Embed presentation
Downloaded 93 times

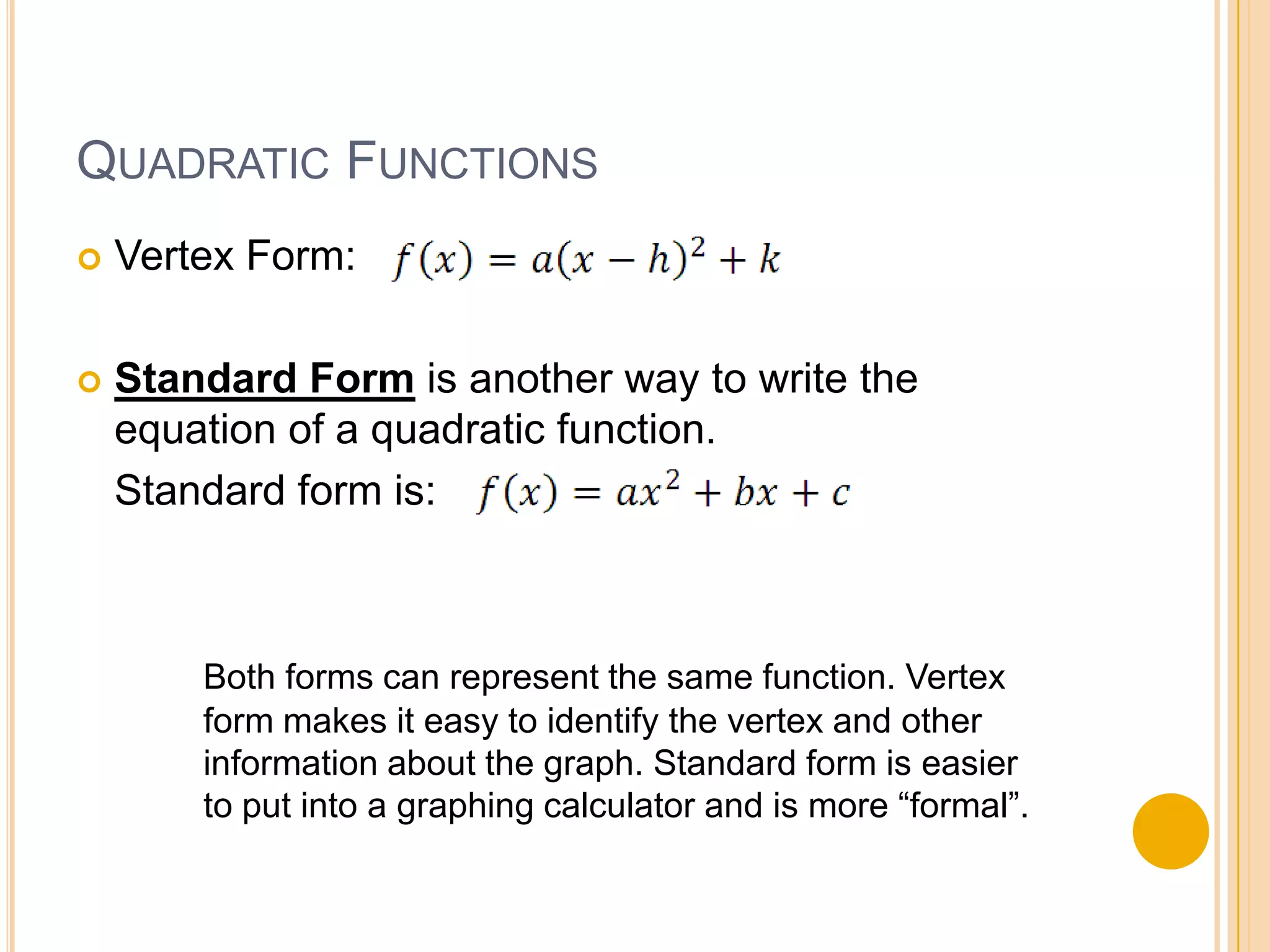
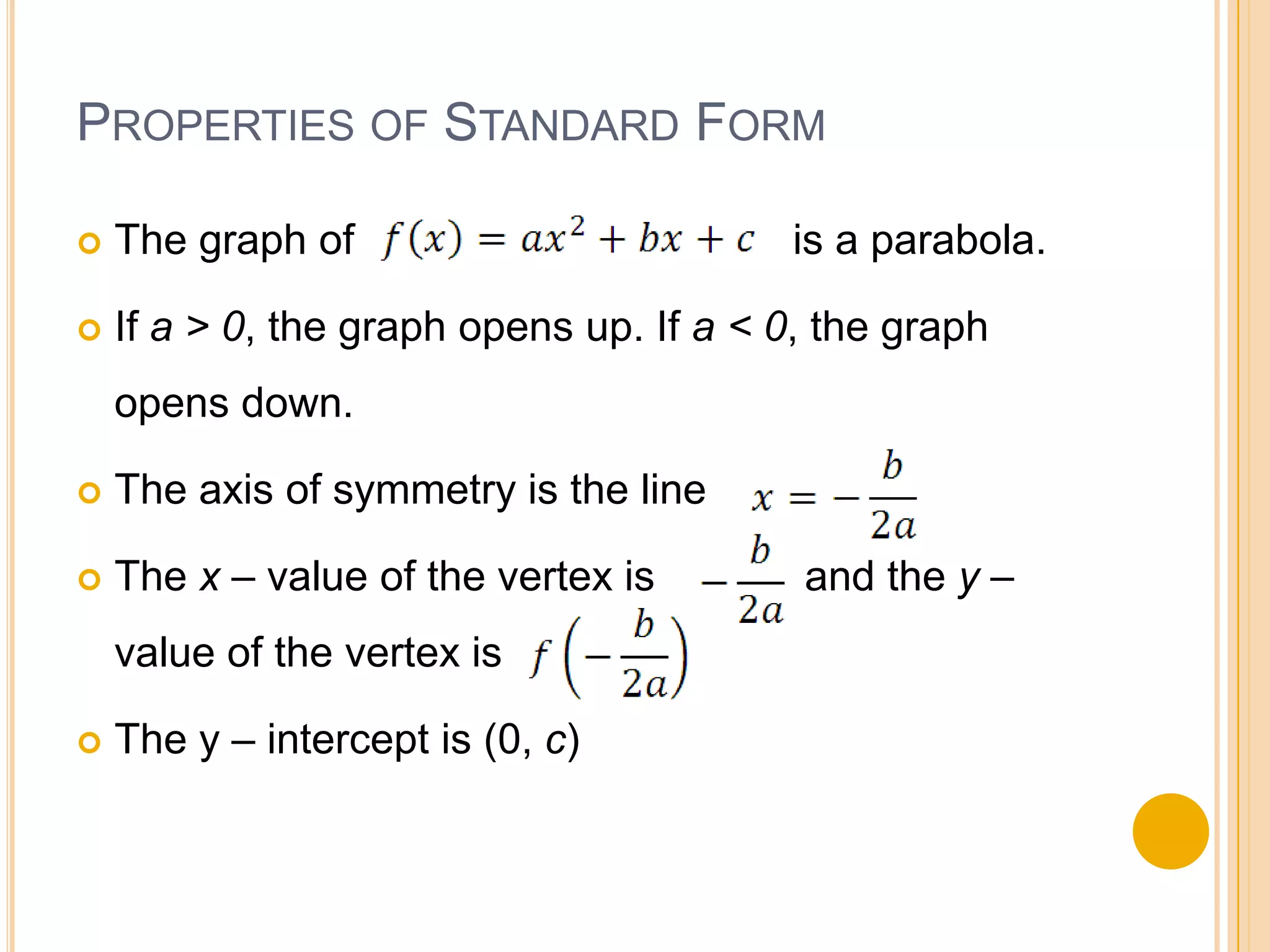


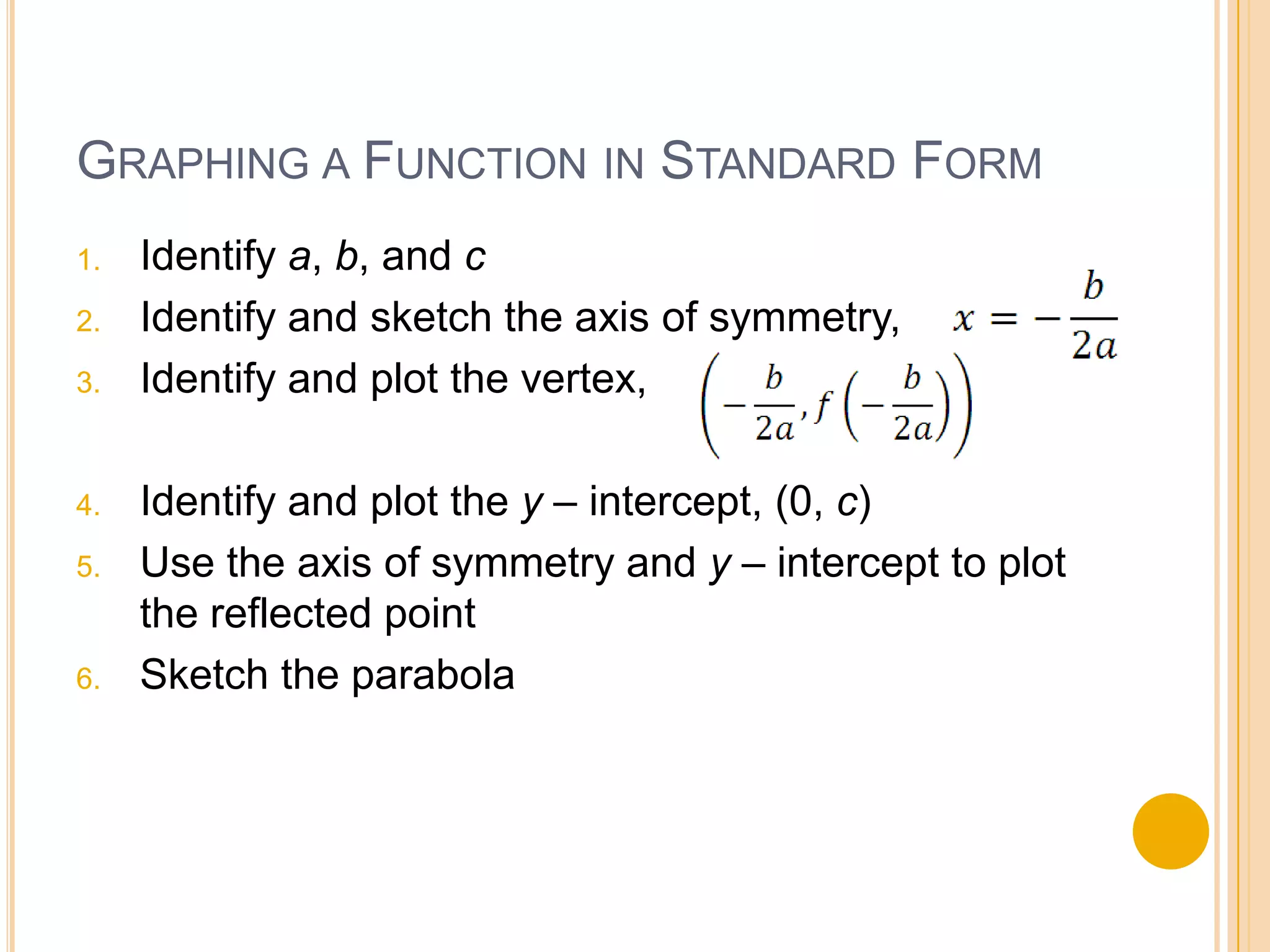
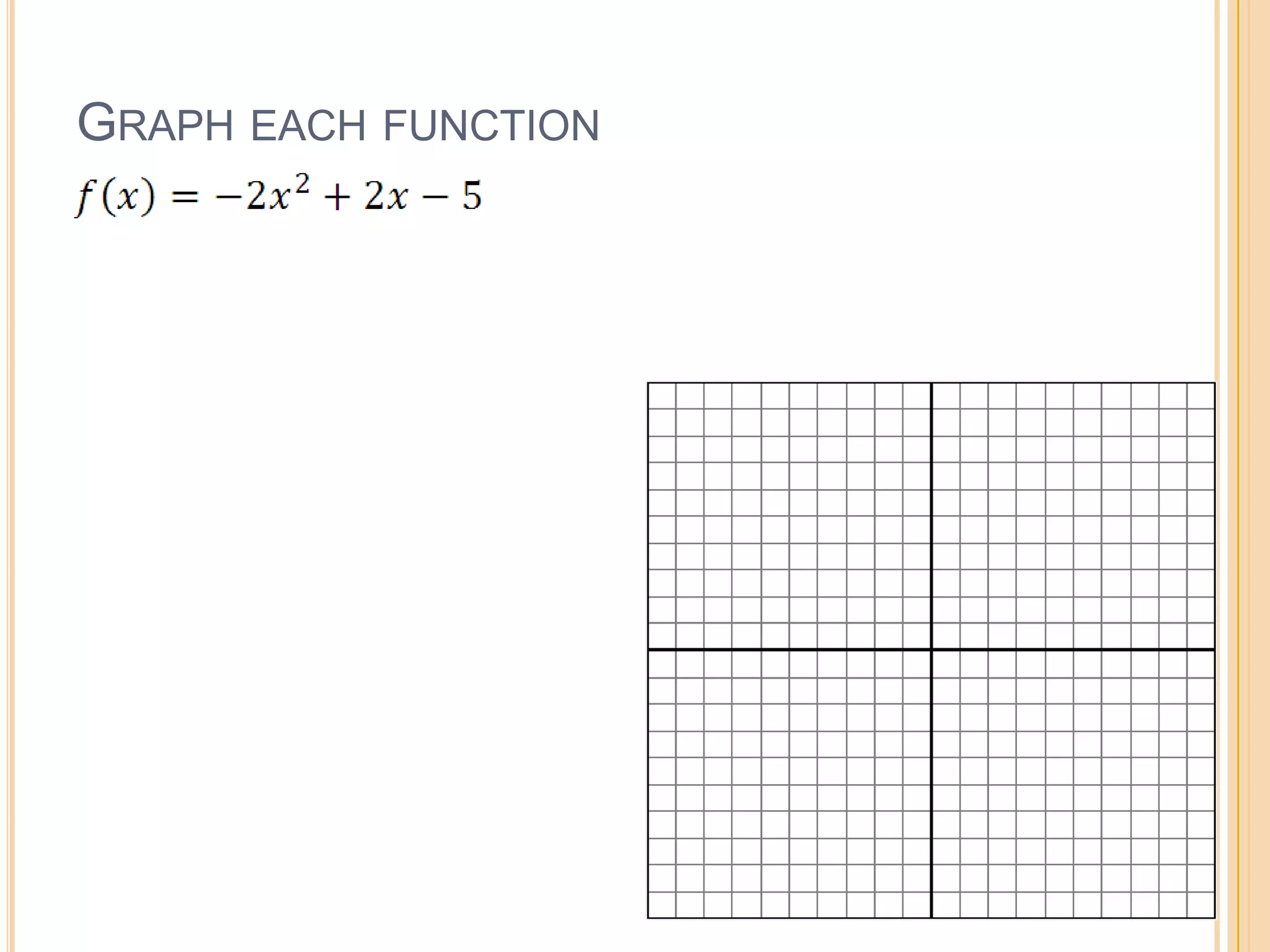
Standard form of a quadratic function is f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c. The graph is a parabola that opens up if a > 0 and opens down if a < 0. The axis of symmetry is the line x = -b/2a and the vertex is (-b/2a, f(-b/2a)). To graph in standard form, identify a, b, c, find the axis of symmetry and vertex, then plot the y-intercept and use reflection to sketch the parabola. The document provides an example of using standard form to identify the vertex, axis of symmetry, minimum/maximum value, and range of a parabola.








Introduction to standard form of quadratic functions, comparison with vertex form, and its graphing usability.
Key properties of the standard form, including direction of opening (a>0 or a<0), axis of symmetry, vertex coordinates, and y-intercept.
