The document provides details about the structure and features of pine trees (Pinus). Key points include:
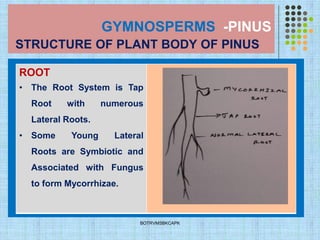
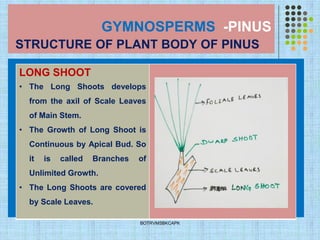
- Pine trees are coniferous evergreen trees that are important forest makers. They have a taproot system and produce dimorphic branches and leaves.
- The internal structure of pine needles, roots, and stems show adaptations for photosynthesis, conduction, storage, and protection. Pine needles have epidermis, mesophyll and stele tissues. Roots and stems develop secondary tissues over time.
- Pine trees are gymnosperms that reproduce via pollen cones and seed cones. Their systematic position is in the division Gymnospermae, class Coniferophyta, order Coniferales