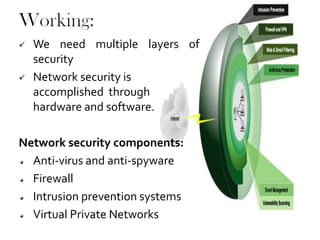
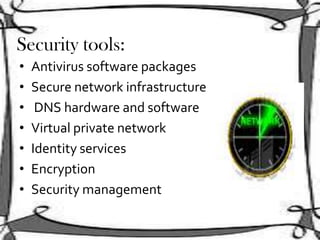
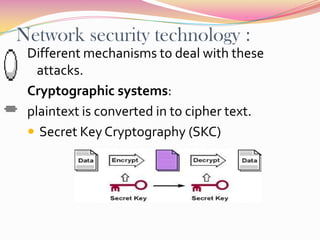
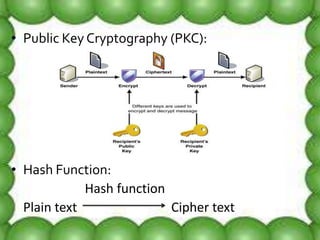
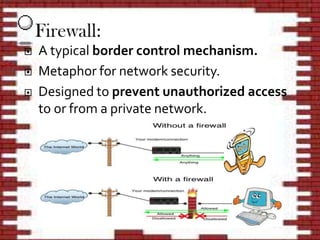
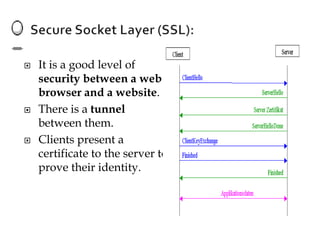
Network security involves protecting computer networks from unauthorized access. It aims to achieve access control, confidentiality, authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation. Throughout history, as hacking and crimes emerged in the 1980s and the Internet became public in the 1990s, security concerns increased tremendously. Network security employs multiple layers including physical security, perimeter protection, user training, encryption, and firewalls among other hardware and software components. As threats continue to evolve, the field of network security must also evolve rapidly to protect information and system resources.