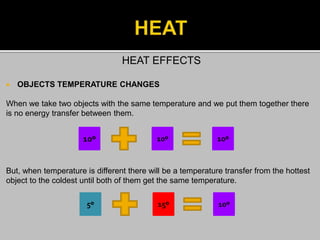
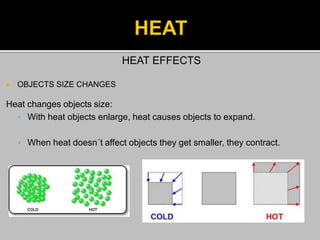
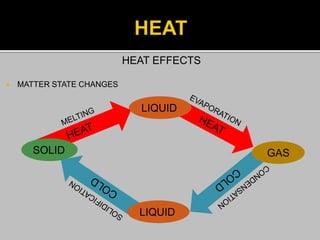
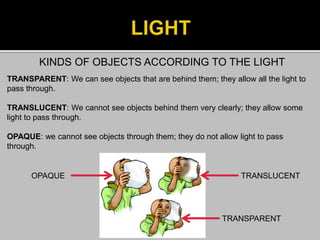
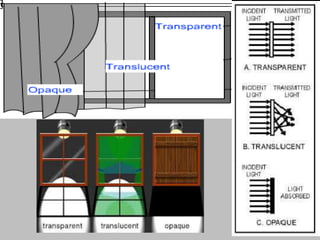
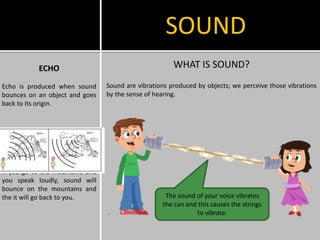
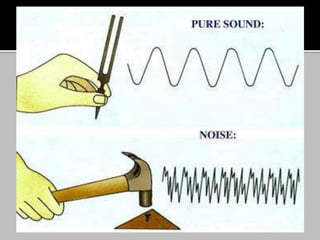
This document provides information about heat, light, and sound. It discusses that heat is produced by the movement of atoms and molecules and is transferred from hotter to colder objects. Light allows us to see objects when it bounces off them and enters our eyes. Objects can be transparent, translucent, or opaque depending on how much light they allow to pass through. Sound is vibrations that propagate through a medium like air and are perceived through hearing.