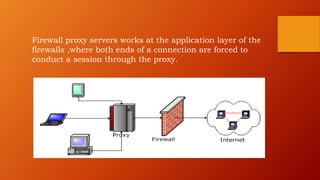
This document discusses different types of firewalls, including hardware and software firewalls, and how they work using packet filtering, proxy services, and stateful inspection. It describes the history of firewalls and why they are needed for both personal and business use to protect networks from threats like viruses, malware, and unauthorized access. Next generation firewalls are also introduced which can provide more application visibility, control, and threat prevention compared to traditional firewalls.