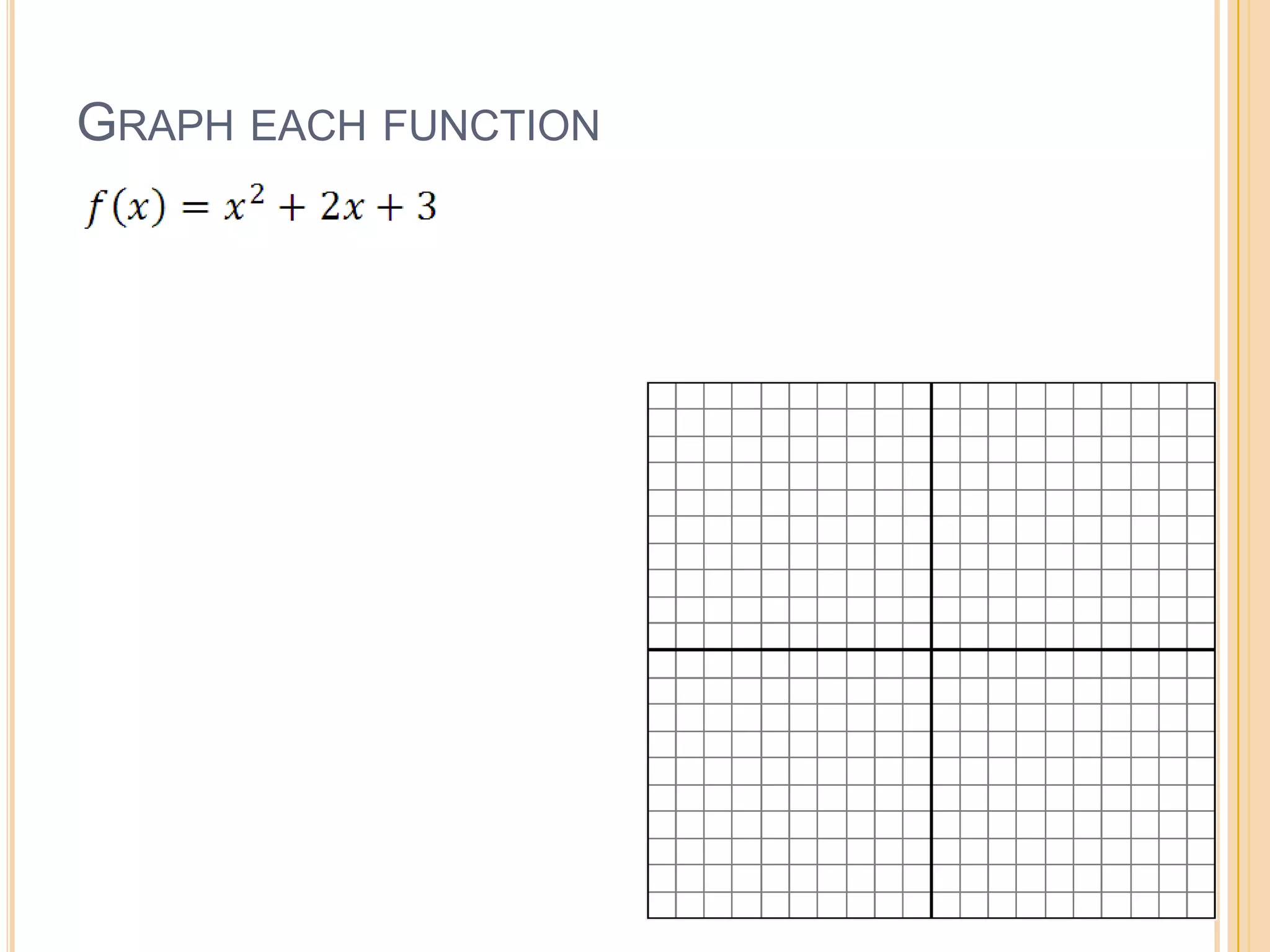
Practical examples focusing on identifying the vertex, axis of symmetry, and determining the maximum or minimum values.
Detailed steps for graphing quadratic functions in standard form, including identifying key points and sketching the curve.
Interactive tasks aimed at practicing the skills of graphing quadratic functions based on standard form.