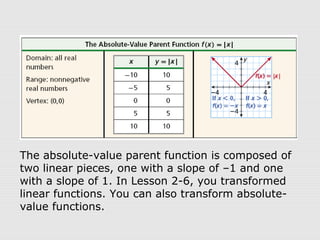
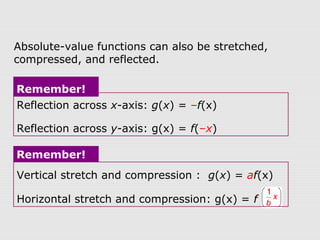
1. Absolute-value functions can be transformed through translations, reflections, stretches, and compressions. Translations move the graph up/down or left/right and change the vertex. Reflections flip the graph across an axis. Stretches and compressions make the graph wider/narrower or taller/shorter.
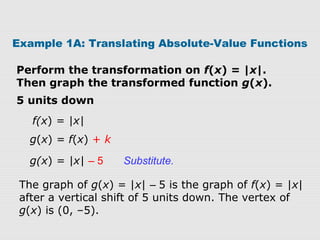
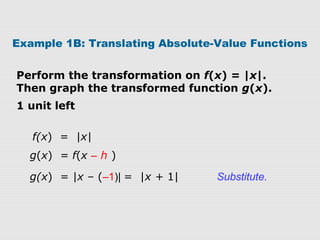
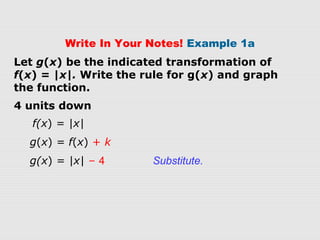
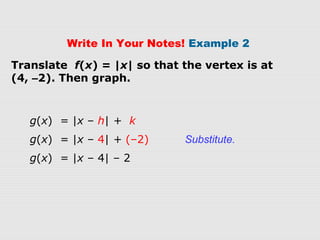
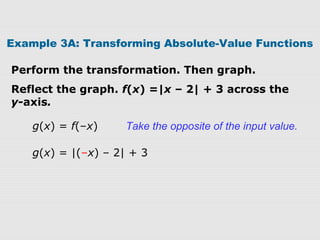
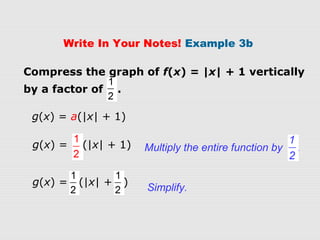
2. Examples show how to write the rule for a transformed absolute-value function g(x) based on an original function f(x). The transformations can be vertical/horizontal shifts, reflections, or vertical/horizontal stretches/compressions.
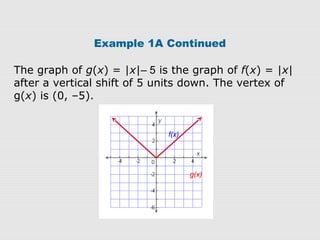
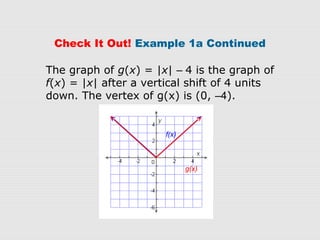
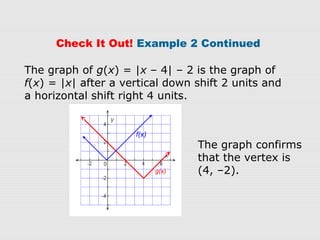
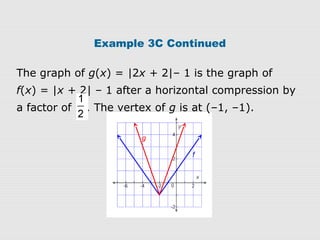
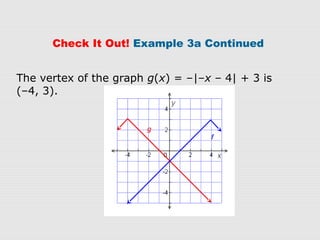
3. Graphs confirm that the transformations are applied as expected to f(x), resulting in the graph of g(x) with the