This document discusses intrusion detection systems (IDS), beginning with historical examples of cyber attacks. It describes the role of firewalls in network security and how IDS serve as a complementary technique to firewalls by monitoring network traffic and detecting intrusions. The document outlines different types of IDS, including host-based, network-based, and hybrid systems. It also covers common intrusion detection techniques and the limitations of IDS in providing comprehensive security.



![4
Points to Ponder
Typical businesses spend only about 0.15% of annual sales
on the security needs of their corporate network [1]
This amount is even less than most of these companiesThis amount is even less than most of these companies
spend on coffee for the staffspend on coffee for the staff
60% of firms do not have a clue about how much these
security breaches are costing them [2]
Approximately 70 percent of all cyber attacks onApproximately 70 percent of all cyber attacks on
enterprise systems are believed to beenterprise systems are believed to be
perpetrated by trusted insidersperpetrated by trusted insiders](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idspresentation-140819105538-phpapp01/85/Intrusion-Detection-System-4-320.jpg)
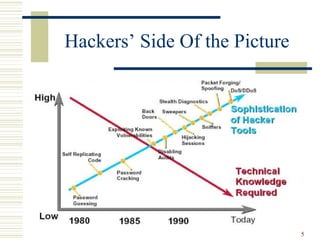
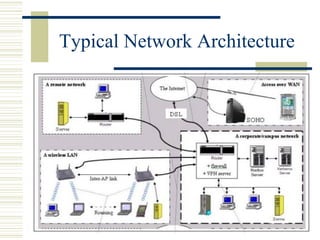

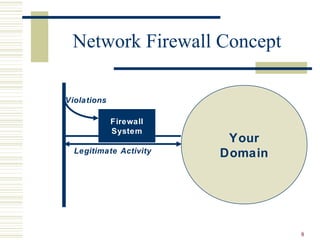
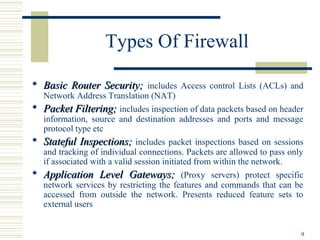









![24
Bibliography
[1] “Inoculating The Network”
By Mathias Thurman
EBSCO HOST Research Databases
[2] National Strategy To Secure Cyberspace
Draft September 2002
www.securecyberspace.gov
[3] An Introduction to Intrusion Detection / Assessment
By Rebecca Bace
http://www.icsalabs.com
[4] White paper on “The Science Of Intrusion Detection System
– Attack Identification”
http://www.cisco.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idspresentation-140819105538-phpapp01/85/Intrusion-Detection-System-24-320.jpg)