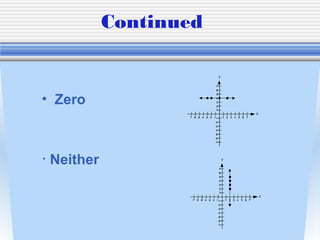
This document defines slope and provides examples for teaching students about slope. It explains that slope is the ratio of vertical to horizontal change and can be positive, negative, zero, or undefined. The objectives are for students to identify slope from graphs, calculate slope using rise over run, and apply the slope formula to find slope given two points. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating slope from graphs and points using rise over run and the slope formula.